
What is the largest water treatment plant in the US?
Water Treatment Plants. DWR operates and maintains 12 Public Water Systems (PWS) along the State Water Project (SWP). PWSs are also known as Water Treatment Plants (WTP). The 12 WTPs provide drinking water to staff and irrigation and fire flow supplies to the SWP facilities. California Health and Safety Code [HSC] §116275 (h) defines a Public Water Systems (PWS) as …
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Our two main sources of water are the Cape Fear River and underground aquifers (Castle Hayne & PeeDee). WATER SYSTEMS SWEENEY WATER TREATMENT PLANT (PWS #04-65-010) Sweeney WTP treats and distributes water within the City of Wilmington, parts of Ogden, Monkey Junction, King’s Grant and the Flemington/421 Corridor.
What is the purpose of a water treatment plant?
· Water leaving our homes generally goes either into a septic tank in the back yard where it seeps back into the ground, or is sent to a wastewater-treatment plant through a sewer system. Different treatment is used depending on the type of water coming into the plant and the water-quality requirements of water leaving the plant.
What are the steps of the water treatment process?
Treatment Plant Operator, a magazine for wastewater and water operators, engineers and lab technicians, covers municipal and industrial treatment plants. ... "In a receiving stream like the Illinois River or the Little Vermilion River, people have the concept that the plants are dumping sewage into the water. In reality, we're cleaning the ...
Where are the water treatment plants in cities skylines?
You want to place your pumping station upstream of any sewage drains so that it will not be contaminated by water pollution. Water towers may be built anywhere on land, but you must ensure there is no ground pollution near the water tower or your water supply will be contaminated and citizens will become sick.
How many water treatment plants are there in the UK?
Treated water for reuse there are 7,078 sewage treatment works in England and Wales. there are 10,814 sewage treatment works and community septic tanks in Scotland and Northern Ireland. 98% of urban and rural households connect to the UK's sewerage service.
Where does water from water treatment plants go?
What happens to the treated water when it leaves the wastewater treatment plant? The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
How many wastewater treatment plants are there in the US?
16,000Today, more than 16,000 publicly-owned wastewater treatment plants operate in the United States and its territories.
Where does poop go when you flush the toilet?
When you press the flush button, your wee, poo, toilet paper and water go down a pipe called a sewer. The toilet flushes the wastes down the sewer pipe. The sewer pipe from your house also collects and removes other wastes.
Where does my wastewater go UK?
Every day in the UK about 347,000 kilometres of sewers collect over 11 billion litres of waste water. This is treated at about 9,000 sewage treatment works before the treated effluent is discharged to inland waters, estuaries and the sea. from these effects.
Where does washing machine water go?
Wastewater from your washing machine and dishwasher may either go to your septic tank and/or cesspool or to a separate disposal system called a dry well. This wastewater can be problematic due to its high concentrations of soaps and detergents, grease and paper.
What happens to poop at the water treatment plant?
During the first stage, all of the waste that accumulates in the city's pipes just sits in a tank for hours. This stage allows the solids to settle at the bottom of the tank. The water at the top of the tank is skimmed off and sent off to be processed. Your poop remains in the sludge that's left over.
What happens to human waste at treatment plants?
In the secondary treatment plant oxygen is added to the wastewater to speed up the growth of micro-organisms. These microbes then consume the wastes and settle to the bottom of the secondary settling tanks. After secondary treatment, 80-90% of human waste and other solids have been removed.
What are the largest wastewater treatment plants in the United States?
The Blue Plains Wastewater Treatment Facility in Washington DC, USA, is the largest advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant of its kind in the world. It treats 330 million gallons of waste water every day. Blue Plains produces nitrogen, which can degrade water quality.
How long does a sewage treatment plant last?
Answer: The Ensign sewage treatment plant is one of the most economic, efficient and environmentally friendly systems on the market. As long as the plant is installed correctly, the system is odourless and operates virtually silent. It is backed with a 25-year structural guarantee.
What happens to sludge from a sewage treatment plant?
Once treated, sewage sludge is then dried and added to a landfill, applied to agricultural cropland as fertilizer, or bagged with other materials and marketed as “biosolid compost” for use in agriculture and landscaping.
How many water systems does DWR maintain?
DWR operates and maintains 12 Public Water Systems (PWS) along the State Water Project (SWP). PWSs are also known as Water Treatment Plants (WTP). The 12 WTPs provide drinking water to staff and irrigation and fire flow supplies to the SWP facilities.
When is a CCR required for a small water system?
Every year each permitted small water system (SWS) is required by HSC §116470 to provide an annual Consumer Confidence Report (CCR) to its water users by July 1. To request a CCR for one of the 2 SWP SWSs, contact us.
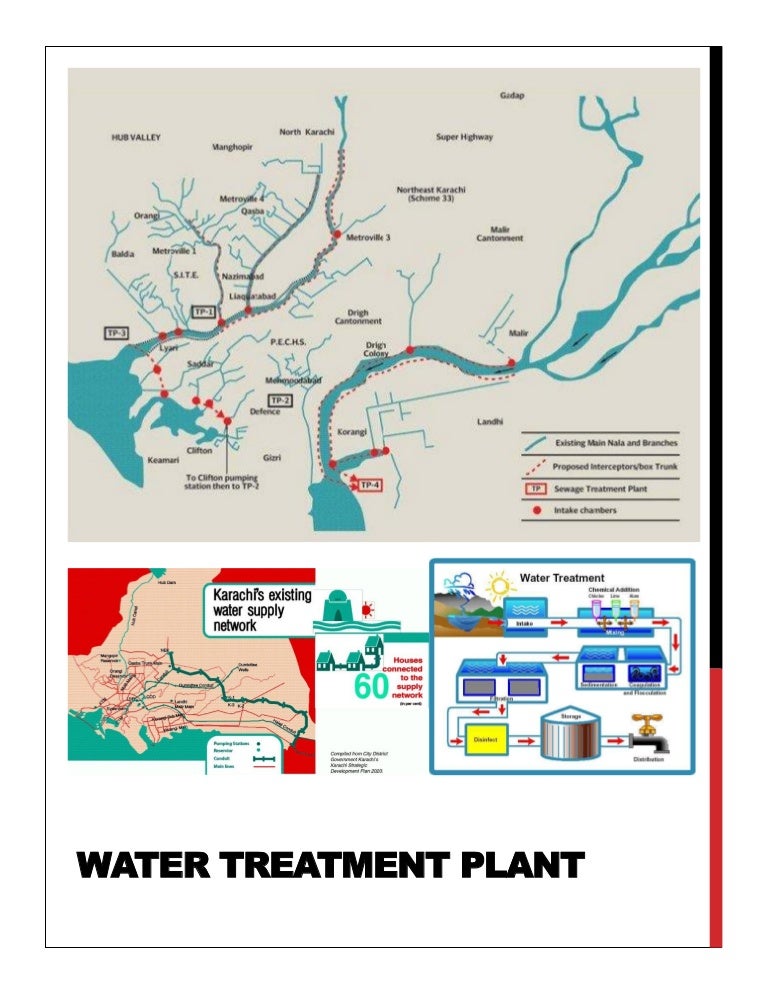
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
Why is chlorine added to water?
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.
Why do people use water treatment units?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: Remove specific contaminants. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system. Improve the taste of drinking water.
Where does Richardson WTP water come from?
Richardson WTP distributes water to northern New Hanover County including Murrayville, Wrightsboro, Porters Neck, and parts of Castle Hayne and Ogden. It supplies groundwater to this system via wells which draw from the Castle Hayne and Pee Dee Aquifers.
What agency is responsible for water distribution?
Water distributed by the CFPUA is constantly measured against safety standards established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) and the NC Department of Environmental Quality (NCDEQ).
What is the water supply system in New Hanover County?
There are 3 basic parts to the water supply system: source, treatment and distribution. Our two main sources of water are the Cape Fear River and underground aquifers (Castle Hayne & PeeDee).
When is CFPUA water report?
Water Quality Reports are compiled and made available to our customers by June 1 annually.
Can school groups tour water treatment facilities?
We welcome school groups and organization s to tour either of our 2 water treatment facilities. Learn more about where your water comes from, how it’s treated and delivered to our homes and businesses. Tours are age appropriate and offer an exciting behind-the-scenes look at the treatment process. Tours must be requested and scheduled in advance.
Governance
The Facility is jointly owned by the cities of San José and Santa Clara, and is managed and operated by the City of San José’s Environmental Services Department. The city councils of San José and Santa Clara, the Treatment Plant Advisory Committee (TPAC), and the Technical Advisory Committee (TAC) oversee the Facility’s activities.
Virtual Tour
Enjoy a virtual tour of the San José-Santa Clara Regional Wastewater Facility and follow the three-step treatment process to remove solids, pollutants, and harmful bacteria from wastewater.
Why are there two source water plants in Monroe County?
Basically, the two-source configuration means that water need only be pumped half as far as in the past, which reduces costs, helps keep water rates affordable, and significantly reduces both energy consumption and the Water Authority’s carbon footprint.
How does a backwash plant work?
The plant takes advantage of the region’s often-cold temperatures by using a natural freeze-dry process for treatment of backwash sludge. Instead of highly energy-intensive conventional treatment methods such as presses or centrifuges, each winter the settled backwash residuals are spread in a thin layer and allowed to freeze. This breaks the bonds of hydration and allows the particulate material to separate and settle as the water is returned to the lake. The annual energy savings of this process are well above 100,000 kilowatt hours.
How is Monroe County water tested?
Water is tested daily in an on-site laboratory to ensure the standards are met, and results are reported to the Monroe County Health Department. Once the water properties are verified, it is pumped into some 10 miles of new water mains and transmission facilities that connect the plant to the distribution system.
What is the process of adding chemicals to water?
As an initial step at the plant, chemicals are added to the water in tiny quantities – literally one drop at a time. In this coagulation process, alum (aluminum sulfate) and polymers attract impurities and help them to form clumps called “floc” that are large enough to be captured by the filters.
Why is lake water used?
Naturally chilled lake water is used to cool the plant, reducing cost and energy consumption.
Is Webster Water Treatment Plant green?
From construction to operation, the Webster Water Treatment Plant stands as a “green” facility that respects the environment.

Community Water Treatment
Water Fluoridation
- Community water fluoridation prevents tooth decay safely and effectively. Water fluoridation has been named one of 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century 1. For more information on the fluoridation process and to find details on your water system’s fluoridation, visit CDC’s Community Water Fluoridationpage. Top of Page
Consumer Confidence Reports
- Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water. 1. View the CDC’s guide to Understandi…
Household Water Treatment
- Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1. Remove specific contaminants 2. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3. Improve the taste of drinking water Household water treatment systems are composed of two categories: point-of-us…