
Should patients with ischemic stroke take antithrombotic drugs before thrombolytic therapy?
Dec 11, 2018 · The clot blocks blood flow to a part of the brain. This causes brain cells in that area to stop functioning and die quickly. The blood clot that triggers a thrombotic stroke usually forms inside an artery that already has been narrowed by atherosclerosis. This is a condition in which fatty deposits (plaques) build up inside blood vessels.
Is hypertension a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy of acute myocardial ischemia?
Sep 01, 1996 · thrombolytic therapy cannot be recommended for persons excluded from the ninds study 6 for one of the following reasons: (1) current use of oral anticoagulants or a prothrombin time greater than 15 seconds (international normalized ratio [inr] greater than 1.7); (2) use of heparin in the previous 48 hours and a prolonged partial thromboplastin …
When should thrombolytic therapy not be used in the treatment of thrombosis?
Results: In patients with acute ischemic stroke, we recommend IV recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (r-tPA) if treatment can be initiated within 3 h (Grade 1A) or 4.5 h (Grade 2C) of symptom onset; we suggest intraarterial r-tPA in patients ineligible for IV tPA if treatment can be initiated within 6 h (Grade 2C); we suggest against the use of mechanical …
What is the treatment for thrombotic stroke?
Abnormal blood glucose (<50 mg/dL) No. Yes. Relative Contraindications/Warnings to tPA. Only minor or rapidly improving stroke symptoms. No. Yes. Major surgery or serious non-head trauma in the previous 14 days. No.
Is aneurysm contraindication for tPA?
Patients with vascular malformations such as unruptured cerebral aneurysms are traditionally deemed ineligible for tPA. This exclusion is due to a theoretical increase in the risk of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) from aneurysm rupture postthrombolysis.Dec 8, 2011
Why is thrombolytic therapy contraindicated in hemorrhagic stroke?
Intravenous thrombolysis for stroke is contraindicated if the patient is taking therapeutic doses of LMWH because of the presumed high risk of hemorrhagic complications. Reports of IV thrombolysis given to patients taking LMWH are scarce in the literature.
How do you treat a thrombotic stroke?
Thrombolysis – "clot buster" medicine Ischaemic strokes can often be treated using injections of a medicine called alteplase, which dissolves blood clots and restores blood flow to the brain.
When is thrombolytic therapy contraindicated?
Relative contraindications (not absolute) to fibrinolytic therapy include: Uncontrolled hypertension (BP > 180/110), either currently or in the past. Intracranial abnormality not listed as absolute contraindication (i.e. benign intracranial tumor) Ischemic stroke more than 3 months prior.
Is heparin contraindicated in a patient with a hemorrhagic CVA?
The common practice of administering heparin soon after cardioembolic stroke is associated with an increased risk for serious bleeding, according to an article in the Archives of Neurology. However, it appears that anticoagulation with warfarin therapy may safely begin shortly after stroke.Jul 16, 2008
What causes thrombotic stroke?
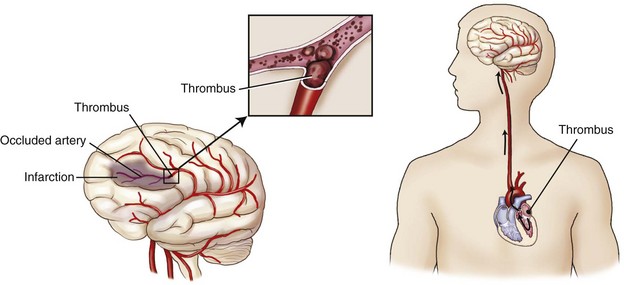
Thrombotic strokes are strokes caused by a thrombus (blood clot) that develops in the arteries supplying blood to the brain. This type of stroke is usually seen in older persons, especially those with high cholesterol and atherosclerosis (a buildup of fat and lipids inside the walls of blood vessels) or diabetes.
What are 3 treatments for a stroke?
Stroke treatmentClot-breaking drugs. Thrombolytic drugs can break up blood clots in your brain's arteries, which still stop the stroke and reduce damage to the brain. ... Mechanical thrombectomy.Stents. ... Surgery. ... Medications. ... Coiling. ... Clamping. ... Surgery.
What is the best treatment option for hemorrhagic strokes?
Options include physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy. The primary goal of therapy is to restore as much function as possible.
How are thrombolytics administered?
The “clot-busting” drug will be delivered through a peripheral intravenous (IV) line, usually through a visible vein in your arm. Performed at your bedside in an intensive care unit while your heart and lung functions are monitored. The drug circulates within the blood stream until it reaches the clot.
What is an absolute contraindication for thrombolytic therapy?
Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis (excluding menses) Significant closed head trauma or facial trauma within 3 months. Intracranial or intraspinal surgery within 2 months. Severe uncontrolled hypertension (unresponsive to emergency therapy)Aug 4, 2021
What is endovascular therapy for stroke?
Endovascular treatment of stroke is the non-surgical treatment for the sudden loss of brain function due to blood clots. The treatment uses microcatheters (thin tubes visible under X-rays) which are inserted into the blood clot from the groin or the arm.
Why is thrombolytic therapy contraindicated in hypertension?
Thrombolytic therapy is contraindicated in patients with a systolic blood pressure greater than 185 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure greater than 110 mmHg. Elevated blood pressure can lead to a delay in thrombolytic therapy, which is associated with increased morbidity.
What is the other type of ischemic stroke?
Vs. embolic stroke. The other type of ischemic stroke is an embolic stroke. In this case, the blood clot, called an embolus, forms in another part of the body. It moves with your blood to an artery in your brain where it gets stuck and blocks off the artery.
What are the risk factors for a thrombotic stroke?
The risk factors for a thrombotic stroke are the same as for atherosclerosis. They include: high cholesterol. high blood pressure.
What is the best treatment for ischemic stroke?
The current standard treatment for an ischemic stroke is a “clot buster” drug called alteplase. This tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) must be given via a vein within 4.5 hours of stroke onset. It breaks up the clot and opens the artery, so blood can flow to the brain tissue again.
Why does the brain get injured?
This means a part of the brain gets injured because the artery that normally supplies blood to it gets blocked, so blood flow is reduced or stops completely. According to the National Stroke Association, almost 90 percent of all strokes are ischemic. About 10 percent are due to bleeding in your brain from a torn or ruptured blood vessel.
What is the thrombus made of?
The thrombus is made up of a hardened buildup of cholesterol and other substances , which is called plaque. The disease causing the buildup is called atherosclerosis. Your body sees this buildup as an injury, so it responds by sending clotting factors to form a blood clot.
How long after a stroke can you have a mechanical thrombectomy?
It must be done within six hours of the stroke.
How long does it take to recover from a stroke?
A thrombotic stroke can be difficult. It can leave a person unable to walk, talk, or think clearly. But when diagnosed and successfully treated within a few hours, complete recovery is possible.
Thrombotic Stroke
What do you think of when you hear the word 'stroke?' It may bring to mind a tennis stroke or a golf stroke. There are also strokes that can occur in your body. A stroke is a loss of blood supply to the brain that causes the death of brain tissue. The formal name for a stroke is a cerebrovascular accident, abbreviated as CVA.
Symptoms
You must be thinking that brain tissue dying must cause some type of symptoms in the body since the brain controls the body. If you thought this, then you are correct! Exactly what symptoms are seen will depend on the part of the brain that is dying.
Treatments
The best way to solve almost any problem is to address what caused the problem. That is how it works with treating a person that has had a stroke. If the cause was a thrombus, then the goal of treatment is to dissolve the blood clot. A thrombolytic drug is a drug that breaks up or dissolves a blood clot.
Lesson Summary
A stroke, also called a cerebrovascular accident, or CVA for short, is a loss of blood supply to the brain that causes the death of brain tissue. A thrombotic stroke is a stroke that is caused by a thrombus, which is a stationary blood clot.
What Is It?
In a thrombotic stroke, a blood clot (thrombus) forms inside one of the brain's arteries. The clot blocks blood flow to a part of the brain. This causes brain cells in that area to stop functioning and die quickly.
Disclaimer
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
How many people were in the NINDS study?
The NINDS Study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial consisting of two parts. 6 In part I, 291 persons were enrolled in a project that assessed early response to treatment, although data about long-term outcome were also collected. In part II, 333 persons were recruited into a study to examine the effects of treatment at 3 months. Because the results of part I were not known before part II was completed, combined data were reported. Persons with ischemic stroke in either the carotid or vertebrobasilar circulation and a wide range of severity of signs were treated within 3 hours of onset. Patients with isolated neurological deficits such as ataxia alone, sensory loss alone, dysarthria alone, or minimal weakness that could not be assessed by the NIH Stroke Scale were not enrolled. Persons with rapidly resolving neurological symptoms were also excluded. The trial's design required very early entry of a large proportion of persons; as a result, 302 persons were treated within 90 minutes of onset of stroke. Persons assigned to active treatment received r-TPA in a dose of 0.9 mg/kg up to a maximum of 90 mg; 10% of the dose was given in a bolus, and the remainder was infused over 60 minutes. Blood pressure was managed closely, and no anticoagulants or antiplatelet aggregating drugs were given within 24 hours of treatment. No significant differences in mortality were noted acutely or at 3 months (Table 3) (Level of Evidence I). A significant increase in improvement at 24 hours and favorable outcomes at 3 months were noted among persons treated with r-TPA (Level of Evidence I). Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage was significantly increased with treatment, although the overall rate (6.4%) was lower than that reported in other studies (Level of Evidence I). Despite the hemorrhages, the rate of death or severe disability was less in the actively treated groups.
How long after stroke can you take streptokinase?
The Australian Streptokinase Trial was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of intravenous streptokinase (1.5 million U) given within 4 hours of stroke. 3 On the basis of an interim analysis of 300 persons (72 treated less than 3 hours after stroke), the trial's safety committee recommended that recruitment of persons seen more than 3 hours after stroke onset be halted because of a significant increase in adverse experiences among those given streptokinase. Subsequently the entire trial was stopped. Among persons treated 3 to 4 hours after stroke, unfavorable outcomes (death or death/severe disability) were significantly more frequent among persons treated with streptokinase (Level of Evidence I) (Table 2 ).
How long does it take to administer r-TPA?
1. Intravenous r-TPA (0.9 mg/kg, maximum 90 mg) with 10% of the dose given as a bolus followed by an infusion lasting 60 minutes is recommended treatment within 3 hours of onset of ischemic stroke (Grade A recommendation). The benefit of intravenous r-TPA for acute ischemic stroke beyond 3 hours from onset of symptoms is not established. At this time intravenous administration of r-TPA for a person who has had a stroke more than 3 hours earlier cannot be recommended outside the clinical investigation setting. Intravenous r-TPA is not recommended when the time of onset of stroke cannot be ascertained reliably, including strokes recognized upon awakening.
When was the thrombolytic therapy for stroke approved?
Adams “Guidelines for Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Stroke: A Supplement to the Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke” was approved by the American Heart Association Science Advisory and Coordinating Committee on June 20, 1996.
What is the most feared complication of thrombolysis?
Bleeding is the most feared complication. Hemorrhagic events generally are divided into those that directly affect the central nervous system and those that involve other organs. The treatment of thrombolysis-related bleeding is guided by (1) the location and size of the hematoma, (2) the likelihood that the bleeding can be controlled mechanically, (3) the risk of neurological worsening or death, (4) the interval between administration of the drug and the onset of hemorrhage, and (5) the thrombolytic drug used. Information is scarce to guide recommendations about treatment of hemorrhagic complications of thrombolytic therapy (Levels of Evidence III through V).
Can you take antiplatelet therapy before a stroke?
Many patients who might be eligible for thrombolytic therapy have been taking antithrombotic and antiplatelet aggregating drugs before ischemic stroke. Persons who had been taking antiplatelet agents have been treated successfully, but persons with a prolonged prothrombin time (secondary to warfarin) or a prolonged partial thromboplastin time (secondary to heparin) were excluded because of the concern about brain hemorrhage. In the NINDS Study, patients taking oral anticoagulants were excluded. In addition, the use of antithrombotic or antiplatelet drugs was forbidden for 24 hours after treatment. This is the only trial with positive results on improving outcome. 6 Pending the results of additional studies of thrombolytic therapy, the same prohibition should be applied to the clinical setting.
Is thrombolytic drug superior to other drugs?
There is no evidence that one thrombolytic drug is superior to others in terms of rates of recanalization or safety when used for local or intra-arterial thrombolysis. 3. The usefulness of supplementary techniques to speed recanalization with intra-arterial administration of thrombolytic drugs is not determined.
What is the risk of a TPA?
The principal risk of tPA is symptomatic or fatal hemorrhage. It is essential that patients be evaluated for any history or risk factors that would put them at an increased risk of a hemorrhagic outcome. Eligibility for tPA. Age ≥18. No.
Can you give tpa to a stroke patient?
Because of the risk of hemorrhage is thought to outweigh any potential benefits, patients with any absolute contraindication should not be given tPA.
Is tpa necessary for stroke patients?
tPA for patients with acute ischemic stroke is associated with a significant increase in symptomatic in tracranial hemorrhage, so it is essential to adhere to accepted protocols and to engage in shared decision making with the patient or their family when considering administering tPA. The evidence and strength of recommendations for giving tPA in ...
How does Alteplase IV work?
Doctors administer Alteplase IV r-tPA through an IV in the arm, dissolving the clot and improving blood flow to the part of the brain being deprived. Many people don’t arrive at the hospital in time to receive the medication, which can save lives and reduce long-term effects of stroke.
What is Alteplase IV?
Medication Treatment with Alteplase IV r-tPA. Considered the gold standard, tissue plasminogen activator, r-tPA, (known as alteplase) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat ischemic stroke.
How do doctors remove a clot from the brain?
In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever. They thread a catheter through an artery in the groin up to the blocked artery in the brain. The stent opens and grabs the clot. Special suction tubes may also remove the clot.
What is the best way to remove a clot?
Mechanical Treatment to Remove the Clot. An endovascular procedure or a mechanical thrombectomy is a strongly recommended option to remove a clot in eligible patients with a large vessel occlusion, or LVO. In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever.
What are some examples of anticoagulants?
Anticoagulants prevent blood clots by changing the chemical composition of the blood in a way that prevents clots from forming. Warfarin, apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban are examples of anticoagulants for long-term use. There are also a number of anticoagulants called heparins, which can only be given by injection ...
How to remove blood clots from brain?
A small device is passed through the catheter into the artery in the brain. The blood clot can then be removed using the device, or through suction.
How do statins help with cholesterol?
Statins reduce the level of cholesterol in your blood by blocking a chemical (enzyme) in the liver that produces cholesterol. You may be offered a statin even if your cholesterol level is not particularly high, as it may help reduce your risk of stroke whatever your cholesterol level is.
What is the term for a stroke that causes a person to lose balance?
Surgery can also be done to treat a complication of haemorrhagic strokes called hydrocephalus. This is where damage resulting from a stroke causes cerebrospinal fluid to build up in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain, causing symptoms such as headaches, sickness, drowsiness, vomiting and loss of balance.
What is the best medicine for a clot?
Most people will be offered a regular dose of aspirin. As well as being a painkiller, aspirin is an antiplatelet, which reduces the chances of another clot forming. Other antiplatelet medicines may be used, such as clopidogrel and dipyridamole.
How long after stroke can you take Alteplase?
Alteplase is most effective if started as soon as possible after the stroke occurs – and certainly within 4.5 hours. It's not generally recommended if more than 4.5 hours have passed, as it's not clear how beneficial it is when used after this time.
What is the procedure to remove blood from the brain?
This is usually done using a surgical procedure known as a craniotomy. During a craniotomy , a section of the skull is removed to allow the surgeon access to the source of the bleeding.

What Is A Thrombotic Stroke?
Symptoms
Diagnosis
- To diagnose a stroke, your doctor will need an image of your brain. Two different brain imaging tests can be useful. They are a computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. Usually the CT scan is done first because it can be obtained more quickly than an MRI. If the CT scan shows bleeding in or around the brain, then you have had a hemorrh…
Expected Duration
- Recovery depends on how long blood flow to the brain is blocked. If blood circulation in the brain is restored within minutes to a few hours, the person can recover rapidly, within hours to a day. For a small thrombotic stroke (lacunar stroke), symptoms often improve within a few days, even if the blood clot has not dissolved. When the blood supply is interrupted for longer periods of time…
Prevention
- If you have had one stroke, you have a high risk of having another. You can help to prevent thrombotic strokes. You and your doctor should carefully manage the factors that put you at risk of atherosclerosis. Risk factors for atherosclerosis include: 1. High blood pressure. Treating high blood pressure with almost any medication reduces the risk of stroke. Several medicines have b…
Treatment
- The most effective treatment for ischemic stroke is a clot-busting drug, such as tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA). The drug must be given within several hours after stroke symptoms begin. For this reason, it is important to seek emergency treatment immediately if you have symptoms of a stroke. Do not wait to see if the symptoms go away on their ...
When to Call A Professional
- If you or someone you are with develops any of the symptoms of stroke, call your medical emergency hot line (911 in the United States). Transport to an emergency department needs to occur right away. It is important to have an evaluation even if your symptoms last only a few minutes. A TIA can be a warning sign that you are going to have a stroke soon.
Prognosis
- If the brain's blood supply is restored quickly and completely, it is possible to recover from a stroke with little or no disability. People with symptoms that start to resolve quickly after the onset of a stroke have an excellent prognosis. The prognosis for recovery is less favorable when stroke symptoms become more prominent over the first 24 to 48 hours.
Further Information
- Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Medical Disclaimer