What are the early signs of osteoporosis?
Jun 11, 2007 · Somewhere around 1940 he defines postmenopausal osteoporosis and begins treating women with the condition with estrogen. But estrogen therapy can only prevent damage to the skeleton by stemming bone loss. In the 1940s it was virtually impossible to detect the minimal bone loss seen in the early stages of the disease. Detecting Bone Loss
How bad was AIDS when it was first discovered?
Conjugated Estrogens/Bazedoxifen. A combination of conjugated estrogens with bazedoxifene (Duavee, Pfizer) received FDA approval in 2013 for use in postmenopausal women with an intact uterus for the prevention of osteoporosis and for the …
What are facts about osteoporosis?
In this Series paper, we trace the evolution of drug therapy for osteoporosis, which began in the 1940s with the demonstration by Fuller Albright that treatment with oestrogen could reverse the negative calcium balance that developed in women after menopause or oophorectomy.
What doctor treats osteoporosis?

What was the first treatment for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates are usually the first choice for osteoporosis treatment. These include: Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill. Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill.
When was Fosamax invented?
Fosamax (alendronate sodium) is a prescription drug used to treat and prevent osteoporosis in adults. It was first introduced to the U.S. market in 1995 by the drug manufacturer Merck.
Why was Fosamax taken off the market?
Researchers say that the fractures occurred because alendronate stops the body from breaking down bone. This creates thick, but brittle bones. In October 2010, the FDA ordered Merck to change its drug label to reflect the bone-fracture connection. Fosamax use may also make fractures more difficult to heal.
What is the newest treatment for osteoporosis?
Romosozumab (Evenity). This is the newest bone-building medication to treat osteoporosis. It is given as an injection every month at your doctor's office and is limited to one year of treatment.Aug 21, 2021
Who coined the term "osteoporosis"?
The link between age-related reductions in bone density goes back to the early 1800s. French pathologist Jean Lobstein coined the term osteoporosis. The American endocrinologist Fuller Albright linked osteoporosis with the postmenopausal state.
How to diagnose osteoporosis?
The diagnosis of osteoporosis can be made using conventional radiography and by measuring the bone mineral density (BMD). The most popular method of measuring BMD is dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry .
Why do humans lose bones?
Age-related bone loss is common among humans due to exhibiting less dense bones than other primate species. Because of the more porous bones of humans, frequency of severe osteoporosis and osteoporosis related fractures is higher. The human vulnerability to osteoporosis is an obvious cost but it can be justified by the advantage of bipedalism inferring that this vulnerability is the byproduct of such. It has been suggested that porous bones help to absorb the increased stress that we have on two surfaces compared to our primate counterparts who have four surfaces to disperse the force. In addition, the porosity allows for more flexibility and a lighter skeleton that is easier to support. One other consideration may be that diets today have much lower amounts of calcium than the diets of other primates or the tetrapedal ancestors to humans which may lead to higher likelihood to show signs of osteoporosis.
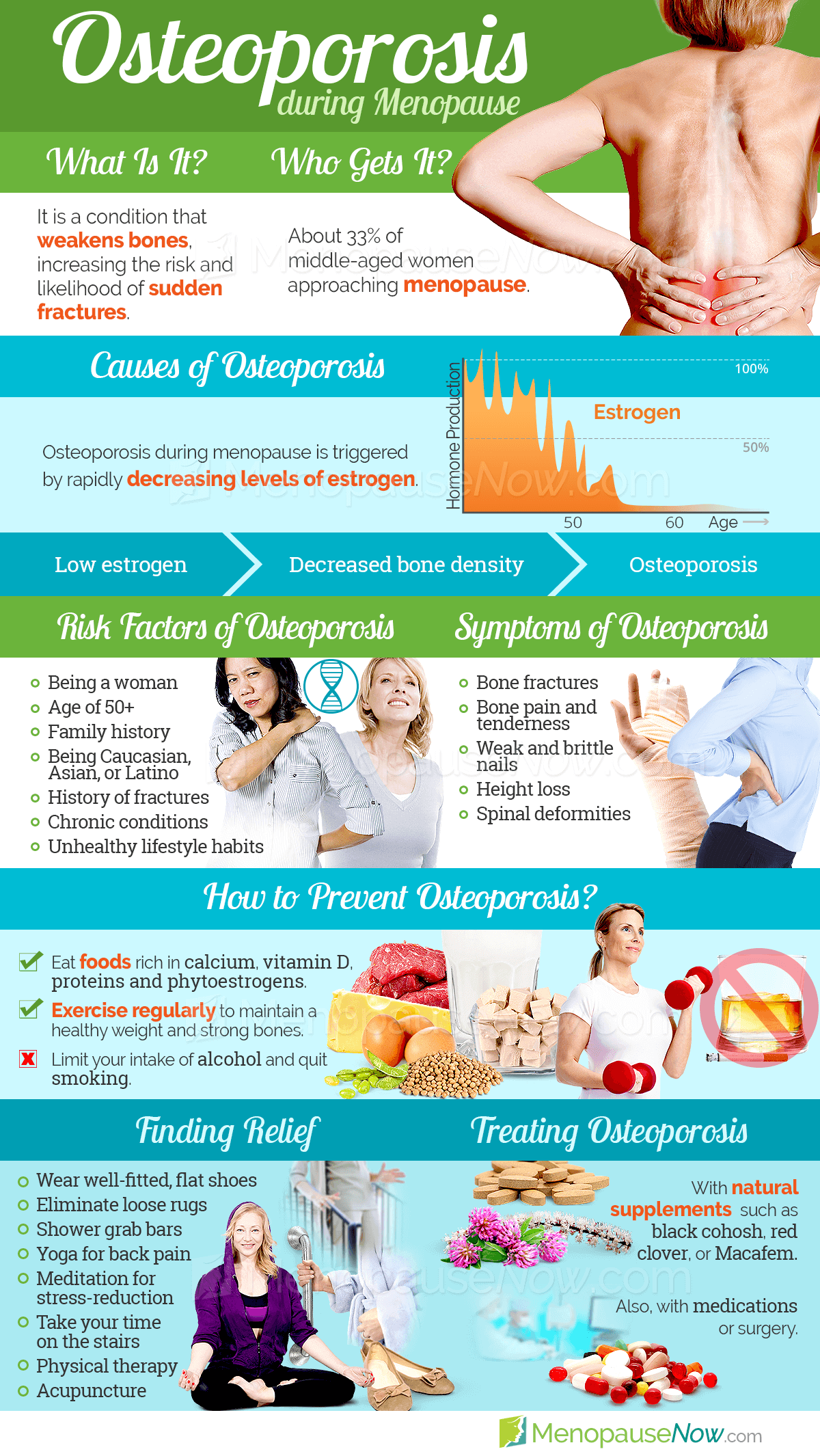
What happens to bone after menopause?
Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after menopause due to lower levels of estrogen.
How to prevent osteoporosis?
This is typically measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Prevention of osteoporosis includes a proper diet during childhood and efforts to avoid medications that increase the rate of bone loss. Efforts to prevent broken bones in those with osteoporosis include a good diet, exercise, and fall prevention.
What are the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Fractures are a common symptom of osteoporosis and can result in disability. Acute and chronic pain in the elderly is often attributed to fractures from osteoporosis and can lead to further disability and early mortality. These fractures may also be asymptomatic. The most common osteoporotic fractures are of the wrist, spine, shoulder and hip. The symptoms of a vertebral collapse (" compression fracture ") are sudden back pain, often with radicular pain (shooting pain due to nerve root compression) and rarely with spinal cord compression or cauda equina syndrome. Multiple vertebral fractures lead to a stooped posture, loss of height, and chronic pain with resultant reduction in mobility.
How many genes are associated with osteoporosis?
At least 30 genes are associated with the development of osteoporosis. Those who have already had a fracture are at least twice as likely to have another fracture compared to someone of the same age and sex. Build: A small stature is also a nonmodifiable risk factor associated with the development of osteoporosis.

Overview
Signs and symptoms
Osteoporosis itself has no symptoms; its main consequence is the increased risk of bone fractures. Osteoporotic fractures occur in situations where healthy people would not normally break a bone; they are therefore regarded as fragility fractures. Typical fragility fractures occur in the vertebral column, rib, hip and wrist.
Fractures are a common symptom of osteoporosis and can result in disability. Acute and chroni…
Risk factors
Risk factors for osteoporotic fracture can be split between nonmodifiable and (potentially) modifiable. In addition, osteoporosis is a recognized complication of specific diseases and disorders. Medication use is theoretically modifiable, although in many cases, the use of medication that increases osteoporosis risk may be unavoidable. Caffeine is not a risk factor for osteoporosis.
Pathogenesis
The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation. In normal bone, matrix remodeling of bone is constant; up to 10% of all bone mass may be undergoing remodeling at any point in time. The process takes place in bone multicellular units (BMUs) as first described by Frost & Thomas in 1963. Osteoclasts are assisted by transcription factor PU.1 to degrade the bone matrix, while osteoblastsrebuild the bone matri…
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of osteoporosis can be made using conventional radiography and by measuring the bone mineral density (BMD). The most popular method of measuring BMD is dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
In addition to the detection of abnormal BMD, the diagnosis of osteoporosis requires investigations into potentially modifiable underlying causes; this may be done with blood tests. D…
Prevention
Lifestyle prevention of osteoporosis is in many aspects the inverse of the potentially modifiable risk factors. As tobacco smoking and high alcohol intake have been linked with osteoporosis, smoking cessation and moderation of alcohol intake are commonly recommended as ways to help prevent it.
In people with coeliac disease adherence to a gluten-free dietdecreases the risk of developing ost…
Management
Weight-bearing endurance exercise and/or exercises to strengthen muscles improve bone strength in those with osteoporosis. Aerobics, weight bearing, and resistance exercises all maintain or increase BMD in postmenopausal women. Fall prevention can help prevent osteoporosis complications. There is some evidence for hip protectors specifically among those who are in care homes.
Complication
In addition to making you more susceptible to breaks and fractures, osteoporosis can lead to other complications. Bone fractures which are results from osteoporosis can lead to disability and even an increased chance of death after the injury.
Depressionis considered to be one of the complications of osteoporosis. People with osteoporosis lose indepedence and being isolated due to less physical activity. This will further …