Procedures
To cure cervical dysplasia naturally takes steps:
- Knowledge: listen to other women’s experiences and understand the facts, equip yourself!
- Prevention: remember the list I mentioned above? ...
- Immunity: Keep your immunity up up UP! ...
- Self-love: positive affirmations are one of the greatest tools. ...
Nutrition
- Use a condom or other protection when having sex.
- Consider getting the HPV vaccine if you are between the ages of 11 and 26.
- Avoid smoking cigarettes.
- Wait to have sex until you are at least 18 years old.
How to reverse cervical dysplasia?
- Risk Factors. The main risk factor for cervical dysplasia is the presence of HPV.
- Screenings and Prevention. Naturopathic doctors follow the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines for dysplasia and HPV screenings in women 21-65 years old, utilizing the Pap Smear and ...
- Diagnosis. ...
- Treatment. ...
How does it take to develop cervical dysplasia?
“In addition, mild cervical dysplasia does not lead to cervical cancer. Severe cervical dysplasia, however, can lead to cervical cancer if not treated. “Fortunately, treatments such as a cone biopsy are very effective in preventing this process from turning into cervical cancer. “For some women with severe dysplasia, hysterectomy may also be an appropriate treatment option.
How do doctors treat cervical dysplasia?
Does cervical dysplasia always turn into cancer?

What more serious problem can develop from cervical dysplasia?
It can sometimes cause cervical cancer if left unmonitored and untreated. As cervical dysplasia typically has no symptoms, the best way to diagnose and treat this condition before cancer can develop is by getting regular Pap smears.
What is the prognosis for cervical dysplasia?
In most cases, mild dysplasia resolves on its own and doesn't become cancerous. Your doctor may recommend follow-up in a year to check for additional changes. If you have severe dysplasia (CIN II or III), your doctor may recommend treatment, such as surgery or other procedures to remove the abnormal cells.
Can cervical dysplasia come back after treatment?
Most of the time, cervical cell changes (abnormal cells) don't come back after treatment. However, sometimes they do and may need further treatment. These cell changes are also called persistent or recurrent cell changes.
What happens if LEEP doesnt work?
If LEEP doesn't remove all of the abnormal cells, you may have to have LEEP again, or your doctor or nurse may recommend more tests or a different treatment.
What is severe cervical dysplasia?
If you have severe cervical dysplasia, it means that severely abnormal cells have been found on your cervix. You don't have cancer, and it doesn't necessarily mean you'll develop cancer. Rather, it's a precancerous condition. Cervical dysplasia is also known as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
Why do I need a second LEEP procedure?
In some cases, abnormal cells are found again. If this happens, you may require another LEEP. Following a normal Pap and negative HPV test, patients are required to come back a year later for another screening.
Is a second LEEP procedure common?
3.2% (7 patients) were diagnosed with HSIL and underwent a second LEEP. This study found that 14.0% of patients (n = 31) required further follow up based on findings at the second colposcopy follow up visit.
What happens if abnormal cells come back after LEEP?
What happens if abnormal cells come back. Usually you can have more laser treatment or a LLETZ. You may need to have a cone biopsy. But if the abnormal cells come back more than once, or if your doctor thinks the risks are too great, they may ask you to have a hysterectomy.
Will CIN 3 come back after LEEP?
[6]. Authors [7], in particular, reported that the rate of persistence of HPV infection after conization for CIN 3 was approximately 20, and 46% of these patients with persistent HPV infection developed CIN relapse at 4–10 months after treatment.
How often do abnormal cells come back after LEEP?
How often will depend upon many factors, including your individual case and your family history. In general, women who have had LEEP procedures need to have a follow-up Pap in 1 year.
Can LEEP be repeated?
In conclusion, repeat LEEP could be safely performed 4-12 weeks after the first procedure without any impact on pathological specimen examination.
How often does cervical dysplasia come back?
Most cases of moderate dysplasia also spontaneously reverted to normal, but the risk of progression from moderate dysplasia was 16%within two years and 25%within five years. The relative risk of progression to cancer was 2.5 for moderate dysplasia and 4.2 for severe dysplasia compared with mild dysplasia.
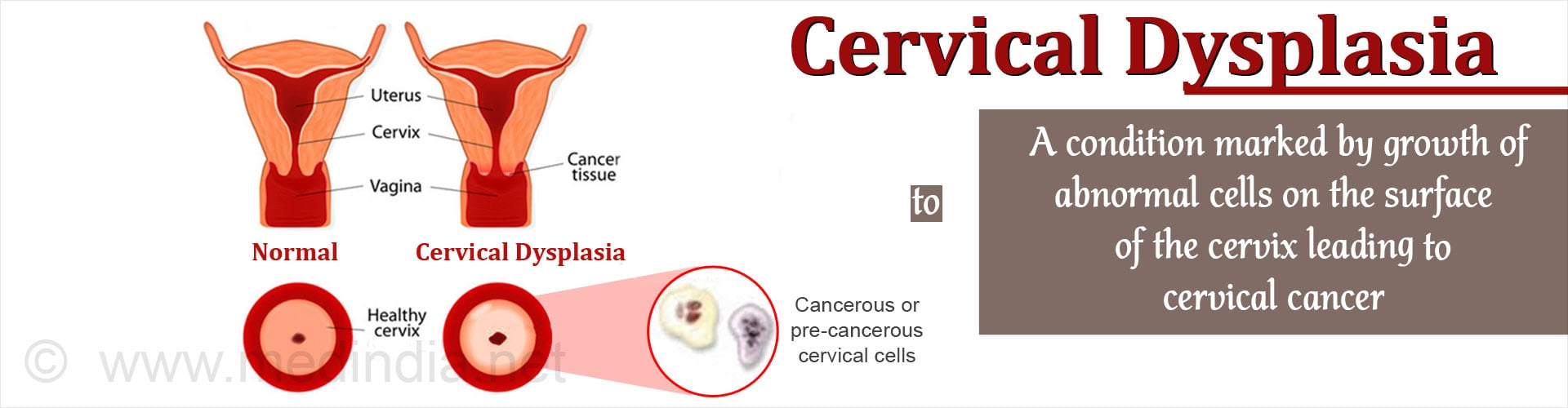
What is cervical dysplasia?
Cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition in which abnormal cell growth occurs on the surface lining of the cervix or endocervical canal, the opening between the uterus and the vagina. It is also called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Strongly associated with sexually transmitted human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, ...
How long does cervical dysplasia last?
But moderate-to-severe cervical dysplasia -- and mild cervical dysplasia that persists for two years -- usually requires treatment to remove the abnormal cells and reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
What is the procedure called to check for abnormal cells in the cervical canal?
Endocervical curettage, a procedure to check for abnormal cells in the cervical canal. Cone biopsy or loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), which are performed to rule out invasive cancer; during a cone biopsy, the doctor removes a cone-shaped piece of tissue for lab examination.
What test can identify cervical cancer?
HPV DNA test, which can identify the HPV strains which are known to cause cervical cancer. The treatment of cervical dysplasia depends on many different factors, including the severity of the condition and the age of the patient.
What tests are needed for cervical dysplasia?
These include: Repeat Pap tests. Colposcopy, a magnified exam of the cervix to detect abnormal cells so that biopsies can be taken. Endocervical curettage, a procedure to check ...
What is the term for a condition in which abnormal cell growth occurs on the surface lining of the cervi
Cervical Dysplasia. Cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition in which abnormal cell growth occurs on the surface lining of the cervix or endocervical canal, the opening between the uterus and the vagina. It is also called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Strongly associated with sexually transmitted human papillomavirus (HPV) ...
How often do you need a Pap test for cervical dysplasia?
Mild cervical dysplasia sometimes resolves without treatment, and may only require careful observation with Pap tests every three or six months.
How to prevent cervical dysplasia?
While abstinence is the only definite way to prevent cervical dysplasia, you can do a number of things to reduce your risk of getting HPV and cervical dysplasia: Use a condom or other protection when having sex. Consider getting the HPV vaccine if you are between the ages of 11 and 26. Avoid smoking cigarettes.
What are the risk factors for cervical dysplasia?
There are several risk factors for cervical dysplasia, some of which relate directly to the risk of HPV: having an illness that suppresses the immune system. being on immunosuppressant drugs. having multiple sexual partners. giving birth before the age of 16. having sex before the age of 18. smoking cigarettes.
Why does the cervix dilate during childbirth?
It’s the cervix that dilates during childbirth to allow the fetus to pass through. In cervical dysplasia, the abnormal cells aren’t cancerous, but can develop into cancer if not caught early and treated.
What is the procedure to remove a cervix?
laser therapy. loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), which uses electricity to remove affected tissue. cone biopsy, in which a cone-shaped piece of the cervix is removed from the location of the abnormal tissue. Dysplasia is usually caught early because of regular Pap tests.
What is a colposcopy?
A colposcopy is an in-office procedure that allows the doctor to get a very close view of your cervix. A vinegar solution is applied to the cervix and a special light is used. This makes any abnormal cells stand out. The doctor can then take a small piece of ...
Can cervical dysplasia return?
Dysplasia is usually caught early because of regular Pap tests. Treatment typically cures cervical dysplasia, but it can return. If no treatment is given, the dysplasia may get worse, potentially turning into cancer.
What are the factors that influence the choice of treatment for cervical dysplasia?
Factors influencing the choice of treatment for cervical dysplasia include the extent and severity of the dysplasia, the age of the woman, and whether or not she has any other gynecological problems. Often the experience of the physician or other clinician, and the availability of equipment are also major factors.
What is the best treatment for dysplasia?
If a woman with dysplasia or carcinoma-in-situ does not want to bear children in the future, then a hysterectomy may be chosen. It has the lowest recurrence rate of any treatment, but it is a major surgical procedure. If a has other problems that may be helped by hysterectomy , then this operation may be the best treatment, one that will take care of all of the problems at the same time. Even after a hysterectomy the dysplasia can come back on the vagina, so it is essential to get regular pap smears even if a hysterectomy is done.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of laser cervix?
Another important advantage is that the cervix usually heals with the squamo-columnar junction visible, so that future evaluation is easily carried out. The major disadvantage of the laser over the cryo is that it requires sophisticated equipment, and most gynecologists do not have a laser in their office.
Is freezing a good treatment for dysplasia?
In spite of these problems, most authorities agree that freezing is an acceptable treatment for small areas of mild or moderate dysplasia. Cryotherapy has a high failure rate for treating large areas of dysplasia and dysplasia that extends into the cervical canal, so other methods are preferable when they are available.
Is loop excision good?
It is not unusual to see a woman who has had several loop excision procedures done when there was essentially nothing wrong with the cervix. When indicated, loop excision may be an excellent treatment method, but should be used only for significant problems and not just an "atypical" pap test.
Can dysplasia recur?
No! No matter how dysplasia is treated there is a possibility that it can recur. Usually a recurrence will not be a serious problem if it is detected early, but it can eventually develop into cancer if it is not treated. It is therefore essential to have regular checkups following treatment.
How to treat cervical dysplasia?
The most common treatments for cervical dysplasia are: 1 LEEP which uses an electrified fine wire loop to remove precancerous tissue. LEEPs are an outpatient procedure done under local anesthesia. 2 Cold knife conization uses a scalpel to remove a cone-shaped portion of your cervix. This is an outpatient procedure done under general anesthesia.
How many people are diagnosed with cervical dysplasia in the US each year?
Other times dysplasia requires treatment to facilitate resolution. Between 250,000 and 1 million people are diagnosed with cervical dysplasia in the US each year. Most people are 25 to 35 years old, although it can occur at any age.
What instrument is used to check for cervical cancer?
If your HPV and Pap tests come back with abnormal results, your doctor will examine your cervix using a colposcope, an electric magnification instrument that looks for abnormal cells.
What is it called when you have a change in your cervix?
Sometimes screening tests show you have changes to your cervix’s surface, but the changes aren’t yet cancer. This is called cervical precancer, cervical dysplasia, or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. A pathologist will classify these changes as low grade or high grade.
Can cervical dysplasia come back?
Cervical dysplasia can come back, or recur, in the future, especially if you have a persistent HPV infection. You may need more frequent follow-ups with Pap and HPV tests or colonoscopies, every few months for the first couple of years after treatment. This is because some severe cases of dysplasia can develop into cervical cancer.
What test is used to diagnose cervical dysplasia?
Doctors use findings from routine gynecological visits and the Pap test (Pap smear) to diagnose cervical dysplasia. Treatment for cervical dysplasia depends on the amount of cell changes in the cervix.
What is the condition that causes abnormal changes in the cervix?
Conditions We Treat: Cervical Dysplasia. Cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition in which abnormal changes occur in the cells of the cervix. If left untreated, cervical dysplasia can cause cervical cancer.
What is the name of the condition where the cervix is enlarged?
Cervical Dysplasia: What You Need to Know. The cervix is the lower narrow part of the uterus (womb) that opens into the vagina. An HPV infection can cause the cells of the cervix to change and grow, which is known as cervical dysplasia — a precancerous condition. HPV infection and cervical dysplasia typically do not cause any noticeable symptoms.
What to do if you have severe cin II?
If you have severe dysplasia (CIN II or III), your doctor may recommend treatment, such as surgery or other procedures to remove the abnormal cells. Whether you have mild or severe dysplasia, it's likely your doctor will recommend Pap and HPV testing in a year to monitor your condition and check for recurrences of dysplasia.
Can you treat cervical dysplasia on its own?
Often, with mild dysplasia (CIN I), no treatment is needed. In most cases, mild dysplasia resolves on its own and doesn't become cancerous. Your doctor may recommend follow-up in a year to check for additional changes.
