
HIV medicine is recommended for everyone with HIV, and people with HIV should start HIV medicine as soon as possible after diagnosis, even on that same day. People on HIV treatment take a combination of HIV medicines (called an HIV treatment regimen).
When to start antiretroviral therapy for HIV?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis. HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are. Talk to your health care provider about any medical conditions you …
What are the guidelines on HIV/AIDS treatment?
Providers should use a laboratory-based antigen/antibody (Ag/Ab) combination assay as the first test for HIV, unless persons are unlikely to follow up with a provider to receive their HIV test results; in those cases screening with a rapid POC test can be useful. Preliminary positive screening tests for HIV should be followed by supplemental ...
How long does it take for HIV medicine to work?
Start HIV Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis. Get in care and take medicine to treat HIV (called antiretroviral therapy or ART). Taking HIV medicine can reduce the amount of HIV in the blood (called viral load). HIV medicine can make the viral load very low (called viral suppression). Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of …
When should HIV testing be performed?
Treatment, Care, and Prevention for People with HIV. minus. Related Pages. Routine care and treatment is the best way to keep people with HIV (PWH) healthy. PWH who take medication as prescribed can achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load (or viral suppression), resulting in effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
When should a HIV positive person begin treatment?
At what stage can HIV be treated?
Further, in the early stages after contracting HIV your viral load is very high and that means you're at greater risk of transmitting HIV.
When do you start taking highly active antiretroviral therapy?
Can HIV be treated at early stage?
At what CD4 level should antiretroviral therapy start?
When do you start antiretroviral CD4 count?
When does HAART CD4 start?
What happens if you take ARVs while negative?
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
Diagnostic Considerations
HIV infection can be diagnosed by HIV 1/2 Ag/Ab combination immunoassays. All FDA-cleared HIV tests are highly sensitive and specific. Available serologic tests can detect all known subtypes of HIV-1. The majority also detect HIV-2 and uncommon variants of HIV-1 (e.g., group O and group N).
Acute HIV Infection
Providers serving persons at risk for STIs are in a position to diagnose HIV infection during its acute phase.
Treatment
ART should be initiated as soon as possible for all persons with HIV infection regardless of CD4+ T-cell count, both for individual health and to prevent HIV transmission ( https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/inline-files/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf#N#pdf icon external icon#N#).
Other HIV Management Considerations
Behavioral and psychosocial services are integral to caring for persons with HIV infection. Providers should expect persons to be distressed when first informed that they have HIV.
STI Screening of Persons with HIV Infection in HIV Care Settings
At the initial HIV care visit, providers should screen all sexually active persons for syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia, and perform screening for these infections at least annually during the course of HIV care ( 425 ). Specific testing includes syphilis serology and NAAT for N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis at the anatomic site of exposure.
Partner Services and Reporting
Partner notification is a key component in the evaluation of persons with HIV infection. Early diagnosis and treatment of HIV among all potentially exposed sexual and injecting drug sharing partners can improve their health and reduce new infections.
Special Considerations
All pregnant women should be tested for HIV during the first prenatal visit.
How to start HIV treatment?
Start HIV Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis 1 Get in care and take medicine to treat HIV (called antiretroviral therapy or ART). 2 Taking HIV medicine can reduce the amount of HIV in the blood (called viral load ). 3 HIV medicine can make the viral load very low (called viral suppression ). Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood. 4 HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test can’t detect it (called an undetectable viral load ). 5 Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load (or staying virally suppressed) is the best thing you can do to stay healthy. Having an undetectable viral load also helps prevent transmission to others. In fact, if you have an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. 6 Learn more about the benefits of HIV treatment.
How long does it take to get HIV under control?
Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Learn more about the benefits of HIV treatment. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
Can you get rid of HIV?
Unlike some other viruses, the human body can’t get rid of HIV completely. Once you have HIV, you have it for life. But with proper medical care, HIV can be controlled. People with HIV who get effective HIV treatment can live long, healthy lives and protect their partners.
What is a primary health care provider?
A primary health care provider is someone who manages your regular medical care and annual tests.
Can HIV be detected?
HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test can’t detect it (called an undetectable viral load ). Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load (or staying virally suppressed) is the best thing you can do to stay healthy. Having an undetectable viral load also helps prevent transmission to others.
What is the best thing to do to stay healthy?
Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load (or staying virally suppressed) is the best thing you can do to stay healthy. Having an undetectable viral load also helps prevent transmission to others.
When should antiretroviral therapy be initiated?
Anti-retroviral therapy should ideally be initiated within the first 2 weeks ...
What is the first step in HIV testing?
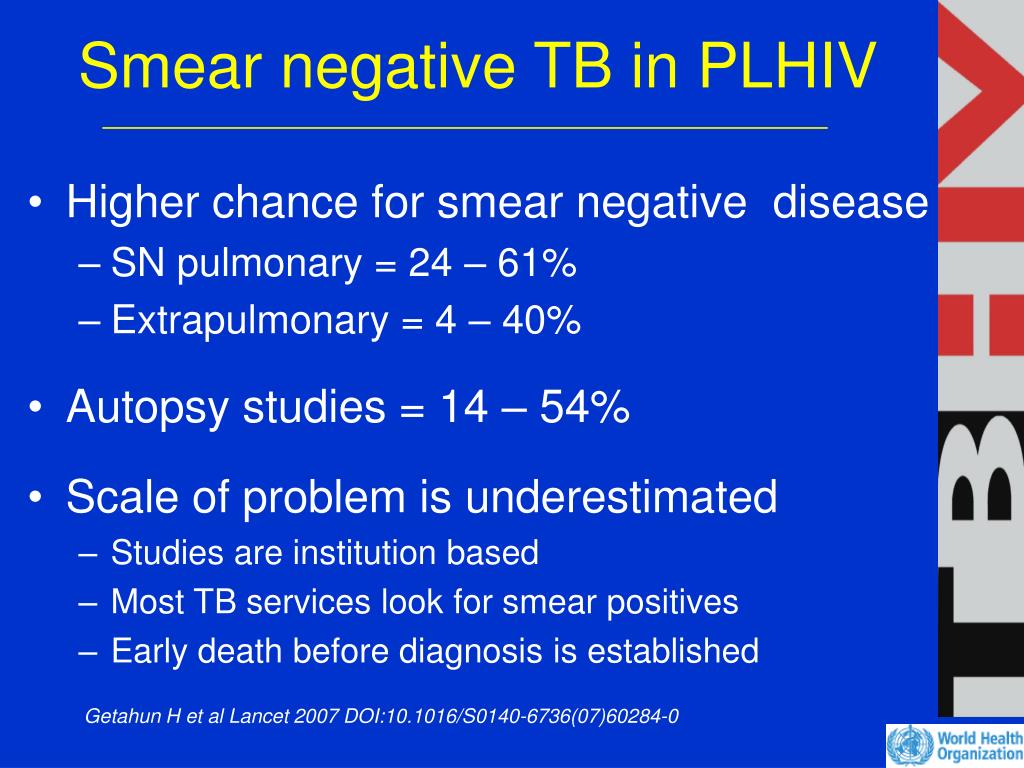
The first step is to ensure that people with HIV are tested for TB infection. If found to have TB infection, further tests are needed to rule out TB disease. The next step is to start treatment for latent TB infection or TB disease based on test results.
How to treat TB in HIV?
The recommended treatment of TB disease in adults infected with HIV is a 6-month daily regimen consisting of: 1 An intensive phase of isoniazid (INH), a rifamycin (see Drug Interactions below), pyrazinamide (PZA), and ethambutol (EMB) for the first 2 months. 2 A continuation phase of INH and a rifamycin for the last 4 months.
How long does HIV treatment last?
In the uncommon situation in which HIV-infected patients do NOT receive antiretroviral therapy during TB treatment, prolonging treatment to 9 months (extend continuation phase to 7 months) is recommended. Prolonging treatment to 9 months (extend continuation phase to 7 months) for HIV-infected patients with delayed response to therapy (e.g., ...
Can rifamycin be used for HIV?
Rifamycins ( a category of drugs for TB disease and latent TB infection treatment) can interact with certain medicines (antiretrovirals) used to treat HIV. One concern is the interaction of rifampin (RIF) with certain antiretroviral agents (some protease inhibitors [PIs] and nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors [NRTIs]).
What is DOT therapy?
Directly observed therapy (DOT) and other adherence promoting strategies should be used in all patients with HIV-related TB. The care for HIV-related TB should be provided by, or in consultation with, experts in management of both TB and HIV. The care for persons with HIV-related TB should include close attention to adherence to both regimens of TB and antiretroviral treatment, drug-drug interactions, paradoxical reaction or Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS), side effects for all drugs used, and the possibility of TB treatment failure or relapse.
Is 5 mm positive for HIV?
Annually based on risk; TST result of 5 mm is positive in persons with HIV infection; chest radiography recommended for positive result or if patient has a history of tuberculosis; patients with advanced HIV disease can have false-negative results; repeat screening after ART restores immunocompetence.
What is the goal of HIV physical examination?
The goal of the initial history and physical examination is to assess for clinical manifestations of HIV infection and related conditions. The initial history should elicit details about sexually transmitted infections, hepatitis, substance use, and sexual practices. It should include any history of previous HIV treatment and information about the patient's family and social networks. Except in cases of acute or advanced HIV infection, the initial physical examination generally shows no HIV-related manifestations. The presence of thrush, oral or anogenital ulcers or warts, lymphadenopathy, rashes, or skin lesions should prompt further evaluation, 11 especially when persistent or substantial immunosuppression is present (as indicated by a CD4 lymphocyte count less than 200 cells per mm 3 [0.20 × 10 9 per L]).
Is HIV treatment prevention?
Large research studies with newer HIV medications have shown that treatment is prevention. These studies monitored thousands of male-female and male-male couples in which one partner has HIV and the other does not over several years. No HIV transmissions were observed when the HIV-positive partner was virally suppressed.
How does HIV medication help?
In addition to preventing sexual transmission of HIV there are other benefits of taking HIV medication to achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load: 1 It reduces the risk of mother-to-child transmission from pregnancy, labor, and delivery. If a woman living with HIV can take HIV medication as prescribed throughout pregnancy, labor, and delivery and if HIV medication is given to her baby for 4-6 weeks after delivery, the risk of transmission from pregnancy, labor, and delivery can be reduced to 1% or less. Scientists don’t know if a woman living with HIV who has her HIV under control can transmit HIV to her baby through breastfeeding. While it isn’t known if or how much being undetectable or virally suppressed prevents some ways that HIV is transmitted, it is reasonable to assume that it provides some risk reduction. 2 It may reduce HIV transmission risk for people who inject drugs. Scientists do not yet know whether having a suppressed or undetectable viral load prevents HIV transmission through sharing needles or other injection drug equipment, but it is reasonable to assume that it provides some risk reduction. Even if you are taking HIV medication and are undetectable, use new equipment each time you inject and do not share needles and syringes with other people.
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV Medication to Stay Healthy and Prevent Transmission. If you have HIV, it is important to start treatment with HIV medication (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) as soon as possible after your diagnosis. If taken every day, exactly as prescribed, HIV medication can reduce the amount of HIV in your blood (also called the viral load) ...
How long does it take for HIV to be undetectable?
Almost everyone who takes HIV medication daily as prescribed can achieve an undetectable viral load, usually within 6 months after starting treatment. There are important health benefits to getting the viral load as low as possible. People living with HIV who know their status, take HIV medication daily as prescribed, ...
Can HIV be transmitted to HIV-negative people?
People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
Can HIV be transmitted through breastfeeding?
Scientists don’t know if a woman living with HIV who has her HIV under control can transmit HIV to her baby through breastfeeding . While it isn’t known if or how much being undetectable or virally suppressed prevents some ways that HIV is transmitted, it is reasonable to assume that it provides some risk reduction.
Why is viral suppression important?
Viral suppression helps keep you healthy and prevents illness. If your viral load is so low that it doesn’t show up in a standard lab test, this is called having an undetectable viral load. People living with HIV can get and keep an undetectable viral load by taking HIV medication every day, exactly as prescribed.
