Is weight loss a part of diabetes management?
Weight loss can be an important part of a type 2 diabetes management plan, but if you’ve heard a blanket recommendation to lose weight without any instruction on how to get there or a sole focus on weight loss, then you should think about if that’s working for you.
Is diabetes one size fits all?
Every person with diabetes is unique, so each treatment plan is individualized — what’s best for one person may not be ideal for another. “Nothing about diabetes is one size fits all,” says Chauntae Reynolds, PharmD, CDCES, a spokesperson for the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists based in Indianapolis.
What is shared decision making?
Shared decision-making isn’t just a buzzword; it’s essential in a good diabetes plan. “Shared decision-making is where you have a partnership with the healthcare professionals who are seeing you, and you work together to come up with a plan for your care ,” says Reynolds.
Who is the expert on you?
You are the expert on you, says Josie Bidwell, DNP, an associate professor at The University of Mississippi School of Medicine in Jackson. “Healthcare providers are experts about the physiology of how medications work, but people are the experts on what they feel like they can do or have access or the means to acquire and do,” she explains.
How can parents help prevent diabetes?
Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family: Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks. Eating more fruits and vegetables. Making favorite foods healthier. Making physical activity more fun.
When does Type 2 diabetes start?
Type 2 diabetes most often develops in people over age 45, but more and more children, teens, and young adults are also developing it.
How does diabetes affect children?
Childhood obesity rates are rising, and so are the rates of type 2 diabetes in youth. More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But it’s not always because family members are related; it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family: 1 Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks 2 Eating more fruits and vegetables 3 Making favorite foods healthier 4 Making physical activity more fun
How to get a diabetes educator?
Whether you were just diagnosed with diabetes or have had it for some time, meeting with a diabetes educator is a great way to get support and guidance, including how to: 1 Develop a healthy eating and activity plan 2 Test your blood sugar and keep a record of the results 3 Recognize the signs of high or low blood sugar and what to do about it 4 If needed, give yourself insulin by syringe, pen, or pump 5 Monitor your feet, skin, and eyes to catch problems early 6 Buy diabetes supplies and store them properly 7 Manage stress and deal with daily diabetes care
Who manages diabetes?
Unlike many health conditions, diabetes is managed mostly by you, with support from your health care team (including your primary care doctor, foot doctor, dentist, eye doctor, registered dietitian nutritionist, diabetes educator, and pharmacist), family, and other important people in your life. Managing diabetes can be challenging, but everything you do to improve your health is worth it!
How to check blood sugar?
Recognize the signs of high or low blood sugar and what to do about it. If needed, give yourself insulin by syringe, pen, or pump. Monitor your feet, skin, and eyes to catch problems early. Buy diabetes supplies and store them properly.
Can high blood sugar cause kidney disease?
Eventually your pancreas can’t keep up, and your blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and can cause other serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
How to treat diabetes type 2?
Type 2 diabetes can be treated by a number of different methods, ranging from lifestyle adjustments to tablet medication and injections, through to bariatric (weight loss) surgery. Lifestyle changes are advised for everyone with type 2 diabetes; your doctor will recommend treatment alongside these changes if your blood glucose levels are too high.
Is weight loss good for type 2 diabetes?
When it comes to diet, weight loss is often a primary goal for those with type 2 diabetes. If you are overweight, losing weight can help to improve insulin sensitivity and make diabetes easier to manage.
What are the different types of insulin?
There are now a number of different injectable medications available for treating diabetes. These fall into two main groups: 1 Insulin 2 Incretin mimetics
Does diabetes medication help with weight loss?
The main role of diabetes medication is to help lower blood glucose levels, although more recently developed medications can also aid weight loss. Each form of medication has side effects and it is important to be aware of which side effects can occur from any medication you are taking. Known side effects will be detailed in ...
Does metformin help with diabetes?
Metformin is often the first tablet prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes and stronger-acting medication may be prescribed in addition to metformin, or in place of it, if blood glucose levels remain too high.
Can you take metformin with type 2 diabetes?
Metformin is often the first tablet prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes and stronger-acting medication may be prescribed in addition to metformin, or in place of it, if blood glucose levels remain too high.
What is the most well known type of injectable medication for diabetes?
Insulin is the most well-known type of injectable medication for diabetes. Insulin is the hormone which helps to move sugar out of the blood and into cells to be used as energy or to be stored as fat.
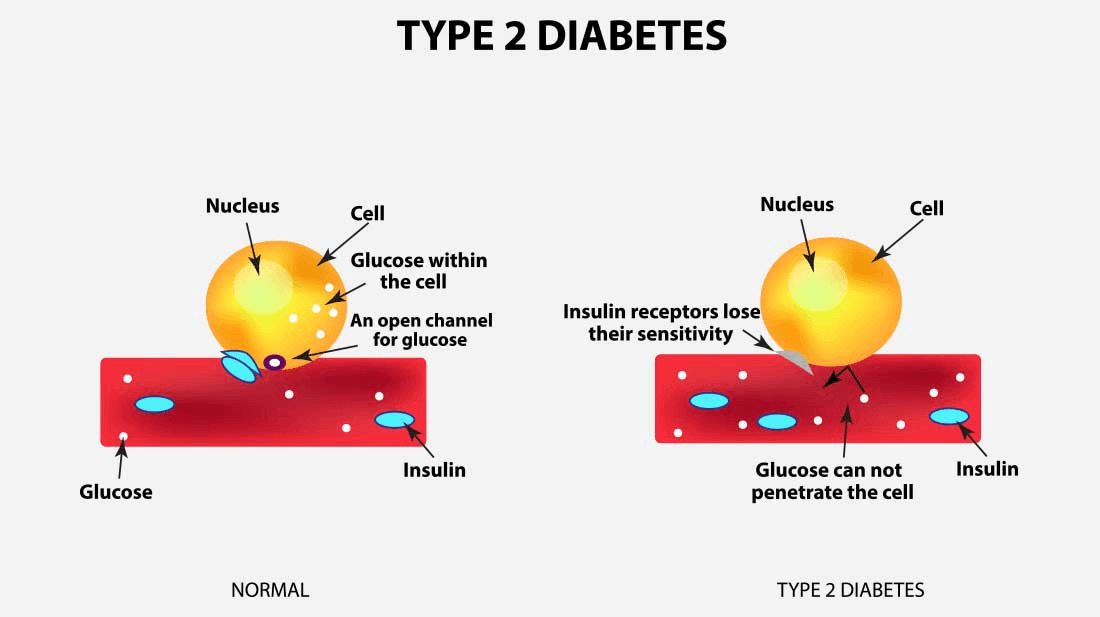
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 DM (formerly known as NIDDM) is a common metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance, relative impairment in insulin secretion, and certain degree of genetic predisposition, the prevalence of which markedly ris es with the degree of obesity[1].
Does type 2 diabetes cause insulin resistance?
Indeed, it is now well known that type 2 DM usually presents with var ying degrees of insulin resistance, consequent relative insulin deficiency, and hyperglycaemia which further impair pancreatic β-cell function, resulting in a vicious cycle of metabolic state worsening[23].
Is diabetes mellitus a metabolic disease?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus ( DM) is a lifelong metabolic disease, characterized by hyperglycaemia which gradually leads to the development and progression of vascular complications. It is recognized as a global burden disease, with substantial consequences on human health (fatality) as well as on health-care system costs.
What is diabetes mellitus?
INTRODUCTION. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is chronic, lifelong progressive metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycaemia due to absolute or relative insulinopaenia. There are several different types of DM and each are caused by a complex interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
How many people have diabetes in 2017?
It is estimated that in 2017, there were 451 million people (ages 18-99 years) with diabetes worldwide[2], and this number is expected to rise, mostly due to type 2 DM.
What is DM type 2?
The majority of patients, however, belong to the group with insulin resistance as the core pathophysiological disorder rather than insulin deficiency [1], classified as type 2 DM. This type of DM is phenotypically often accompanied by central obesity, hypertension and dyslipidaemia.
What is metabolic dysregulation?
The metabolic dysregulation that contributes to hyperglycaemia includes diminished insulin secretion, impaired glucose utilization or increased glucose production, and eventually causes pathophysiological changes in multiple organs and organ systems[1].
Is metformin a good treatment for diabetes?
In many people, diet and exercise are not enough to reach this goal, and one or more medications may be needed. Metformin is a tried and tested medicine that has been used for many decades to treat type 2 diabetes, and is recommended by most experts as first-line therapy.
Is metformin safe for diabetes?
Metformin is a tried and tested medicine that has been used for many decades to treat type 2 diabetes, and is recommended by most experts as first-line therapy. It is affordable, safe, effective, and well tolerated by most people. When metformin does not adequately control blood sugar, another medication must be added.
How many people in the US have diabetes?
One in 10 people in the US has diabetes, according to the CDC. However, despite considerable progress in diabetes treatment over the past 20 years, fewer than half of those with diabetes actually reach their target blood sugar goal. In part, this may be because doctors can be slow to make changes to a patient’s treatment plan, ...
What hormone is used to make sugar?
Our bodies produce a hormone called insulin which enables sugar from carbohydrates in food we eat to reach the cells and be used as energy. In type 2 diabetes, insulin’s ability to do its job is compromised, and over time the body actually produces less of it. This means less sugar in the cells for fuel, and more sugar in ...
What happens if you have high blood sugar?
Having high levels of blood sugar over time can cause damage to vital organs like the heart, kidneys, nerves, and eyes. Some risk factors that predispose people to developing type 2 diabetes, such as genetics and age, are not modifiable.
What are the risk factors for diabetes?
Other risk factors, such as being overweight or having obesity, can be altered. This is why losing 5% to 10% of one’s baseline weight by healthful eating and physical activity remains the backbone of type 2 diabetes management.
What is the A1C for diabetes?
The blood sugar goal for most adults with diabetes is an A1C of below 7%. (A1C is a measure of a person’s average blood sugar over a period of about three months.) In many people, diet and exercise are not enough to reach this goal, and one or more medications may be needed.