
What are the treatment guidelines for hepatitis B (HBV)?
Feb 18, 2020 · For the purposes of initiating HBV treatment, most experts and guidelines define chronic HBV infection as the presence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for at least 6 months. [ 4] Goals of Therapy with Treatment of Chronic HBV When considering treatment for persons with chronic HBV, it is important to consider the following goals of therapy.
How long does it take for HBV symptoms to appear?
Jan 02, 2019 · When to Treat Chronic HBV Hepatitis B People living with HBsAG+ should begin treatment with antivirals based on the following. Cirrhosis With low level virema (less than 2,000 IU/ml) Regardless of eAg and ALT Decompensated cirrhosis Regardless of HBV DNA, eAg, and ALT Pregnant If HBV DNA is greater than 2,000 IU/ml Regardless of eAg and ALT
What are the treatment options for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection?
Prophylactic treatment is indicated in HBV-related liver transplantation patients to prevent recurrence, in the last trimester of pregnancy in women with high viraemia to prevent vertical transmission and in patients receiving immunosuppression/chemotherapy to prevent the reactivation of HBV. Treatment is also indicated in patients with co-infections, extrahepatic …
Can HIV prep help people with HBV?
Feb 18, 2020 · Name three key factors to consider when initiating treatment for chronic HBV infection. List the four phases of immune responses that characterize HBV infection. Summarize key recommendations in major guidance documents regarding when to initiate HBV treatment. Discuss the clinical circumstances that warrant antiviral therapy in persons with chronic HBV …
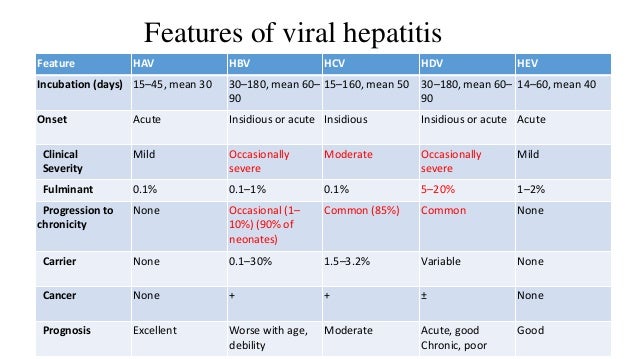
How old do you have to be to have symptoms of HBV?
Not all people with acute HBV infection have symptoms. The presence of signs and symptoms varies by age. Most children <5 years of age and newly infected immunosuppressed adults are generally asymptomatic, whereas 30%–50% of people age ≥5 years have signs and symptoms ( 6 ).
When should I test for HBs?
Testing should not be performed before age 9 months in order to avoid detection of anti-HBs from hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) administered during infancy and to avoid detection of HBsAg from vaccine (HBsAg can be transiently positive for 1–18 days after vaccination).
What to do if you have positive HBsAg?
People with positive HBsAg should be referred to a specialist in the management of hepatitis B infection and receive further serologic evaluation, prevention counseling, and evaluation for antiviral treatment (see Management of HBsAg-Positive Persons ).
What does HBsAG stand for?
Sex partners of people testing positive for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) Sexually active people who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship (e.g., people with more than one sex partner during the previous 6 months) People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted infection.
What drugs target B lymphocytes?
Rituximab and other drugs that target B lymphocytes (black box warning), high-dose steroids, and. anti-TNF agent; with HIV infection who have discontinued therapy with antiretroviral drugs that also have activity against HBV; undergoing solid organ or bone marrow transplantation; and.
Do you need a booster for hemodialysis?
Only certain people should receive a booster dose in specific situations. For hemodialysis patients, if annual testing for antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) shows a decline to <10 mlU/mL, a booster dose should be administered.
Can yeast get hepatitis B?
Anyone who has had a serious allergic reaction to a prior dose of hepatitis B vaccine, a component of the hepatitis B vaccine, or yeast should not receive hepatitis B vaccine. When hepatitis B vaccine is administered as part of a combination vaccine, contraindications to other vaccines should be checked.
Occupational Exposure and Non-occupational Exposure
National Clinicians Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Hotline (PEPline) external icon Hotline providing clinicians with 24-hour guidance on managing occupational exposures to HIV, viral hepatitis, and other bloodborne pathogens
Perinatal Exposure
Infants born to HBV-infected mothers should receive hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. See the Perinatal Transmission page for complete guidelines on postexposure prophylaxis for newborns.
