Medication
Positive – you now have the virus in your blood. If you have a reactive antibody test and a positive NAT for HCV RNA, you will need to talk to a doctor about treatment. Treatments are available that can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks. Printable version of this page: English [PDF – 864 KB] Spanish [PDF – 973 KB]
Procedures
7 rows · It is essential to test for HCV RNA 12 weeks (or longer) after treatment completion. ...
Self-care
Jul 24, 2020 · If a person tests positive for HCV antibodies, hepatitis C testing is not considered complete unless the initial positive anti-HCV test is followed by a test for HCV RNA as per CDC guidelines. A positive test for HCV RNA is needed before a patient can be diagnosed with current HCV and begin receiving treatment.
Nutrition
To guide implementation of hepatitis C treatment as a prevention strategy, studies are needed to define the best candidates for treatment to stop transmission, the additional interventions needed to maximize the benefits of HCV treatment (eg, preventing reinfection), and the cost-effectiveness of the strategies when used in target populations.
When are laboratory tests indicated in the treatment of hepatitis C (HCV)?
Oct 12, 2020 · Testing for HCV RNA can be completed anytime prior to starting DAA therapy, and an HCV genotype and subtype should be obtained if the planned treatment regimen is not a pangenotypic regimen. All patients initiating DAA therapy should be assessed for coinfection with HIV and hepatitis B virus (HBV) with the following laboratory studies:
Who should get an HCV test?
4 rows · † It is recommended before initiating antiviral therapy to retest for HCV RNA in a subsequent ...
Do you need treatment if you are HCV positive?
Initial Treatment of Adults with HCV Infection Initial treatment of HCV infection includes patients with chronic hepatitis C who have not been previously treated with interferon, peginterferon, ribavirin, or any HCV direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agent, whether investigational, or US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved.
When to test for HCV RNA after treatment completion?
How soon after hep C treatment should I get tested?
Who is eligible for HCV treatment?
Do you still test positive for hep C after treatment?
After a successful course of treatment for hepatitis C, the hepatitis C antibody remains detectable, but the hepatitis C RNA will be undetectable. If you plan to donate blood, you will be tested for the hepatitis C antibody and will be turned away even if you do not have an active infection.
What is the window period for HCV?
Does Medi-Cal cover Hep C treatment?
Do hep C antibodies ever go away?
How long do hep C antibodies last?
Does hep C stay in your body forever?
What is the normal range of HCV viral load?
What is a positive hep C result?
What is the best treatment for hepatitis C?
Liver transplantation. If you have developed serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection, liver transplantation may be an option. During liver transplantation , the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver.
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
As a result, people experience better outcomes, fewer side effects and shorter treatment times — some as short as eight weeks.
How old do you have to be to get tested for hepatitis C?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults ages 18 to 79 years be screened for hepatitis C, even those without symptoms or known liver disease. Screening for HCV is especially important if you're at high risk of exposure, including: Anyone who has ever injected or inhaled illicit drugs.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to clear?
The goal of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 weeks after you complete treatment.
How to get rid of hepatitis C?
These measures will help keep you healthy longer and protect the health of others as well: Stop drinking alcohol. Alcohol speeds the progression of liver disease.
How to prevent liver damage?
Avoid medications that may cause liver damage. Review your medications with your doctor, including over-the-counter medications you take as well as herbal preparations and dietary supplements. Your doctor may recommend avoiding certain medications. Help prevent others from coming in contact with your blood.
How to prevent a virus from spreading?
Cover any wounds you have and don't share razors or toothbrushes. Don't donate blood, body organs or semen, and advise health care workers that you have the virus. Also tell your partner about your infection before you have sex, and always use condoms during intercourse.
Diagnosis
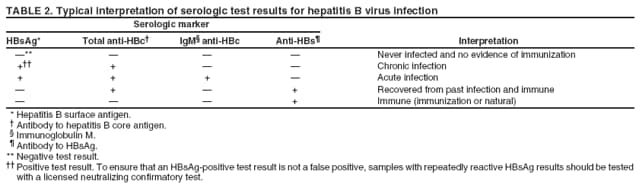
Testing for HCV infection should include use of an FDA-cleared test for antibody to HCV (i.e., immunoassay, EIA, or enhanced CIA and, if recommended, a supplemental antibody test) followed by NAAT to detect HCV RNA for those with a positive antibody result ( 1370 ).
Treatment
HCV infection is curable, and persons with diagnosed HCV infection should be linked to care and treatment. Providers should consult existing guidelines to learn about the latest advances in treating HCV infection ( https://www.hcvguidelines.org#N#external icon#N#) and with hepatitis specialists, as needed.
Management of Sex Partners
Because incident HCV has not been demonstrated to occur among heterosexual couples followed over time ( 1334, 1371 – 1373 ), condom use might not be necessary in such circumstances. Persons with HCV infection with one long-term, steady sex partner do not need to change their sexual practices.
Other Management Considerations
All persons with HCV infection for whom HIV and HBV infection status is unknown should be tested for these infections. Those who have HIV or HBV infection should be referred for or provided with recommended care and treatment. Persons without previous exposure to HAV or HBV should be vaccinated.
Prevention
Reducing the burden of HCV infection and disease in the United States requires implementing both primary and secondary prevention activities.
Postexposure Follow-Up
No PEP has been demonstrated to be effective against HCV infection. Testing for HCV is recommended for health care workers after percutaneous or perimucosal exposures to HCV-positive blood. Prompt identification of acute infection is vital because outcomes are improved when treatment is initiated early during the illness course.
Special Considerations
All pregnant women should be screened with each pregnancy for HCV antibodies at the first prenatal visit in settings where the HCV prevalence is >0.1% ( https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hcv/index.htm) ( 154, 155 ).
CDC Recommendations for Hepatitis C Screening Among Adults in the United States
Universal hepatitis C screening :#N#Hepatitis C screening at least once in a lifetime for all adults aged 18 years and older, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection (HCV RNA‑positivity) is less than 0.1%*#N#Hepatitis C screening for all pregnant women during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection (HCV RNA‑positivity) is less than 0.1%*.
Testing Sequence
Hepatitis C testing should be initiated with a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)‑approved anti‑HCV test. People testing anti‑HCV positive/reactive should have follow-up testing with an FDA‑approved nucleic acid test (NAT) for detection of HCV RNA. See complete Recommended Testing Sequence for Identifying Current Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection.
USPSTF Recommendations
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force – Screening for Hepatitis C Virus Infection#N#external icon#N#The USPSTF recommends screening for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in adults aged 18 to 79 years. Grade: B Recommendation.
Resources
Testing for HCV infection: An update of guidance for clinicians and laboratorians.
How long does it take for ribavirin to reduce hemoglobin?
Ribavirin causes hemolysis. Patients receiving ribavirin should have hemoglobin levels checked during treatment, often after 2 weeks, and the ribavirin dose reduced if the patient develops significant anemia, often defined as hemoglobin <10 g/dL.
Does ribavirin cause hemolysis?
Ribavirin causes hemolysis. Patients receiving ribavirin should have hemoglobin levels checked during treatment, often after 2 weeks, and the ribavirin dose reduced if the patient develops significant anemia, often defined as hemoglobin <10 g/dL. Ribavirin causes fetal death and fetal abnormalities in animals.
Can you take ribavirin while pregnant?
The safety of ribavirin-free DAA regimens in humans has not been established during pregnancy and for nursing mothers, so counseling should be offered to women of childbearing age before beginning HCV treatment. (See ribavirin pregnancy recommendations below.) I, C.
What happens if you don't achieve SVR?
Patients who do not achieve SVR retain the possibility of continued liver injury, progression of hepatic fibrosis, and the potential to transmit HCV infection to others . Such patients should be considered for retreatment per the Retreatment of Persons in Whom Prior Therapy Has Failed section.
What is DAA monitoring?
This section provides guidance on monitoring patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection who are starting direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment , are on treatment, or have completed therapy. It is divided into 4 parts: pretreatment and on-treatment monitoring; post-treatment follow-up for persons in whom treatment failed to clear the virus; post-treatment follow-up for those who achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR; virologic cure); and additional considerations if treatment includes ribavirin.
How long does it take for HCV to show up?
The window period for acute HCV infection before the detection of antibodies averages 8 to 11 weeks, with a reported range of 2 weeks to 6 months. In addition, some people might lack the immune response necessary to develop detectable antibodies within this time range ( 31, 32 ).
Can HIV be transmitted through sex?
Although less frequent, HCV can also be spread through: Sex with an HCV -infected person (an inefficient means of transmission, although HIV-infected men who have sex with men [MSM] have increased risk of sexual transmission) Sharing personal items contaminated with infectious blood, such as razors or toothbrushes.
Why is it important to avoid alcohol?
the importance of avoiding alcohol, because alcohol consumption can accelerate cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease; the need to follow a healthy diet and stay physically active, especially for patients who are overweight (i.e., those with body mass index [BMI] ≥25kg/m 2) or obese (BMI ≥30kg/m 2 ); and.
What is the goal of treatment for HCV?
Goal of Treatment. The goal of treatment of HCV-infected persons is to reduce all-cause mortality and liver-related health adverse consequences , including end-stage liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma, by the achievement of virologic cure as evidenced by a sustained virologic response.
What is the goal of treatment of HCV-infected persons?
The goal of treatment of HCV-infected persons is to reduce all-cause mortality and liver-related health adverse consequences , including end-stage liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma, by the achievement of virologic cure as evidenced by a sustained virologic response. I, A.
What is SVR in hepatitis C?
Successful hepatitis C treatment results in sustained virologic response (SVR), which is tantamount to virologic cure and, as such, is expected to benefit nearly all chronically infected persons. When the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first interferon-sparing treatment for HCV infection, many patients who had previously been ...
Can HCV be remediated?
Treatment is recommended for all patients with acute or chronic HCV infection, except those with a short life expectancy that cannot be remediated by HCV therapy, liver transplantation, or another directed therapy. Patients with a short life expectancy owing to liver disease should be managed in consultation with an expert.
What is SVR in HCV?
SVR is a marker for cure of HCV infection and has been shown to be durable in large prospective studies in more than 99% of patients followed-up for ≥5 years ( Swain, 2010 ); ( Manns, 2013 ). While follow-up studies after cure using DAAs are limited, durability of SVR appears to be just as high ( Sarrazin, 2017 ); ( Reddy, 2018 ). Patients in whom SVR is achieved have HCV antibodies but no longer have detectable HCV RNA in serum, liver tissue, or mononuclear cells, and achieve substantial improvement in liver histology ( Marcellin, 1997 ); ( Coppola, 2013 ); ( Garcia-Bengoechea, 1999 ). Assessment of viral response, including documentation of SVR, requires use of an FDA-approved quantitative or qualitative nucleic acid test (NAT) with a detection level of ≤25 IU/mL.
Is hepatitis C a lymphoproliferative disease?
Chronic hepatitis C is associated with a syndrome of cryoglobulinemia, an immune complex and lymphoproliferative disorder that leads to arthralgia, fatigue, palpable purpura, renal disease (eg, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis), neurologic disease (eg, peripheral neuropathy, central nervous system vasculitis), and reduced complement levels ( Agnello, 1992 ). Glomerular disease results from deposition of HCV-related immune complexes in the glomeruli ( Johnson, 1993 ). Because patients with chronic hepatitis C frequently have laboratory evidence of cryoglobulins (>50% in some series), antiviral treatment is imperative for those with the syndrome of cryoglobulinemia and symptoms or objective evidence of end-organ manifestations. Limited data with DAA therapy in the setting of vasculitis end-organ disease related to cyroglobulinemia have demonstrated responses in 20% to 90% of patients ( Comarmond, 2017 ); ( Emery, 2017 ). Despite this, patients with severe end-organ disease may still require treatment with plasmapheresis or rituximab ( Emery, 2017 ).
Is fibrosis progression a variable disease?
Fibrosis progression is variable across different patient populations as well as within the same individual over time. Many of the components that determine fibrosis progression and development of cirrhosis in an individual are unknown. However, certain factors, such as coinfection with HIV or the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and prevalent coexistent liver diseases (eg, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH]), are well recognized contributors to accelerated fibrosis progression (see Table below).
Can HBV reactivate after interferon?
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation associated with severe hepatitis flare has been increasingly recognized as a potential adverse event associated with HCV DAA therapy. [ 17] Previous reports have described HBV reactivation after interferon-based therapy, but in these prior cases, clinically significant hepatitis was rare. Chronic HCV has been known to suppress HBV replication in persons coinfected with HCV and a reciprocal interaction between these viruses has long been postulated. The elimination of HCV can result in a potential loss of immunologic control of HBV infection and result in HBV reactivation.
How many cases of HBV reactivation in DAA?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a drug safety warning on October 4, 2016 in which they identified 24 cases of confirmed reactivation of HBV infection in persons receiving DAA medications for treatment of HCV. [ 18] The FDA warning was based on a number of cases reported to the FDA and from published literature. [ 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24] The FDA has published findings that summarized a total of 29 patients (5 from the United States) with confirmed HBV reactivation during DAA therapy; their summary was based on published reports and cases detected via their Adverse Event Reporting System database between November 2013 and October 2016. [ 25] The following summarizes key findings from this report:
Is ribavirin safe for pregnant women?
For persons taking ribavirin, regular monitoring of hemoglobin is recommended. Ribavirin is a teratogenic drug in rodents and may cause birth defects and fetal harm when administered to women who are pregnant. It is therefore contraindicated in pregnant women and in men whose female partners are pregnant. In addition, extreme care must be taken to prevent pregnancy in females taking ribavirin and in female partners of male patients taking ribavirin. Accordingly, ribavirin should not be started unless there is a documented report of a negative pregnancy test immediately prior to planned initiation of ribavirin. Women taking ribavirin (and women who have a male partner taking ribavirin) should be instructed to use at least two forms of effective contraception during treatment that includes ribavirin and for 6 months after treatment has been stopped. Women receiving ribavirin (and women who have a male partner taking ribavirin) should have monthly pregnancy tests during ribavirin treatment and for 6 months after treatment has been completed.
What is the treatment for HCV?
Initial treatment of HCV infection includes patients with chronic hepatitis C who have not been previously treated with interferon, peginterferon, ribavirin, or any HCV direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agent, whether investigational, or US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved.
What is recommended regimen?
Recommended regimens are those that are favored for most patients in a given group, based on optimal efficacy, favorable tolerability and toxicity profiles, and treatment duration.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
Diagnosis
- Antiviral medications
Hepatitis C infection is treated with antiviral medications intended to clear the virus from your body. The goal of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 weeks after you complete treatment. Researchers have recently made significant advances in treatmen… - Liver transplantation
If you have developed serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection, liver transplantation may be an option. During liver transplantation, the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver. Most transplanted livers come from decease…
Treatment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Management of Sex Partners
- If you receive a diagnosis of hepatitis C, your doctor will likely recommend certain lifestyle changes. These measures will help keep you healthy longer and protect the health of others as well: 1. Stop drinking alcohol.Alcohol speeds the progression of liver disease. 2. Avoid medications that may cause liver damage.Review your medications with your doctor, including o…
Other Management Considerations
- If you think you may have a risk of hepatitis C, see your family doctor. Once you've been diagnosed with a hepatitis C infection, your doctor may refer you to a specialist in liver diseases (hepatologist) or infectious diseases.
Prevention
Postexposure Follow-Up
Special Considerations
CDC Recommendations For Hepatitis C Screening Among Adults in The United States
Testing Sequence
USPSTF Recommendations
- No PEP has been demonstrated to be effective against HCV infection. Testing for HCV is recommended for health care workers after percutaneous or perimucosal exposures to HCV-positive blood. Prompt identification of acute infection is vital because outcomes are improved when treatment is initiated early during the illness course.
Resources