
Medication
- Antiviral Agents / therapeutic use*
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular / prevention & control*
- Disease Management*
- Hepatitis B, Chronic / drug therapy*
- Humans
- Time
Procedures
There is no cure for HBV at this time, but treatment can stop the virus from replicating and triggering liver damage. HBV treatments lower the risk of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer. What treatments are available for chronic hepatitis B? Treatment is an oral antiviral medication. In rare cases, injections may be used.
Self-care
in viremic patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). Vonafexor met the primary endpoint of lowering HBsAg by an average of = 1 log10, a key biomarker of viral activity in the liver, after 16 weeks of treatment. These results in CHB patients are further ...
Nutrition
Treatment generally involves antiviral medications, such as: Antiviral medications can help to reduce symptoms and prevent liver damage. But they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is to have the lowest viral load possible.
When to initiate HBV treatment?
Does HBV have a treatment?
When to treat chronic HBV?
Can HBV be cured?
How many treatments are there for hepatitis B treatment?
There are now 7 approved drugs for hepatitis B in the United States -- 2 types of injectable interferons and 5 oral antivirals – that control the hepatitis B virus. A cure, however, may be in the near future because there is exciting research being done today to generate promising new drugs.
How is HBV cured?
A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there's no cure if you have the condition. If you're infected, taking certain precautions can help prevent spreading the virus to others.
What is the first line treatment for hepatitis B?
Currently, pegylated interferon alfa (PEG-IFN-a), entecavir (ETV), and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) are the first-line agents in the treatment of hepatitis B disease.
How long does HBV treatment last?
Advantages: 1 pill taken daily; few side effects, effective in controlling the virus in most people. Disadvantages: Treatment is long-term, possibly lifelong. Does every patient need to be on medication? It is important to know that not every person with chronic HBV needs to be on medication.
Can tenofovir cure hepatitis B?
Tenofovir will not cure hepatitis B and may not prevent complications of chronic hepatitis B such as cirrhosis of the liver or liver cancer. Tenofovir may not prevent the spread of hepatitis B to other people.
When should hepatitis B treatment start?
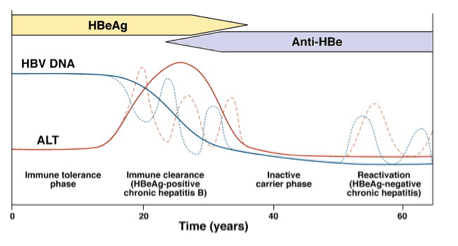
Current guidelines recommend initiating antiviral therapy in HBeAg-positive patients who have ALT levels ≥2 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) and HBV DNA levels ≥20,000 IU/ml.
Is HBV treatment lifelong?
Available therapies for HBV require lifelong treatment and surveillance, as reactivation frequently occurs following medication cessation and the occurrence of HCC is decreased but not eliminated, even after years of successful viral suppression.
Can hepatitis B positive change negative?
The hepatitis B e-antigen test result is often used to monitor the effectiveness of many hepatitis B drug therapies that aim to change a chronically infected person's e-antigen status from “positive” to “negative.” By achieving a “negative” e-antigen result, this means that the hepatitis B drug successfully stopped or ...
Is Egg good for hepatitis B patient?
Olive oil, canola oil and flaxseed oil are all healthy fats that are recommended as part of a diet for patients with Hepatitis. Healthy proteins in the form of low-fat milk and dairy products along with lean meats, beans, eggs and soy products can also be a part of a healthy liver diet.
How long can you live with hepatitis B?
A "silent disease." It can live in your body for 50+ years before you have symptoms. Responsible for 80 percent of all liver cancer in the world. Harder to fight off the younger you are; 90 percent of babies will go on to develop a chronic infection compared to 5 to 10 percent of adults.
What is hepatitis B positive?
HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen) - A "positive" or "reactive" HBsAg test result means that the person is infected with hepatitis B. This test can detect the actual presence of the hepatitis B virus (called the “surface antigen”) in your blood.
Is banana good for hepatitis B patient?
Bananas have emerged as the best candidate to deliver a bite-sized vaccine for hepatitis B virus (HBV) to millions of people in developing countries, according to an article scheduled for the June 1 issue of ACS' >Biotechnology Progress, a bi-monthly journal co-published with the American Institute of Chemical ...
What is the best treatment for hepatitis B?
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B may include: Antiviral medications. Several antiviral medications — including entecavir (Baraclude), tenofovir (Viread), lamivudine (Epivir), adefovir (Hepsera) and telbivudine (Tyzeka) — can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. These drugs are taken by mouth.
What to do if you have hepatitis B?
Receive kidney dialysis. Take medications that suppress the immune system, such as those used to prevent rejection after an organ transplant. Use illegal injected drugs. Are in prison. Were born in a country where hepatitis B is common, including Asia, the Pacific Islands, Africa and Eastern Europe.
What is the best way to test for liver damage?
Liver ultrasound. A special ultrasound called transient elastography can show the amount of liver damage. Liver biopsy. Your doctor might remove a small sample of your liver for testing (liver biopsy) to check for liver damage.
How to get rid of hepatitis A?
Eat a healthy diet full of fruits and vegetables, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Take care of your liver. Don't drink alcohol or take prescription or over-the-counter drugs without consulting your doctor. Get tested for hepatitis A and C. Get vaccinated for hepatitis A if you haven't been exposed.
Does hepatitis B go away on its own?
Treatment for acute hepatitis B infection. If your doctor determines your hepatitis B infection is acute — meaning it is short-lived and will go away on its own — you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend rest, proper nutrition and plenty of fluids while your body fights the infection.
How to treat hepatitis B?
Current treatments for hepatitis B fall into two general categories: 1 Immune modulator Drugs – These are interferon-type drugs that boost the immune system to help get rid of the hepatitis B virus. They are given as a shot (similar to how insulin is given to people with diabetes) over 6 months to 1 year. 2 Antiviral Drugs – These are drugs that stop or slow down the hepatitis B virus from reproducing, which reduces the inflammation and damage of your liver. These are taken as a pill once a day for at least 1 year and usually longer.
How many drugs are there for hepatitis B?
There are now 7 approved drugs for hepatitis B in the United States -- 2 types of injectable interferons and 5 oral antivirals – that control the hepatitis B virus. A cure, however, may be in the near future because there is exciting research being done today to generate promising new drugs.
What is the HBF drug watch?
Hepatitis B Drug Watch. The Hepatitis B Foundation created the HBF Drug Watch to keep track of approved and promising new treatments. In 1991, “interferon alpha” was the first drug approved for hepatitis B and given as a series of injections over 1 year. In 1998, “lamivudine” was approved as the first oral antiviral drug taken once a day.
Is it important to know that not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs to be treated?
It is important to know that not everyone with chronic hepatitis B infection needs to be treated. This can be difficult to accept when first diagnosed because taking a drug to get rid of the virus seems like the first step to getting better.
Hepatitis B and Pregnancy
Because their immune systems aren’t fully developed, infants and young children are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B, so it’s important to limit their exposure to the virus. All expecting women should be screened for hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Treatment: Medication
There are five FDA-approved oral medications and one injection available to treat hepatitis B. The newer oral medications are stronger and less likely to develop viral resistance and have very few side effects.
Hepatitis B Treatment: Liver Transplant
A referral for a liver transplant evaluation may be needed if chronic hepatitis B infection leads to cirrhosis (severe scarring of the liver), liver cancer or end stage liver disease and its complications. Rarely, acute hepatitis B can lead to severe liver failure which requires liver transplantation.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of acute or chronic HBV infection requires serologic testing (Table 5). Because HBsAg is present in both acute and chronic infection, presence of IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (IgM anti-HBc) is diagnostic of acute or recently acquired HBV infection.
Treatment
No specific therapy is available for persons with acute HBV infection; treatment is supportive. Persons with chronic HBV infection should be referred for evaluation to a provider experienced in managing such infections.
Prevention
Two products have been approved for HBV prevention: hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) for PEP and hepatitis B vaccine ( 12 ).
Other Management Considerations
All persons with HBV infection should be tested for HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia.
Management of Persons Who Are HBsAg Positive
Recommendations for management of all persons with HBsAg include the following:
Special Considerations
Regardless of whether they have been previously tested or vaccinated, all pregnant women should be tested for HBsAg at the first prenatal visit and again at delivery if at high risk for HBV infection (see STI Detection Among Special Populations).

Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
General Goals of HBV Treatment
- Treatment to prevent hepatitis B infection after exposure
If you know you've been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and aren't sure if you've been vaccinated, call your doctor immediately. An injection of immunoglobulin (an antibody) given within 12 hours of exposure to the virus may help protect you from getting sick with hepatitis B. Because this tre… - Treatment for acute hepatitis B infection
If your doctor determines your hepatitis B infection is acute — meaning it is short-lived and will go away on its own — you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend rest, proper nutrition and plenty of fluids while your body fights the infection. In severe cases, antivira…
Carefully Review Criteria Before Initiating Antiviral Treatment For HBV
- If you've been infected with hepatitis B, take steps to protect others from the virus. 1. Make sex safer. If you're sexually active, tell your partner you have HBVand talk about the risk of transmitting it to him or her. Use a new latex condom every time you have sex, but remember that condoms reduce but don't eliminate the risk. 2. Tell your sexual partner to get tested. Anyone wit…
General Information on HBV Medications
- If you've been diagnosed with hepatitis B infection, the following suggestions might help you cope: 1. Learn about hepatitis B.The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is a good place to start. 2. Stay connected to friends and family.You can't spread hepatitis B through casual contact, so don't cut yourself off from people who can offer support. 3. Take care of yourself.Ea…
First Line
- You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. However, in some cases, you may be referred immediately to a specialist. Doctors who specialize in treating hepatitis B include: 1. Doctors who treat digestive diseases (gastroenterologists) 2. Doctors who treat liver diseases (hepatologists) 3. Doctors who treat infectious diseases
Related Resources
- To suppress HBV DNA and normalize ALT
- To achieve loss of HBeAg (if initially HBeAg positive)
- To achieve loss of HBsAg (this occurs rarely)
- To reduce the likelihood of cirrhosis and HCC