How long after stroke can you take aspirin?
1. Exercise Regularly...
2. Eat Healthy...
3. Reduce Weight...
4. Manage Stress...
5. Quit Smoking...
Learn More...When should I talk to my doctor about taking an aspirin?
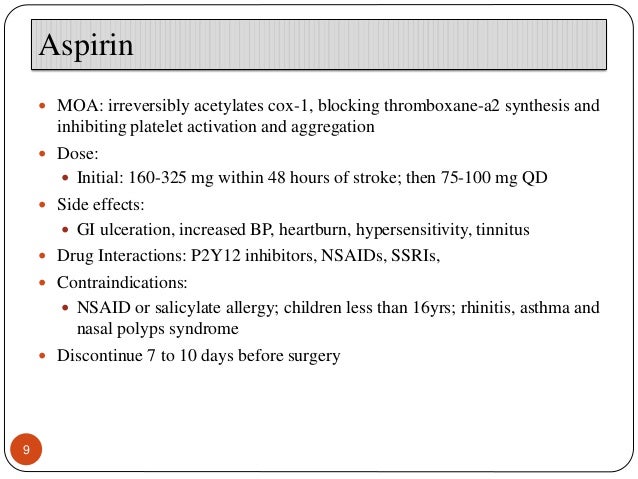
Aspirin has a larger time frame and can be administered within 24-48 hours after stroke onset When blood thinning medication like aspirin is used during hemorrhagic stroke, it could worsen the bleeding and, as a result, worsen patient outcomes.
Is daily aspirin therapy right for You?
If you're between ages 60 and 69, consider talking with your health care provider about daily aspirin therapy and how it may affect you. Daily low-dose aspirin therapy may be recommended for the primary prevention of heart attack or stroke if:
What is the basis for the prescribing information for aspirin?
Daily aspirin therapy can be a lifesaving option, but it's not for everyone. Get the facts before considering a daily aspirin. Taking aspirin every day may lower the risk of heart attack and stroke, but daily aspirin therapy isn't for everyone.

Why is aspirin prescribed for a stroke?
Aspirin, which thins the blood and thereby prevents clots, is currently used to reduce the long-term risks of a second stroke in patients who've had an ischemic stroke. But giving aspirin to patients who've had a hemorrhagic stroke is considered dangerous, as it can cause more bleeding and more damage.
What is the first line of treatment for a stroke?
An IV injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) — also called alteplase (Activase) or tenecteplase (TNKase) — is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke. An injection of TPA is usually given through a vein in the arm within the first three hours.
Should I take aspirin after a mini stroke?
Aspirin is already given to people who have had a stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA – often called a 'mini-stroke') to prevent further strokes after they have been assessed in hospital and in the longer-term, reducing the subsequent stroke risk by about 15%.
What are 3 treatments for a stroke?
Treating ischaemic strokesThrombolysis – "clot buster" medicine. ... Thrombectomy. ... Aspirin and other antiplatelets. ... Anticoagulants. ... Blood pressure medicines. ... Statins. ... Carotid endarterectomy.
What is a common medication used after a stroke?
Warfarin and heparin are common examples. There are also medicines called direct oral anticoagulant and these include: Apixaban (Eliquis), dabigatran (Pradaxa), edoxaban (Lixiana, Savaysa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto). Anticoagulants are aggressive drugs.
What should you do immediately after a TIA?
If you experience TIA symptoms, call 911 or have someone bring you to an emergency room right away. Once you are at the ER, the attending doctor will assess you and perform or order tests to determine why you had the symptoms.
Does aspirin stop TIA?
Aspirin is a well-recognised treatment for ischaemic stroke and TIA. It is also usual practice to administer aspirin to suspected TIA patients once they have been assessed by medical personnel.
Is aspirin recommended for stroke prevention?
Guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) for primary prevention of CVD and stroke advise aspirin for patients with a ten-year risk of 10 percent or more. The AHA and American Stroke Association recommend the drug for primary prevention of stroke if ten-year risk is at least 6 to 10 percent.
How long after stroke can you take aspirin?
Aspirin has a larger time frame and can be administered within 24-48 hours after stroke onset.
What About Daily Aspirin for Stroke Prevention?
After a stroke has been treated, doctors should follow up with suggested protocol to help prevent a second stroke.
How long does it take for aspirin to dissolve a blood clot?
If the stroke is diagnosed as ischemic, doctors can administer aspirin within 24-48 hours to dissolve the blood clot and treat the stroke. When a stroke is diagnosed as hemorrhagic, aspirin should be avoided as it can worsen bleeding in the brain. Taking aspirin for both emergency stroke treatment and stroke prevention carry their own risks.
What to do if someone has a stroke in 2020?
If someone is showing signs of a possible stroke, immediately call for emergency help and do not give the person any medication like aspirin. Doing this can save a life. The only person who should provide aspirin for emergency stroke treatment is a doctor who has performed a brain scan and can confirm ...
Why is it important to know the type of stroke?
Knowing the type of stroke is critical for effective treatment, because each type is treated differently.
Does aspirin cause a stroke?
Some studies report that long-term aspirin use increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Taking a daily low-dose aspirin can also cause other complications such as risk of stomach bleeding. Drinking alcohol worsens these complications.
Can you give aspirin after a stroke?
When Doctors Can Safely Administer Aspirin for Stroke. There is a specific time window that drugs can be safely administered after a stroke. This is another reason why it’s critical to seek emergency treatment. Here are the best known times to administer tPA or aspirin after a stroke:
Does aspirin help with stroke?
Aspirin has been proven to prevent ischemic stroke in a variety of settings. Despite the frequency at which aspirin continues to be prescribed in patients at risk of ischemic stroke, there remains confusion in clinical practice as to what minimum dose is required in various at-risk patients.
Is aspirin individualized?
Available evidence suggests that aspirin dosing must be individualized according to indication. Recommendations provided by national guidelines at times recommend lower doses of aspirin than have been proven effective. Higher doses are indicated for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (325 mg) ….
Can aspirin be used for stroke prevention?
Novel oral anticoagulant drugs, such as oral direct thrombin inhibitors and oral factor Xa inhibitors, might further diminish the role of aspirin for stroke prevention in AF. Nonetheless, aspirin use should continue in the early stages following presentation of a patient with AF and acute coronary syndrome, and after stenting, ...
Is aspirin safe for stroke?
For the majority of patients with AF, aspirin has a limited role in stroke prevention, being an inferior strategy and not necessarily safer than the anticoagulant warfarin, especially in the elderly.
Is aspirin safer than warfarin?
For the majority of patients with AF, aspirin has a limited role in stroke prevention, being an inferior strategy and not necessarily safer than the anticoagulant warfarin, espe …. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a major cause of stroke and thromboembolism, resulting in substantial morbidity and mortality. For the majority of patients ...
How long after stroke can you take aspirin?
In particular, the result for patients randomized 7 to 12 hours after stroke onset merely illustrates the statistical problems of subgroup analyses and does not indicate that aspirin is much less effective for such patients than for those random ized 0 to 6 or 13 to 48 hours after stroke onset.
How long does it take for aspirin to reduce stroke?
The reduction in further stroke or death from just a few weeks of early aspirin use is 9 per 1000 within 1 month, which compares favorably with the absolute monthly benefits of antiplatelet therapy in nonacute settings. For example, in the trials of antiplatelet treatment given on a long-term basis (eg, for some years) to patients who have already had a stroke or an episode of transient cerebral ischemia, the average monthly benefit was only 1 per 1000, even though the cumulative benefit eventually became substantial (≈38 per 1000 after 3 years of antiplatelet treatment). 1
What is the absolute risk reduction for ischemic stroke?
For recurrent ischemic stroke, the absolute risk reduction of 7 per 1000 (1.6% versus 2.3%) corresponds to a proportional reduction of 30% (OR 0.70). This overall result is indicated by the broken vertical line in Figure 2, along with the separate results for each of 28 different subgroups of 10 characteristics recorded at baseline. Overall, the amount of heterogeneity between these 28 results is no greater than would be expected by chance alone if the proportional risk reduction was really about the same in all subgroups (global heterogeneity test on 18 df, 20.9, NS). Thus, for recurrent ischemic stroke, there is no good evidence that the proportional reduction is much larger or smaller in any subgroup than in the aggregate of all patients. In particular, the result for patients randomized 7 to 12 hours after stroke onset merely illustrates the statistical problems of subgroup analyses and does not indicate that aspirin is much less effective for such patients than for those randomized 0 to 6 or 13 to 48 hours after stroke onset. Likewise, the apparent difference between the effects in men and women is not conventionally significant, as long as due allowance is made for the number of different comparisons that have been made in Figure 2.
What grants did the Oxford Clinical Trial Service Unit receive?
The Oxford Clinical Trial Service Unit and the Edinburgh Department of Clinical Neurosciences were supported by Medical Research Council special program grants. IST was also supported by the European Union and the Stroke Association. The principal acknowledgment is to the many patients who joined these 2 trials and to the many CAST and IST collaborators (and others) acknowledged in the original reports. 23
Is aspirin good for ischemic stroke?
Background and Purpose —Long-term daily aspirin is of benefit in the years after ischemic stroke, and 2 large randomized trials (the Chinese Acute Stroke Trial [CAST] and the International Stroke Trial [IST]), with 20 000 patients in each, have shown that starting daily aspirin promptly in patients with suspected acute ischemic stroke also reduces the immediate risk of further stroke or death in hospital and the overall risk of death or dependency. However, some uncertainty remains about the effects of early aspirin in particular categories of patient with acute stroke.
Is aspirin a good effect on hemorrhage?
Aspirin had no significant effect on the incidence of another symptomatic cerebral hemorrhage (29 [7.3%] versus 26 [6.9%], NS) and appeared to reduce the incidence of other strokes (1 [0.3%] versus 8 [1.1%], 2 P =0.04).
Does aspirin affect stroke?
Overall, there was no apparent effect of aspirin allocation on the subsequent incidence of strokes of unknown type, either overall (Figure 1) or in any particular subgroup (global heterogeneity test: χ 218 =17.3; NS).
What happens if you stop taking aspirin every day?
If your health care provider has told you to take an aspirin every day, contact him or her before stopping it.
What are possible drug interactions with daily aspirin therapy?
Combining aspirin with a prescription blood-thinning medication (anticoagulant) may greatly increase the risk of major bleeding. Anticoagulants include:
How can aspirin prevent a heart attack?
Aspirin interferes with the blood's clotting action. When a person bleeds, clotting cells, called platelets, collect at the site of the wound. The platelets help form a plug that seals the opening in the blood vessel, stopping the bleeding.
What happens if your blood vessels are narrowed?
If your blood vessels are already narrowed from atherosclerosis — the buildup of fatty deposits in your arteries — a fatty deposit in your vessel lining can burst. Then, a blood clot can quickly form and block the artery. This prevents blood flow to the heart and causes a heart attack.
Can you take aspirin on your own?
You shouldn't start daily aspirin therapy on your own, however. While taking an occasional aspirin or two is safe for most adults to use for headaches, body aches or fever, daily use of aspirin can have serious side effects, including internal bleeding.
Can you take aspirin if you have a heart attack?
If you've had a heart attack or stroke, your doctor will likely recommend you take a daily aspirin unless you have a serious allergy or history of bleeding. If you have a high risk of having a first heart attack, your doctor will likely recommend aspirin after weighing the risks and benefits. You shouldn't start daily aspirin therapy on your own, ...
Can you stop taking aspirin?
If you have been taking daily aspirin therapy and want to stop, it's important to talk to your doctor before making any changes. Suddenly stopping daily aspirin therapy could have a rebound effect that may trigger a blood clot.
What is the purpose of aspirin in stroke?
Strokes: Aspirin use recommended in both men and women to treat mini-strokes (transient ischemic attack --TIA) or ischemic stroke to prevent subsequent cardiovascular events or death. Heart Attacks:
Why should consumers not self medicate for aspirin?
A. FDA emphasizes that consumers should not self-medicate for these serious conditions because it is very important to make sure that aspirin is their best treatment. In these conditions, the risk and benefit of each available treatment for each patient must be carefully weighed.
What is the best medicine for pain?
Pain relief: Aspirin is indicated for the temporary relief of minor aches and pains.
Is aspirin safe for stroke?
Physicians will be better able to prescribe the proper doses for these uses for male and female patients with these medical conditions. Dose-related adverse events for patients with stroke and cardiovascular conditions should be minimized because lower dosages are recommended. The full prescribing information now provided for physicians who treat rheumatologic diseases will enhance the safe and effective prescribing of aspirin to these patients as well.
Is aspirin safe for heart attacks?
A. The information on the uses of aspirin is based on scientific studies that support treatment with aspirin for heart attacks, strokes, and some related conditions in patients who have cardiovascular disease or who have already had a heart attack or stroke. Convincing data support these uses in lower doses than previously believed to be effective in treating heart attacks and strokes in both men and women.
Is aspirin good for rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatologic diseases: Aspirin is indicated for relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, spondylarthropathies, and arthritis and pleurisy associated with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Is aspirin bad for you?
A. There is a wide range of adverse reactions that may result from aspirin use including effects on the body as a whole, or on specific body systems and functions.
How long does it take to take aspirin for a stroke?
The same guidelines recommend aspirin for people with acute ischaemic stroke, as soon as possible within 24 hours, where a diagnosis of intracerebral haemorrhage has been excluded using brain imaging. For those without dysphagia give aspirin 300 mg orally and those with dysphagia can be give the same dose rectally or via an enteral tube.
How long does aspirin stay in your system after a stroke?
Aspirin 300 mg daily should be continued until long term antithrombotic treatment is agreed 2 weeks post stroke or at discharge.
How much aspirin should I take for CVD?
The 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes recommended aspirin for CVD event prevention at a dose of 75-100 mg daily in patients with previous MI or revascularization.
How old do you have to be to take aspirin?
The USPSTF state that there is insufficient current evidence to assess the balance of benefits versus harms of initiating aspirin for primary prevention of CVD and CRC in adults younger than 50 years or 70 years or older. (Grade I).
What is the best treatment for dyspepsia?
A proton pump inhibitor is recommended in addition to aspirin for those with dyspepsia linked to aspirin use.
Is aspirin recommended for DM?
The ESC 2019 guidelines on diabetes (DM), pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular disease state: “Patients with DM and symptomatic CVD should be treated no differently to patients without DM. In patients with DM at moderate CV risk, aspirin for primary prevention is not recommended.
Can you take aspirin without CVD?
The 2016 European guidelines on CVD prevention review the evidence for antiplatelet therapy in individuals without CVD and conclude that current evidence does not support the use of aspirin in those without CVD due to the risk of a major bleed. For more information see: ...