Full Answer
What is the history of acromegaly?
The History of Acromegaly Pierre Marie coined the term 'acromegaly' in 1886 and linked it to a distinct clinical disease with a characteristic clinical picture. However, Pierre Marie was not the first physician to give a full record of the clinical picture of acromegaly; others had preceded him, like the Dutch physician Joha …
What are clinical trials for acromegaly?
The trials look to find new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease and improve quality of life. What are clinical trials for acromegaly? —are part of medical research and involve people like you.
How often do you give acromegaly injections?
Treatment of Acromegaly. Injections are usually given once a month but can be given less frequently to some patients. The injection can be given by a nurse, and can also be given by the patient or the patient’s partner. There is little difference in the effectiveness of these two somatostatin analogs.
What is the age limit for acromegaly in the elderly?
Elderly patients with acromegaly Thirty-one patients (19 female) met the inclusion criteria of group 2 (diagnosis of acromegaly before 65 years and age at the last clinical record ≥65 years).
When did acromegaly start?
The First Medical Descriptions of Acromegaly and Gigantism. In 1886, the French neurologist Pierre Marie (1853-1940; fig. 1) first coined the term 'acromegaly' (initially also known as 'Marie's malady') and linked it to a distinct clinical disease with a characteristic clinical picture.
What is the history of acromegaly?
Abstract. Pierre Marie coined the term 'acromegaly' in 1886 and linked it to a distinct clinical disease with a characteristic clinical picture. However, Pierre Marie was not the first physician to give a full record of the clinical picture of acromegaly; others had preceded him, like the Dutch physician Johannes Wier.
Who first discovered acromegaly?
However, it was Pierre Marie, in 1886, who established the term "acromegaly" for the first time and established a distinct clinical diagnosis with clear clinical descriptions in 2 patients with the characteristic presentation.
What is the first line treatment for acromegaly?
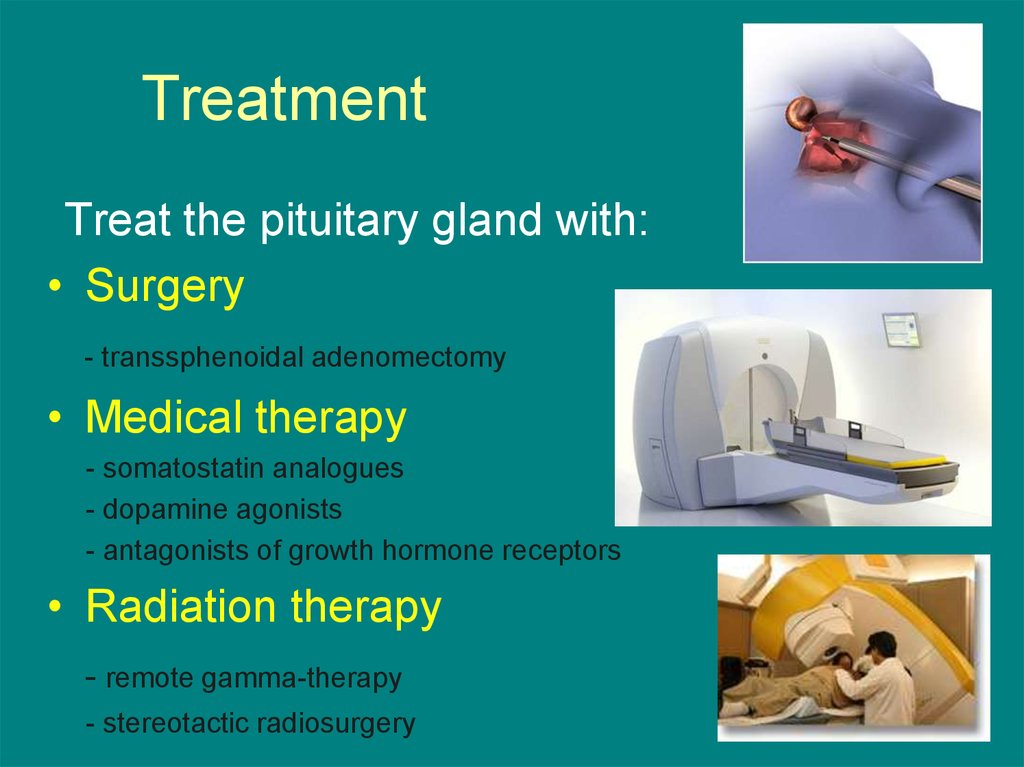
Transsphenoidal surgery is the preferred first-line treatment for patients with acromegaly that have intrasellar microadenomas, noninvasive macroadenomas or patients in whom the tumor is causing compression symptoms.
What is the life expectancy of someone with acromegaly?
In acromegaly, men were younger than women at diagnosis (median 44.5 vs 50 years, P<0.001) and death (67 vs 76 years, P=0.0015). Compared with controls, women (36% vs 25%, P<0.01), but not men (31% vs 28%, P=0.44), had increased mortality.
Is acromegaly reversible?
Can acromegaly be cured? Acromegaly can be put into remission. This means that the disease is stopped and many of the signs and symptoms reversed. But, acromegaly can be a lifelong disease.
What triggers acromegaly?
In adults, a tumor is the most common cause of too much GH production: Pituitary tumors. Most acromegaly cases are caused by a noncancerous (benign) tumor (adenoma) of the pituitary gland. The tumor produces excessive amounts of growth hormone, causing many of the signs and symptoms of acromegaly.
Can you get acromegaly later in life?
Acromegaly is a rare condition where the body produces too much growth hormone, causing body tissues and bones to grow more quickly. Over time, this leads to abnormally large hands and feet, and a wide range of other symptoms. Acromegaly is usually diagnosed in adults aged 30 to 50, but it can affect people of any age.
What is irreversible acromegaly?
As acromegalic skeletal abnormalities are rather irreversible, apneic episodes may persist after normalization of hormonal levels. Aggressive therapy, including surgery, pharmacological treatment and, in some cases, pituitary irradiation, aiming at normalization of IGF-1 levels, is required for arthropathy management.
What is the gold standard for diagnosing acromegaly?
An OGTT with 75 g glucose is considered the gold standard for diagnosing acromegaly. However, similar to IGF-1 assays, the GH assay method can impact the absolute GH concentration reported by a laboratory.
How successful is acromegaly surgery?
Overall, 70-80% of patients with acromegaly achieve remission with surgery, and the resultant normalized GH and IGF-1 levels lead to resolution of many of the associated problems of the disease such as hypertension, diabetes, carpal tunnel syndrome, snoring and sleep apnea.
Who is most likely to get acromegaly?
Who is more likely to develop acromegaly? Acromegaly is most often diagnosed in middle-aged adults, but symptoms can appear at any age. In children, too much growth hormone causes a condition called gigantism link rather than acromegaly.
What is the best treatment for acromegaly?
Somatostatin analogs. The medicines most often used to treat acromegaly are called somatostatin analogs (SSAs). These drugs curb the release of GH and may also reduce the size of the pituitary tumor. Several studies have shown that these drugs are safe and effective for long-term treatment.
Where is acromegaly located?
Rarely, acromegaly is caused by tumors located in the hypothalamus—a small area of the brain near the pituitary gland, pancreas, lungs, or other parts of the chest or abdomen. Some of these tumors make growth hormone themselves. But more often, the tumors produce growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), a hormone that signals the pituitary gland to make growth hormone.
What is acromegaly in the body?
What is acromegaly? Acromegaly is a disorder that occurs when your body makes too much growth hormone (GH). Produced mainly in the pituitary gland, GH controls the physical growth of the body. In adults, too much of this hormone causes bones, cartilage, body organs, and other tissues to increase in size.
What hormones cause acromegaly?
When GH enters the blood, this signals the liver to produce another hormone, called insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). IGF-I is the hormone that actually causes bones and body tissue to grow.
How do doctors remove pituitary tumors?
Doctors can remove most pituitary tumors using a method called transsphenoidal surgery. The operation is done through the nose and sphenoid sinus, a hollow space in the skull behind the nasal passages and below the brain. Two approaches to this surgery are
How do you know if you have acromegaly?
Symptoms of acromegaly can vary from person to person. Common changes in physical appearance include. hands and feet become larger and swollen—you may notice a change in ring or shoe size, especially shoe width. lips, nose, and tongue become larger.
When does Gigantism occur?
rather than acromegaly. Gigantism occurs when excess GH begins before the end of puberty, when children’s growth plates fuse or close. Having too much GH before the growth plates close causes children to grow tall in height.
How is acromegaly treated?
The aims of treatment are to reduce GH and IGF-I production to normal levels in order to reverse or improve the symptoms, and to prevent or minimize damage to the rest of the pituitary gland and surrounding brain tissue by relieving the pressure exerted by the tumor.
What is the only treatment for acromegaly?
If the tumor is completely removed and hormone levels return to normal, then surgery may be the only treatment for acromegaly you will need. There are three different types of drug used to treat acromegaly currently: ‘dopamine agonists’, ‘somatostatin analogs’ and ‘growth hormone receptor antagonists’.
What is the third type of drug treatment?
The third type of drug treatment is a growth hormone receptor antagonist , and the only drug in its class is called pegvisomant (brand name Somavert). Unlike dopamine agonists and somatostatin analogs, pegvisomant does not stop the production of GH by the tumor. Instead it stops the hormone from taking effect in the body.
How often should I take a blood test for GH?
Blood tests to measure GH and IGF-I levels will be taken several times each year. The aim of treatment is to lower your GH level to less than 1 ng/ml and to have your IGF-I level in the normal range for your age. What You Can Expect from Treatment.
Can acromegaly be cured?
Sometimes, although GH levels have been reduced by the operation, the acromegaly is not cured. In these instances you may be given additional treatment such as drug therapy and/or radiotherapy. Route of transsphenoidal surgery.
Does acromegaly affect life expectancy?
Headaches usually improve and eyesight usually returns to normal. Life expectancy is decreased in patients with acromegaly but is restored to normal with successful treatment.
Is dopamine agonist a first line medication?
Dopamine agonists are often thought of as first line medical therapy, however they are less effective than the other medications. However, dopamine agonists are easier to take and are less costly so the may be used in some cases, but other medications are more commonly used to treat acromegaly.
What is acromegaly surgery?
Detailed Description: Acromegaly is a rare disease caused by a growth hormone (GH) producing pituitary adenoma. Surgery is primary treatment, whereas medical treatment with a somatostatin analogue (SA), which suppresses GH secretion and reduces tumour size, is used when surgery is insufficient or unfeasible.
What is the purpose of the study in acromegaly?
Study Description. The aim of the study is to investigate sleep apnea, circulation and metabolism in acromegaly before and after surgery and/or medical treatment. Acromegaly is a rare disease caused by a growth hormone (GH) producing pituitary adenoma. Surgery is primary treatment, whereas medical treatment with a somatostatin analogue (SA), ...
Is Acromegaly before or after treatment?
Acromegaly - Before and After Treatment. The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Know the risks and potential benefits of clinical studies and talk to your health care provider ...
Does acromegaly increase morbidity?
Acromegaly is associated with metabolic abnormalities which contributes to an increased morbidity and mortality if left untreated. To which extend these abnormalities reverses after treatment, and if treatment modality influences the outcome, remain elusive.
Is primary medical therapy a reasonable option?
Primary medical therapy is a reasonable option and is effectively used, while the rate of surgical success is not reduced. A careful cost-benefit balance is suggested. Disease-specific comorbidities are more prevalent in acromegalic patients with a longer follow-up rather than in those diagnosed aged ≥65 years.
Is acromegaly rare?
Acromegaly is a rare disease with a peak of incidence in early adulthood. However, enhanced awareness of this disease, combined with wide availability of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has increased the diagnosis of forms with mild presentation, especially in elderly patients. Moreover, due to increased life expectancy ...
When were psychoactive drugs first used?
Psychoactive drugs have been used since the earliest human civilizations. Problematic use of substances was observed as early as the 17th century. 1. The evolution of addiction treatment, from the mid-18th century to the present, is outlined below.
What is the name of the drug that was used to treat alcoholism?
Disulfiram and other drugs are used to treat alcoholism (1948-1950). Disulfiram, otherwise known as Antabuse, was introduced in the U.S. as a supplemental treatment for alcoholism. Antabuse created feelings of nausea and unpleasant reactions to alcohol.
When was the Drug Addiction Treatment Act passed?
Drug Addiction Treatment Act passed (1999). This bill was introduced in 1999 to amend the Controlled Substances Act with stricter registration requirements for practitioners who dispense narcotic drugs in Schedules III, IV, or V for maintenance and detoxification treatment. 25.
When was methadone first used?
Methadone introduced (1964). Vincent Dole, an endocrinologist, and Dr. Marie Nyswander, a psychiatrist, introduced methadone to treat narcotic addiction. The FDA approved it to treat heroin addiction in 1972. 2 Methadone is a slow-acting opioid agonist that prevents harsh opioid withdrawal symptoms. 18.
When was alcoholism first defined?
American Medical Association defines alcoholism (1952). In 1952 , the American Medical Association (AMA) first defined alcoholism. 2 Eventually, the committee agreed to define alcoholism as a primary, chronic disease with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors influencing the condition’s prognosis. 16.
When was buprenorphine approved?
FDA approves buprenorphine for clinical use (2002). In 2002, the FDA approved buprenorphine, a medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid addiction. Unlike methadone, which is dispensed within a structured clinic, specially qualified physicians can prescribe buprenorphine. 26.
When did the first narcotics farm open?
Narcotics farms open (1935). The first federal narcotics farm opened in Lexington, Kentucky in 1935. 2 Lexington was a center for drug treatment and federal research, and provided free treatment to addicts and alcoholics, including the “Lexington Cure.”.
