
Which treatment will the nurse anticipate administering that will stimulate wound healing?
Because the patient is at risk for delayed wound healing, what treatment will the nurse anticipate administering that will stimulate wound healing? Becaplermin, a recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor gel, actively stimulates wound healing.
What is antibiotic therapy for wounds?
The therapy kills anaerobic bacteria in the wound, preventing further infection. It increases the killing power of WBCs and certain antibiotics. The therapy also promotes angiogenesis (growth of new blood vessels) to facilitate wound healing.
Which medications are used to treat central pain syndromes?
a. A skeletal muscle relaxant b. A tricyclic antidepressant c. An opioid analgesic d. Gabapentin Gabapentin is useful for central pain syndromes and radiculopathy and can help to restore sleep. Skeletal muscle relaxants are useful for muscle spasms.
What are the treatment options for nociceptive pain?
Sometimes the pain can be relieved by an epidural steroid injection combined with physical therapy. If this doesn’t work, your doctor may suggest another approach. Other approaches may include: What’s the outlook for someone with nociceptive pain? The outlook for your pain depends on what’s causing it.
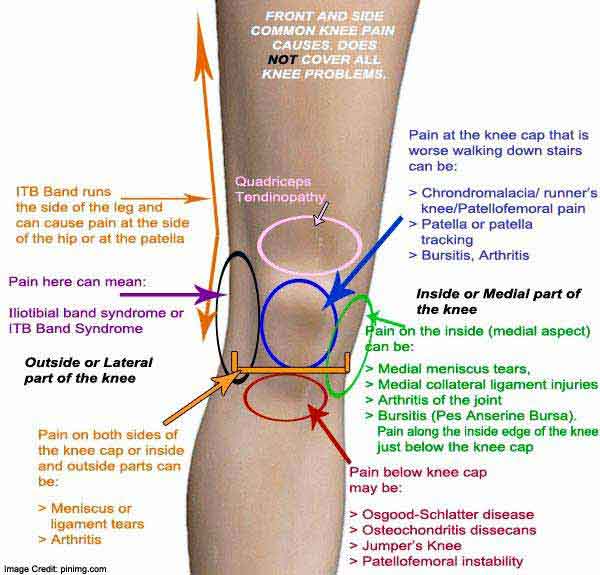
What is the treatment of pain?
pain medicines. physical therapies (such as heat or cold packs, massage, hydrotherapy and exercise) psychological therapies (such as cognitive behavioural therapy, relaxation techniques and meditation) mind and body techniques (such as acupuncture)
How do you manage pain and inflammation?
Here, we've listed eight techniques to control and reduce your pain that don't require an invasive procedure — or even taking a pill.Cold and heat. ... Exercise. ... Physical therapy and occupational therapy. ... Mind-body techniques. ... Yoga and tai chi. ... Biofeedback. ... Music therapy. ... Therapeutic massage.
What is the appropriate treatment for patients with moderate pain?
Acetaminophen is the first-line treatment for most mild to moderate acute pain. Ibuprofen and naproxen (Naprosyn) are good, first-line NSAIDs for mild to moderate acute pain based on effectiveness, adverse effect profile, cost, and over-the-counter availability.
What are 3 different types of pain management?
Pain Management for Specific Types of Pain Acute pain: nonopioids, weak opioids, opioids, nonpharmacological treatments such as ice or bioelectric therapy. Chronic pain: nonopioids, weak opioids, opioids, antidepressants, capsaicin cream, nonpharmacological treatments such as bioelectric therapy, radiation therapy.
How do you reduce swelling from an injury?
You can use ice packs, cold therapy systems, ice baths, or cryotherapy chambers to deliver cold to the affected area. Apply cold several times a day for 20-30 minutes at a time to help keep swelling down, especially in the first several days after an injury.
What is a new treatment to pain that is being developed?
A new study from the University of Michigan School of Dentistry confirms that a low dose of a drug called naltrexone is a good option for patients with orofacial and chronic pain, without the risk of addiction, said first author Elizabeth Hatfield, a clinical lecturer in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery ...
What are the nursing interventions for pain?
Nursing Interventions for Acute PainProvide measures to relieve pain before it becomes severe. ... Acknowledge and accept the client's pain. ... Provide nonpharmacologic pain management. ... Provide pharmacologic pain management as ordered. ... Manage acute pain using a multimodal approach.More items...•
What is pain management nursing?
Pain management nurses are responsible for the care of patients with chronic or acute pain. Once they have assessed a patient's pain, they work closely with doctors and other nurses to create a treatment plan. Pain management nurses administer medications and provide pain relief through other therapeutic methods.
How is acute pain managed?
Simple analgesics, including NSAIDs and acetaminophen, are most effective for treating acute pain because they target the natural inflammation that occurs with an injury. NSAIDs can be more effective than opioids and/or muscle relaxants for treating acute low back pain.
What methods of pain control besides medication might be helpful in the care of and end of life patient?
There are a number of non-drug tools for coping with pain. They can be used on their own or in combination with drug therapies....Some of the options patients have found helpful include:Massage. ... Relaxation techniques. ... Acupuncture. ... Physical therapy. ... Pet therapy. ... Gel packs.
What is the most common treatment for chronic pain?
The most common treatments for chronic pain are NSAIDs, acetaminophen, COX-2 inhibitors, antidepressants and anti-seizure medicines, and opioids.
Why is pain management important in nursing?
Of particular importance to nursing care, unrelieved pain reduces patient mobility, resulting in complications such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolus, and pneumonia.
What does it mean when a patient has intermittent pain from the flank to the groin on the right side?
The medical history of a patient reporting severe intermittent pain from the flank to the groin on the right side shows that the patient is osteoporotic and is on calcium supplements. Which condition should the nurse anticipate?
What is the best treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis?
Oral bisphosphonates should be prescribed to the patients whose serum alkaline phosphotase levels are more than twice the normal range. Calcitonin is useful in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Calcium supplements do not regulate the alkaline phosphotase levels in serum. NSAIDS such as ibuprofen should be prescribed only in conditions of mild to moderate pain.
How to treat osteomyelitis with antibiotics?
Osteomyelitis wounds should be packed with beads made of bone cement impregnated with an antibiotic. This provides direct contact of the antibiotic with the offending organism. Wound irrigation can be done through the window of a cast to clean the wound. A portable device can administer a high concentration of oxygen by hyperbaric therapy, which increases tissue perfusion for patients with chronic unremitting osteomyelitis. Systemic antibiotics are administered for more than 3 months to control the infection. A clean technique is preferred over strict aseptic technique to change dressings for contaminated (dirty) wounds.
What does a BMD score mean?
The BMD test helps to compare the patient's bone density to a healthy 30-year-old adult's bone density. If the patient's BMD is equal to the control, then the T-score will be 0. A T score from -1 to -2.5 indicates osteopenia. A T-score lower than -2.5 indicates osteoporosis. The greater the negative number, the more severe osteoporosis would be.
Why is it important to keep a wound moist?
Keeping the wound moist is extremely important in a red wound. A moist environment helps in granulation and re-epithelialization. Transparent films and adhesive semipermeable dressings are permeable to oxygen and are used in red wounds. Airing out a wound is not recommended because it can dry the wound and prevent formation of granulation tissue. Wound irrigations are usually avoided because unnecessary manipulation can destroy the granulation tissue.
What causes redness and rubor at the inflammatory site?
Rationale. Inflammation causes a release of inflammatory mediators, which results in vasodilation, hyperemia, and increased capillary permeability. Vasodilation causes redness, or rubor, at the inflammatory site. A change in pH releases prostaglandins, causing dolor (pain) at the injury site.
Why does my swollen thigh hurt?
Swelling is caused by fluid shift to interstitial spaces and accumulation of fluid exudate. Redness is a result of hyperemia from vasodilation. Blackish discoloration and ulcers are not indicative of inflammation.
What is the shift to the left in the inflammatory response?
A shift to the left refers to the presence of band neutrophils, which are an early sign of inflammation. p. 161.
What is the initial phase of primary intention healing?
C. Primary intention, initial phase. The inflammatory phase is the initial phase of primary intention healing; this phase occurs three to five days after an injury. The nurse is preparing to apply heat at the site of inflammation to a patient who sustained an injury to the arm.
How does heat help with inflammation?
Heat application is used to localize the inflammatory agents and promote healing by increasing the circulation to the inflamed site and subsequent removal of debris. Cold application decreases congestion and promotes vasoconstriction at the site of inflammation. Immobilizing the inflamed area with a cast prevents further tissue injury.
What is the systemic response to inflammation?
The systemic response to inflammation includes the manifestations of a shift to the left in the white blood cell (WBC) count, malaise, nausea, anorexia, increased pulse and respiratory rate, and fever. The local response to inflammation includes redness, heat, pain, swelling, or loss of function at the site of inflammation.
Why is traction used for radicular pain?
Traction may be used for patients with radicular symptoms to help resolve neurological deficits, although systematic review of research has not clearly identified a benefit to this therapy.REF : Management. 1. A patient comes to a provider with reports of unilateral arm pain and weakness with mild neck pain.
How to reduce pain from osteoarthritis?
Bisphosphonates can decrease pain by preventing growth and development of existing and new bone lesions. Exercise is useful to maintain function and reduce pain. External beam radiation is useful in the majority of patients. Vertebralplasty involves injecting bone cement to stabilize bone. Massage is not recommended.
What is the name of the injection that is given into the bursal sac?
b. Corticosteroid injection into the bursal sac
What is the best treatment for heel bursitis?
Activity modification and bracing, NSAIDs, and RICE are all used initially to treat heel bursitis. Patients should wear open-heeled shoes. Corticosteroid injections should be used cautiously to prevent rupture of the Achilles tendon.REF: Heel Bursitis/Management
What is the first step in management of Achilles tendonitis?
This patient has symptoms consistent with Achilles tendonitis. Immediate cessation of sports and exercise is the first step in management. Crutches and partial weight bearing may be indicated if symptoms do not improve with rest and NSAIDs. Physical therapy is used as adjunctive therapy. Symptoms that do not improve require referral
Can you get a referral for septic bursitis?
Immediate referral is indicated for patients who present with symptoms consistent with septic bursitis, such as with the symptoms above. Lidocaine is injected into a painful joint to evaluate for improvement to determine whether bursitis or tendonitis is present as a result of impingement. This exam is not consistent with fracture. An ultrasound is not indicated.REF: Shoulder Bursitis/Management
Can NSAIDs be used for short periods?
NSAIDs are used for short periods. Splinting is not recommended.REF: Management. 2. A patient reports elbow pain and the examiner elicits pain with resisted wrist flexion, forearm pronation, and passive wrist extension on the affected side.
What is radicular pain?
Radicular pain occurs when the nerve roots are irritated. It goes down your arm or leg through a nerve that comes from the the spinal cord.
What are some examples of neuropathic pain?
Some people say that the neuropathic pain they experience is a constant sensation. Others report episodes that come and go. Diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by multiple sclerosis are some examples of neuropathic pain.
What is the pain of the heart?
Visceral pain. Visceral pain happens when internal organs, such as involuntary muscles in the heart, are injured or inflamed. This type of pain is usually described as aching. The location may seem vague. Here’s more about somatic versus visceral pain, and when to see your doctor.
What causes nociceptive pain?
Injuries that cause nociceptive pain include: pain caused by overuse or joint damage, such as arthritis or sprains. When activated by stimuli, nociceptors notify the brain about the injury with electrical signals sent via the peripheral and central nervous system (CNS).
What are some examples of nociceptive damage?
For example, the damaged areas could include the skin, muscles, bones, or other tissues. The nociceptors can also detect chemical and thermal damage. Chemical damage is caused by contact with toxic or hazardous chemicals. Exposure to extremely hot or cold temperatures leads to thermal damage. Injuries that cause nociceptive pain include: bruises. ...
Why do I feel pain in my nociceptors?
Nociceptors are a type of receptor that exists to feel all and any pain that’s likely to be caused by the body being harmed. Harm can include mechanical or physical damage to various parts of the body.
What is somatic pain?
Somatic pain happens when any of the pain receptors in your tissues, such as muscles, bone, or skin, are activated. This type of pain is often stimulated by movement. It’s usually localized. Headaches and cuts are both considered somatic pain.
