
What happens when you have a ruptured kidney?
Oct 29, 2018 · When you have cirrhosis, blood flow to the liver is impaired. Substances such as ammonia that would normally be cleaned by the liver, escape into the general circulation. Aside from the problems with liver blood flow, when cirrhosis is advanced there aren't enough healthy cells to get all the work done.
What happens when you have hyperparathyroidism?
Dec 09, 2021 · Doctors do not have specific treatments that can cure cirrhosis. However, they can treat many of the diseases that cause cirrhosis. Some of the diseases that cause cirrhosis can be cured. Treating the underlying causes of cirrhosis may keep your cirrhosis from getting worse and help prevent liver failure. Successful treatment may slowly improve some of your liver …
What are the early sign and symptoms of liver cirrhosis?
Feb 06, 2021 · Treatment for complications of cirrhosis Your doctor will work to treat any complications of cirrhosis, including: Excess fluid in your body. A low-sodium diet and medication to prevent fluid buildup in the body may help control ascites and swelling. More-severe fluid buildup may require procedures to drain the fluid or surgery to relieve pressure.

How long can you live with cirrhosis with treatment?
...
Life expectancy by stage.
What happens if you don't treat cirrhosis?
Can liver cirrhosis be stopped?
Can cirrhosis be resolved?
Can the liver regenerate after cirrhosis?
How quickly does cirrhosis progress?
What are the 4 stages of cirrhosis?
- Stage I: Steatosis. The first stage of liver disease is characterized by inflammation of the bile duct or liver. ...
- Stage II: Scarring (fibrosis) of the liver due to inflammation. ...
- Stage III: Cirrhosis. ...
- Stage IV: Liver failure or advanced liver disease or hepatic failure.
Is cirrhosis of the liver painful?
How do you know if your liver is struggling?
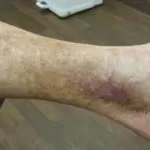
- Skin and eyes that appear yellowish (jaundice)
- Abdominal pain and swelling.
- Swelling in the legs and ankles.
- Itchy skin.
- Dark urine color.
- Pale stool color.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Nausea or vomiting.
What is the fastest way to cure cirrhosis?
- Don't drink alcohol. Whether your cirrhosis was caused by chronic alcohol use or another disease, avoid alcohol. ...
- Eat a low-sodium diet. ...
- Eat a healthy diet. ...
- Avoid infections. ...
- Use over-the-counter medications carefully.
What is the best medicine for liver cirrhosis?
How do I make my liver healthy again?
- Maintain a healthy weight. ...
- Eat a balanced diet. ...
- Exercise regularly. ...
- Avoid toxins. ...
- Use alcohol responsibly. ...
- Avoid the use of illicit drugs. ...
- Avoid contaminated needles. ...
- Get medical care if you're exposed to blood.
Can cirrhosis be slow?
Medications may slow the progression of certain types of liver cirrhosis. For example, for people with primary biliary cirrhosis that is diagnosed early, medication may significantly delay progression to cirrhosis. Other medications can relieve certain symptoms, such as itching, fatigue and pain.
Is there a cure for cirrhosis?
Scientists are working to expand current treatments for cirrhosis, but success has been limited. Because cirrhosis has numerous causes and complications, there are many potential avenues of approach. A combination of increased screening, lifestyle changes and new medications may improve outcomes for people with liver damage, if started early.
How to diagnose cirrhosis of the liver?
People with early-stage cirrhosis of the liver usually don't have symptoms. Often, cirrhosis is first detected through a routine blood test or checkup. To help confirm a diagnosis, a combination of laboratory and imaging tests is usually done .
What is the INR for cirrhosis?
Your international normalized ratio (INR) is also checked for your blood's ability to clot. Based on the blood test results, your doctor may be able to diagnose the underlying cause of cirrhosis. He or she can also use blood tests to help identify how serious your cirrhosis is. Imaging tests.
What tests are needed for cirrhosis?
If you have cirrhosis, your doctor is likely to recommend regular diagnostic tests to monitor for signs of disease progression or complications, especially esophageal varices and liver cancer. Noninvasive tests are becoming more widely available for monitoring.
Can you stop drinking if you have cirrhosis?
If you have cirrhosis, it is critical to stop drinking since any amount of alcohol is toxic to the liver. Weight loss.
Is it safe to drink alcohol with cirrhosis?
If you have cirrhosis, it is critical to stop drinking since any amount of alcohol is toxic to the liver. Weight loss. People with cirrhosis caused by nonalcoholic fatty liver disease may become healthier if they lose weight and control their blood sugar levels. Medications to control hepatitis.
What happens if you don't treat cirrhosis?
If you don't treat the cause of your cirrhosis, it'll get worse, and over time your healthy liver cells won't be able to keep up. You might start to get tired, feel like you don't want to eat, and lose weight without trying. After a while, your liver may not be able to work well or at all.
Why does cirrhosis get worse?
Cirrhosis always develops because of another liver problem or disease. If you don't treat the cause of your cirrhosis, it'll get worse, and over time your healthy liver cells won't be able to keep up. You might start to get tired, feel like you don't want to eat, and lose weight without trying.
What does it mean when your liver is cirrhosis?
If your doctor tells you that you have cirrhosis, it means you have a condition that causes scar tissue to gradually replace your healthy liver cells. It usually happens over a long period of time because of infection or alcohol addiction. Most of the time, you can't fix the damage to your liver, but if you catch it early, ...
Does obesity cause cirrhosis?
Obesity raises your chances of this condition. If your cirrhosis is caused by this disease, you may improve your liver health if you lose weight and keep your blood sugar levels under control. Hepatitis B or hepatitis C. Medicines for these diseases can stop more damage from happening to your liver.
What to do if your doctor suspects cirrhosis?
If your doctor suspects cirrhosis, they’ll do a blood test. It will check for signs that your liver isn't working right, such as: High levels of certain liver enzymes. Buildup of bilirubin, which forms from the metabolism of heme.
How to stop cirrhosis?
Your doctor can suggest a treatment program for addiction. Lose weight if you are obese, especially if your cirrhosis is caused by fat buildup in your liver. Take medications if you have hepatitis B or C. Keep all your doctor's appointments. Eat enough protein.
Can you get liver cancer from cirrhosis?
Your doctor may recommend regular testing to make sure you don't get liver cancer, which can be a complication of cirrhosis. If your cirrhosis is severe, you may need a liver transplant. It's a major operation. You'll likely need to get on a waiting list for a new liver from an organ donor who has died.
Can cirrhosis cause liver failure?
It causes scarring and damage to the liver. This scarring may eventually prevent the liver from functioning correctly, leading to liver failure. Many things can eventually lead to cirrhosis, including: Cirrhosis is a progressive disease, meaning it gets worse over time.
How long does it take to live with cirrhosis?
For someone with cirrhosis, a liver transplant can add years to their life expectancy. The higher someone’s MELD score is, the more likely they are to die within three months. This can move them higher up the list of those waiting for a liver transplant.
What is the liver cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis of the liver is a late-stage consequence of liver disease. It causes scarring and damage to the liver. This scarring may eventually prevent the liver from functioning correctly, leading to liver failure. Many things can eventually lead to cirrhosis, including:
Can cirrhosis be reversed?
Cirrhosis is a progressive disease, meaning it gets worse over time. Once you have cirrhosis, there’s no way to reverse it. Instead, treatment focuses on slowing down its progression. Depending on how severe it is, cirrhosis can have an effect on life expectancy.
How to prevent cirrhosis?
Even if your cirrhosis isn’t related to alcohol, it’s best to abstain because alcohol can damage your liver, especially if it’s already damaged. Limit salt. A cirrhotic liver has a hard time keeping fluid in the blood. Salt intake raises the risk of fluid overload.
Can you drink alcohol with cirrhosis?
Even if your cirrhosis isn’t related to alcohol, it’s best to abstain because alcohol can damage your liver, especially if it’s already damaged. Limit salt. A cirrhotic liver has a hard time keeping fluid in the blood. Salt intake raises the risk of fluid overload.
Can cirrhosis shorten life expectancy?
Cirrhosis is a chronic condition that can shorten someone’s life expectancy. Doctors use several measurements to determine the outlook of someone with cirrhosis, but these only provide estimates. If you have cirrhosis, your doctor can give you a better idea of your outlook and what you can do to improve it.
What is liver cirrhosis?
What is cirrhosis of the liver? Liver cirrhosis results from disease or chemical-induced injuries to the liver over a sustained period. As the injuries kill liver cells, your body attempts to rebuild the damage. In the process, the existing cells are inflamed and scar tissue results, compromising the structure of the liver ...
Does alcohol help with cirrhosis?
Most of those with alcohol-induced cirrhosis experience an improvement in liver function with abstinence from alcohol. Even people with chronic hepatitis B and C can substantially reduce liver damage and slow the progression towards cirrhosis with abstinence from alcohol.
Can you drink alcohol with cirrhosis?
All people with cirrhosis should avoid alcohol. Most of those with alcohol-induced cirrhosis experience an improvement in liver function with abstinence from alcohol. Even people with chronic hepatitis B and C can substantially reduce liver damage and slow the progression towards cirrhosis with abstinence from alcohol.
Can hepatitis C be treated with NSAIDs?
Eradicating hepatitis C virus by using anti-viral medications. Not all patients with cirrhosis due to chronic viral hepatitis are candidates for drug treatment.
What is the study of liver disease?
Hepatology is the study of liver disease, and a liver specialist or hepatologist will likely be part of your medical team in treating liver cirrhosis. Hepatology is a subspecialty of gastroenterology (GI doctor). The liver is the body's largest internal organ, and the study of hepatology includes the study of acute and chronic hepatitis, ...
What is the hepatology of the liver?
Hepatology is a subspecialty of gastroenterology (GI doctor). The liver is the body's largest internal organ, and the study of hepatology includes the study of acute and chronic hepatitis, viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, genetic and metabolic liver diseases and their complications, liver cancer, liver transplantation, ...
Does UDCA cure PBC?
Despite producing clear benefits, UDCA treatment primarily slows progression and does not cure PBC. Other medications such as colchicine ( Colcrys) and methotrexate ( Rheumatrex, Trexall) also may have benefit in subsets of patients with PBC.
Cirrhosis Treatment Options
Cirrhosis is a progressive liver disease. The damage to your liver is irreversible. The goal of treatment is to delay or stop further damage to the liver by:
Cirrhosis Treatment: Liver Transplantation
If you have a severe case of cirrhosis, we may recommend a liver transplant. Learn more about liver transplantation .
Can liver cirrhosis cause death?
It tends to affect more men than women. It’s also one of the top 20 causes of death in several countries like the USA. Liver cirrhosis can usually regrow cells after tissue damage. This condition happens when various factors that damage the liver like infections and alcohol exist long-term.
What causes cirrhosis in the body?
This can cause other symptoms that can be difficult to deal with. There are various causes of cirrhosis. They include long-term alcohol drinking and Hepatitis C. Other causes are obesity although this cause is less common than others like Hepatitis and alcoholism.
What is the first stage of liver cirrhosis?
The first stage involves people with higher-than-average fat in their livers. However, this condition can progress to more serious stages involving conditions like hepatitis. It can then lead to cirrhosis (liver scarring) so it’s critical to know about cirrhosis of the liver the last stage before death.
What is liver cirrhosis?
Liver cirrhosis happens during the last stages of severe liver disease. In many cases, the condition is triggered by long-term toxins like viral infections or alcoholic beverages. The liver is a vital organ and is needed by the body for various functions including: Storing vitamins/sugar for future use.
Can drinking alcohol cause cirrhosis?
Studies show that heavy drinking for 10+ years can often result in cirrhosis. This usually involves men drinking 3+ alcoholic drinks per day and women drinking 2+ beverages. There are other causes of cirrhosis including: Immune system disease .
Can you drink cold turkey if you have cirrhosis?
It’s highly recommended that you quit drinking alcohol cold turkey if you have late-stage cirrhosis. Consider that the body can only process a small amount of alcohol in one day. When there’s already major damage to the vital organ it makes the situation worse.
How many stages of liver disease are there?
Liver disease includes four stages. The final stage includes various health issues that didn’t exist during the previous stages. The reason is the body is unable to recover due to lost liver function. If a patient is in this stage it’s possible to live a couple of years.
What are the symptoms of cirrhosis?
Sharma said symptoms start with decreased appetite, weight loss, nose bleeds/bruising and weakness and progress to mental confusion, abdominal swelling and jaundice - and cirrhosis, which can ultimately lead to death.
Is cirrhosis a death sentence?
“Most people with cirrhosis don’t need a transplant,” she said. “And cirrhosis is not a death sentence.”. Dr. Sanjeev Sharma, a physician affiliated with Tri-City Medical Center, said cirrhosis is a result ...
What is the cause of cirrhosis?
Copy Link URL Copied! Many people believe that the main cause of a liver disease known as cirrhosis is alcohol abuse. However, Dr. Catherine Frenette, medical director of liver transplantation at Scripps Clinics in San Diego, said while over-consumption of alcohol may be the most publicized cause, it’s hardly the most common.
Is cirrhosis more common in men than women?
Cirrhosis is thought to be the seventh leading cause of death in the U.S., and it’s more common in men than in women, with an approximate ratio of 2-to-1. Today, a liver transplant is the only available treatment for end-stage liver disease. While a transplant rids the body of cirrhosis and comes with an 85 percent survival rate after five years, ...
Why is it important to have a healthy liver?
The liver maintains the body’s glucose level, helps in food digestion and removes toxins from the body, so proper liver function is important to overall health.
How many people are waiting for liver transplants?
Sharma said about 17,000 people are awaiting liver transplants, compared to 6,000 liver transplants done annually in the U.S. As a result, Frenette said, 20 ...
What is the virus that causes inflammation of the liver?
Rather, she said, that distinction goes to hepatitis C , a virus that causes inflammation of the liver that’s spread when blood from an infected person enters the body of someone who’s not infected – often by sharing IV drug needles.
What are the complications of cirrhosis of the liver?
Other complications of cirrhosis of the liver that may lead to death are: Edema and Ascites: When the hepatic damage is in an advanced stage, liquid is accumulated in the legs (edema) and in the abdomen (ascites). Ascites can cause bacterial peritonitis, which is a serious infection. Hemorrhages: When the production of proteins necessary ...
What happens when cirrhosis slows the liver?
When this happens, the drugs act for longer than normal and accumulate in the body. This causes a greater sensitivity of the person to the medicines and their side effects. Hepatic Encephalopathy: If the liver fails, it cannot eliminate toxins from ...
Can ascites cause peritonitis?
Ascites can cause bacterial peritonitis, which is a serious infection. Advertisement. Hemorrhages: When the production of proteins necessary for blood coagulation by the liver stops or slows down, the person suffers haemorrhages easily. Portal Hypertension: Cirrhosis slows down the normal circulation of blood, which increases the pressure in ...
Why do blood vessels burst?
Enlarged blood vessels are more likely to burst due to thin walls and increased pressure. If they burst, urgent medical attention will be required. Splenomegaly: When portal hypertension occurs, the spleen often enlarges and retains white blood cells and platelets, decreasing the number of these cells in the blood.
Does cirrhosis cause gallstones?
Gallstones: If cirrhosis does not allow the free flow of bile to and from the gallbladder, bile hardens and gallstones form. Drug Sensitivity: Cirrhosis slows the liver’s ability to filter medications in the blood. When this happens, the drugs act for longer than normal and accumulate in the body. This causes a greater sensitivity ...
What happens if the liver fails?
Hepatic Encephalopathy: If the liver fails, it cannot eliminate toxins from the blood and eventually they accumulate in the brain. The accumulation of toxins in the brain, called hepatic encephalopathy, can cause a decrease in mental functioning and coma.
What are the symptoms of mental health problems?
Signs of decreased mental functioning include confusion, personality changes, memory loss, concentration problems and change in sleep habits. Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes: Cirrhosis causes resistance to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows the body to use glucose as energy. With insulin resistance, the muscles and fats ...
Overview
- Cirrhosis of the liver (hepatic cirrhosis) is fibrosis of the liver tissue with abnormal nodule formation that structurally deforms the liver. It is the end stage of chronic liver disease and a common cause of death worldwide. In countries like the United States, liver cirrhosis is among the top 15 causes of death and the most common cause of liver-related death. Contrary to popular b…
Treatment
- Treatment for cirrhosis varies depending on the cause and stage of the disease. Because liver damage usually cannot be reversed, the aim of all treatment is to keep the disease from getting worse and to reduce complications.Regardless of the cause, anyone with cirrhosis should abstain from alcohol and use caution in taking medications that can make liver disease worse, includin…
- An early sign of cirrhosis is retaining (holding onto) fluid and salt. This may start as a swollen ankle or leg, but can move on to significant fluid retention in the abdomen (ascites). By reducing salt in the diet, and using the right combination of diuretics (water pills), fluid retention can be lessened for some time. In more severe cases, a doctor may need to drain fluid from the abdom…
- According to the Mayo Clinic, there is no known cure for cirrhosis. The scar tissue that results is usually permanent and sometimes spreads. However, the liver itself is regenerative and can function properly if cirrhosis has not spread too far. By eating foods that are good for your liver and your digestive system in general, it may be possible to reverse some of the symptoms of cir…
- In all cases, regardless of the cause, following a healthy diet and avoiding alcohol are essential. The body needs all the nutrients it can get, and alcohol will only lead to more liver damage.
Signs And Symptoms
- In its early stages, cirrhosis often has no symptoms. But as liver cells die, the organ makes less of the proteins that regulate fluid retention and blood clotting and loses its ability to metabolize the pigment bilirubin. This causes symptoms and complications that include: 1. Fatigue 2. Loss of appetite 3. Nausea 4. Weakness 5. Weight loss 6. Fluid accumulation in the legs (edema) and ab…
- The symptoms of cirrhosis depend on the stage of the illness. In the beginning stages, there may not be any symptoms. As the disease gets worse, symptoms may include:
- Some patients with cirrhosis are completely asymptomatic and have a reasonably normal life expectancy. Other individuals have a multitude of the most severe symptoms of end-stage liver disease and a limited chance for survival. Common signs and symptoms may stem from decreased hepatic synthetic function (eg, coagulopathy), portal hypertension (eg, variceal bleedi…
- The clinical features of cirrhosis have been known since ancient times. The Ebers papyrus written around 2600 BC describes ascites, which was known to be associated with a hardness of the liver and excessive alcohol consumption.3 Signs and symptoms of decompensated cirrhosis include abdominal swelling, jaundice, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Sensitivity of these findings varies f…
Causes
- The most common causes of cirrhosis are chronic (long-term) viral infections of the liver (hepatitis types B and C), fatty liver associated with obesity and diabetes, and alcohol abuse. In addition, anything that damages the liver can cause cirrhosis, including the following inherited diseases: Although less likely, other causes of cirrhosis include reactions to prescription drugs, l…
- A number of chronic liver diseases can lead to cirrhosis. The cirrhotic process can take from weeks to many years to develop, depending on the underlying cause and other factors, including patient response to the disease process. For example, chronic hepatitis C infection can take up to 40 years to progress to cirrhosis in some people. 1. Common causes of cirrhosis include: 1. Alc…
- Different types of cirrhosis have different causes. 1. Excessive alcohol consumption. Too much alcohol intake is the most common cause of cirrhosis as liver damage is associated with chronic alcohol consumption. 2. Injury. Injury or prolonged obstruction causes biliary cirrhosis. 3. Hepatitis. The different types of hepatitis can cause postnecrotic cirrhosis. 4. Other diseases. Di…
- Alcohol abuse and viral hepatitis are the most common causes of cirrhosis, although nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is emerging as an increasingly important cause.5 A more detailed list of underlying etiologies is provided in Table 1.6 It is important to determine the cause of cirrhosis because management of the underlying disease (e.g., hepatitis B virus infection) may prevent ad…
Diagnosis
- Your doctor will ask about your medical history, family history of liver disease, diet, alcohol consumption, medications you are taking, and risk factors for hepatitis B and C, such as intravenous drug use. During a physical examination, the doctor determines whether the liver feels harder or larger than normal, looks for skin changes such as bruising and jaundice, and looks fo…
- There are several conditions than can potentially mimic cirrhosis on imaging 10: 1. pseudocirrhosis 2. widespread (miliary type) liver metastases 3. Budd-Chiari syndrome-particularly chronic 4. fulminant hepatic failure 5. hepatic sarcoidosis 6. congenital hepatic fibrosis 7. idiopathic portal hypertension 8. early primary biliary cirrhosis 9. chronic portal vein th…
- Hepatorenal syndromeHepatorenal syndrome is diagnosed when a creatinine clearance rate of less than 40 mL/min is present or when a serum creatinine level of greater than 1.5 mg/dL, a urine volume of less than 500 mL/day, and a urine sodium level of less than 10 mEq/L are present. Urine osmolality is greater than plasma osmolality.Portal hypertensionDuring angiography, a catheter i…
- Ascites should be treated with salt restriction and diuretics.8,15 Diuretic regimens typically include a combination of spironolactone (Aldactone) and a loop diuretic, unless the serum sodium level is less than 125 mEq per L (125 mmol per L).8,11 Patients with new-onset ascites should have diagnostic paracentesis performed, consisting of cell count, total protein test, albumin leve…
Prognosis
- Treatment leads to improvement in most cases when the disease is discovered in its earlier stages. Most patients are able to live a normal life for many years. The outlook is less favorable if liver damage is extensive or if someone with cirrhosis does not stop drinking. People with cirrhosis usually die of bleeding that can't be stopped, serious infections or kidney failure. They …
- Treatment depends on the underlying etiology and presence of complications. One of the key roles of diagnostic radiology is detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Interventional radiology can be very helpful for treatment of portal hypertension and its complications (e.g. TIPS, ascites drainage), as well as chemoembolisation or radiofrequency ablation of HCC.
- 1. This depends on the underlying cause and on the success of the treatment of the underlying cause. Prognosis is discussed in the separate articles for the conditions that can lead to cirrhosis. 2. If someone with alcoholic cirrhosis continues to drink alcohol, the rate of decompensation can be rapid. 3. Patients with fulminant hepatic failure have a 50-80% mortality rate unless they recei…
- The damage done by cirrhosis is not reversible, but if you receive an early diagnosis, treatment can limit further damage. Unfortunately, you may have no noticeable symptoms in the early stages. Left untreated, your liver may not function as it should, which can lead to liver failure or death.
Pathophysiology
- Although several factors have been implicated in the etiology of cirrhosis, alcohol consumption is considered the major causative factor. 1. Necrosis. Cirrhosis is characterized by episodes of necrosis involving the liver cells. 2. Scar tissue. The destroyed liver cells are gradually replaced with a scar tissue. 3. Fibrosis. There is diffuse destruction and fibrotic regeneration of hepatic c…
- Chronic liver disease with associated hepatocyte death, as evidenced by elevated serum transaminase levels, results in inflammation followed by fibrosis. As hepatocytes are lost, the liver loses the ability to metabolize bilirubin (which can result in an increased serum bilirubin level) and to synthesize proteins, such as clotting factors (resulting in an elevated INR) and transaminase…
- Liver cirrhosis develops slowly over years although with severe liver injury it can develop within weeks. It is achieved by activation of hepatic stellate cells which is then transformed into collagen-producing cells that also manufactures chemical mediators of inflammation. Prolonged inflammation of the liver eventually leads to death of hepatocytes. Fibrous septa form by the pro…
Complications
- 1. pulmonary: see pulmonary complications of cirrhosis 2. skeletal: see skeletal complications of cirrhosis 3. CNS: see CNS complications of cirrhosis...
- If complications develop, the patient should be transferred to a specialised liver unit where there is the expertise to manage the complications and where the patient can also be assessed as to their suitability for liver transplantation.
- The complications of hepatic cirrhosis include the following: 1. Portal hypertension. Portal hypertension is the elevation of pressure in the portal vein that occurs when blood flow meets increased resistance. 2. Esophageal varices. Esophageal varices are dilated tortuous veins in submucosa of the lower esophagus. 3. Hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatic encephalopathy may …
- With advanced liver cirrhosis, complications can need treatment as well.Swollen Veins in the Esophagus 1. If you’re vomiting blood or it’s in your stool, your gullet veins, the ones that carry food from throat to stomach, may be swollen, therefore leaking blood. This is called esophageal varices. 2. Seek urgent medical attention if this occurs. Go to your doctor or the nearest emerge…
Prevention
- The most important step you can take to prevent cirrhosis is to avoid excessive drinking. It is best to consume an average of no more than two alcoholic drinks a day for men or one drink a day for women. If you have chronic hepatitis or other liver problems, avoid alcohol completely.Some other causes of cirrhosis can be prevented. To avoid infection with hepatitis B and C, do not inject ille…
- 1. Worldwide, the most important factor in prevention of cirrhosis is immunisation against hepatitis B. 2. There is no vaccine against hepatitis C but some treatments may delay progression and alcohol must be avoided. 3. Sensible drinking is essential for everyone and patients should be advised about the recommended limits. 4. There are various separate articles providing further i…
- Screening for esophageal varices is an important preventive measure in patients with cirrhosis. If the patient has compensated cirrhosis, then screening endoscopy should be performed within 12 months to detect clinically silent varices and repeated every one to two years.8,21 If cirrhosis is complicated (i.e., with bleeding, encephalopathy, ascites, hepatocellular carcinoma, or hepatopul…
- Liver damage from cirrhosis cannot be reversed, but treatment can stop or delay further progression and reduce complications. Treatment should always include complete alcohol avoidance, but also depends on the cause of cirrhosis and any complications a person is experiencing. For example, hepatitis-related cirrhosis is treated with the different types of hepati…
Management
- The aim of treatment is to delay progression of cirrhosis and to prevent and/or treat any complications of cirrhosis. 1. Specific treatment for the underlying cause. 2. Ensure adequate nutrition, including calorie and protein intake. 3. Alcohol: the most important measure for someone with alcoholic cirrhosis is for them to stop drinking. Continued alcohol intake can also …
- Treatment is designed to remove or alleviate the underlying cause of cirrhosis. 1. Diet. The patient may benefit from a high-calorie and a medium to high protein diet, as developing hepatic encephalopathy mandates restricted protein intake. 2. Sodium restriction.is usually restricted to 2g/day. 3. Fluid restriction. Fluids are restricted to 1 to 1.5 liters/day. 4. Activity. Rest and moder…
- Specific medical therapies may be applied to many liver diseases in an effort to diminish symptoms and to prevent or forestall the development of cirrhosis. Examples of such treatments include the following: 1. Prednisone and azathioprine - For autoimmune hepatitis 2. Interferon and other antiviral agents - For hepatitis B and C 3. Phlebotomy - For hemochromatosis 4. Ursodeoxy…
- In 2010, a set of quality indicators for use in the management of cirrhosis was developed by an 11-member panel of specialists from across the country,8 and was rated by three different systems specifying the strength of the evidence. These indicators closely parallel the guidelines of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointe…