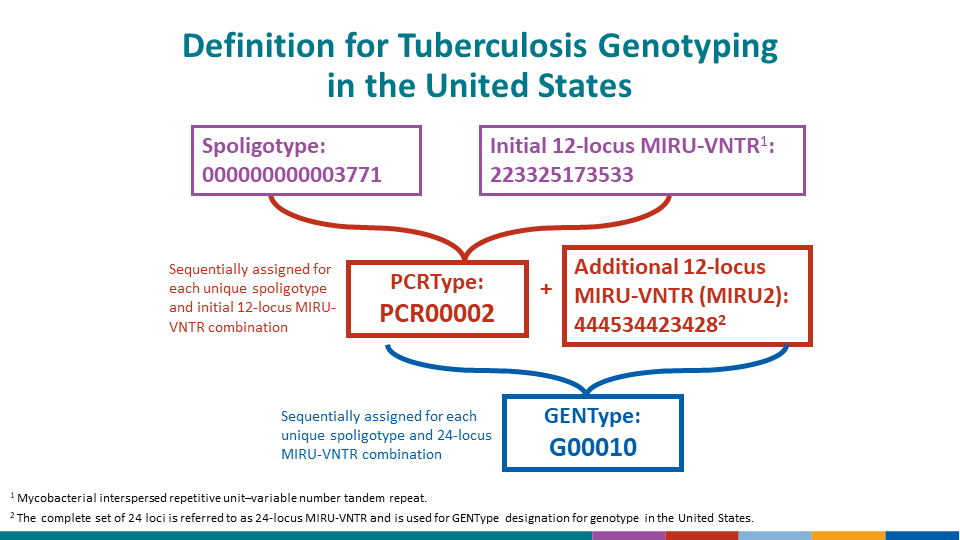
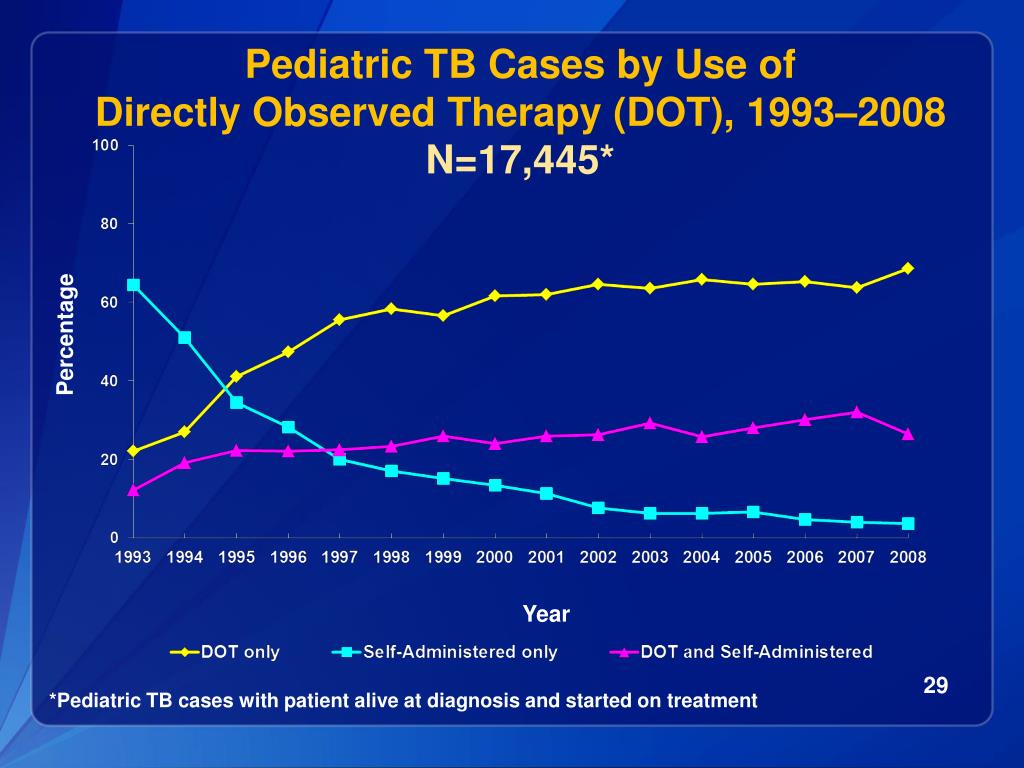
Working with neurosurgeon Sir Hugh Cairns, he had treated children with tubercular meningitis successfully using a combination of purified protein derivative of the tubercle bacillus (PPD) and streptomycin, both intrathecally and intramuscularly. While a resident in Boston, I had seen a number of children die because of tubercular meningitis.
Full Answer
When was streptomycin first used to treat TB?
The first clinical treatments of TB with streptomycin were carried out at the Mayo Clinic in the winter of 1944/45. November 20th 1944 was the day on which streptomycin was first administered to a human being for the treatment of tuberculosis.
What is the history of rifampin therapy for tuberculosis (TB)?
In the 1970s, rifampin found its place as a keystone in the therapy of tuberculosis. The use of rifampin enabled the course of treatment to be reduced to nine months. Incorporation of pyrazinamide into the first-line regimen led to a further reduction of treatment duration to six months.
What is the history of tuberculosis treatment?
The first proposal for a tuberculosis facility was made in paper by George Bodington entitled An essay on the treatment and cure of pulmonary consumption, on principles natural, rational and successful in 1840. In this paper, he proposed a dietary, rest, and medical care program for a hospital he planned to found in Maney.
What caused the resurgence of tuberculosis (TB) in the 1980s?
Decreased attention to tuberculosis control and poor public health infrastructure worldwide led to a resurgence of tuberculosis in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Between 1985 and 1992, tuberculosis cases increased by about 20% in the United States.

How was TB treated in the 1970s?
In the 1970s, rifampin found its place as a keystone in the therapy of tuberculosis. The use of rifampin enabled the course of treatment to be reduced to nine months. Incorporation of pyrazinamide into the first-line regimen led to a further reduction of treatment duration to six months.
How did they cure TB in the old days?
Cod liver oil, vinegar massages, and inhaling hemlock or turpentine were all treatments for TB in the early 1800s. Antibiotics were a major breakthrough in TB treatment. In 1943, Selman Waksman, Elizabeth Bugie, and Albert Schatz developed streptomycin.
What was the first cure for TB?
The Search for the Cure In 1943 Selman Waksman discovered a compound that acted against M. tuberculosis, called streptomycin. The compound was first given to a human patient in November 1949 and the patient was cured.
What year was there a cure for tuberculosis?
The first successful remedy against TB was the introduction of the sanatorium cure, described for the first time in 1854 in the doctoral dissertation "Tuberculosis is a curable disease" by Hermann Brehmer, a botany student suffering himself from TB, who reported his healing after a travel to the Himalayan Mountains [44 ...
How long did the tuberculosis epidemic last?
Although relatively little is known about its frequency before the 19th century, its incidence is thought to have peaked between the end of the 18th century and the end of the 19th century.
How did they treat tuberculosis in the 40s?
Rifampin combined with isoniazid and ethambutol enabled therapy to be shortened to 9 months and led to improved cure rates (35). Pyrazinamide was discovered in the late 1940s, based on the observation that nicotinamide had activity against M. tuberculosis in animal models.
Why is tuberculosis not a pandemic?
The fact remains that the countries with resources, funds, and technical capacity have not invested in the field of TB because the disease has not affected them. In contrast, COVID-19 has gained a great deal of attention from those same countries due to fear of the disease and its impact at home.
How did the US get rid of tuberculosis?
In 1950, with research funding from the American Lung Association, Dr. Edith Lincoln found isoniazid prevented the further spread of infection when given to household members of TB patients. Although the disease is now largely controlled in the United States, it remains a tremendous problem worldwide.
Is streptomycin still used today?
Streptomycin is the first discovered aminoglycoside antibiotic, originally isolated from the bacteria Streptomyces griseus. It is now primarily used as part of the multi-drug treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. It has additional activity against several aerobic gram-negative bacteria.
Was tuberculosis a death sentence?
Tuberculosis was once a death sentence. Doctors could do little to treat it, and almost nothing was known of its spread. Two physicians—Robert Koch and Arthur Conan Doyle—changed that.
Is there a vaccine for tuberculosis?
The BCG vaccine protects against tuberculosis, which is also known as TB. TB is a serious infection that affects the lungs and sometimes other parts of the body, such as the brain (meningitis), bones, joints and kidneys.
How did people get tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria that spread from person to person through microscopic droplets released into the air. This can happen when someone with the untreated, active form of tuberculosis coughs, speaks, sneezes, spits, laughs or sings.
Who was the first person to recognize tuberculosis?
Franciscus Sylvius began differentiating between the various forms of tuberculosis (pulmonary, ganglion). He was the first person to recognize that the skin ulcers caused by scrofula resembled tubercles seen in phthisis, noting that "phthisis is the scrofula of the lung" in his book Opera Medica, published posthumously in 1679. Around the same time, Thomas Willis concluded that all diseases of the chest must ultimately lead to consumption. Willis did not know the exact cause of the disease but he blamed it on sugar or an acidity of the blood. Richard Morton published Phthisiologia, seu exercitationes de Phthisi tribus libris comprehensae in 1689, in which he emphasized the tubercle as the true cause of the disease. So common was the disease at the time that Morton is quoted as saying "I cannot sufficiently admire that anyone, at least after he comes to the flower of his youth, can [sic] dye without a touch of consumption."
Where was TB epidemic?
Epidemic tuberculosis. In the 18 th and 19 th century, tuberculosis (TB) had became epidemic in Europe, showing a seasonal pattern. In the 18 th century, TB had a mortality rate as high as 900 deaths (800–1000) per 100,000 population per year in Western Europe, including in places like London, Stockholm and Hamburg.
What is the most recent common ancestor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex?
Origins. Scientific work investigating the evolutionary origins of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex has concluded that the most recent common ancestor of the complex was a human-specific pathogen, which underwent a population bottleneck.
What disease did Rojas suffer from?
Rojas was suffering from tuberculosis when he painted this. Here he depicts the social aspect of the disease, and its relation with living conditions at the close of the 19th century. Throughout history, the disease tuberculosis has been variously known as consumption, phthisis, and the White Plague. It is generally accepted that the causative ...
How did TB spread?
In South America, reports of a study in August 2014 revealed that TB had likely been spread via seals that contracted it on beaches of Africa, from humans via domesticated animals, and carried it across the Atlantic. A team at the University of Tübingen analyzed tuberculosis DNA in 1,000-year-old skeletons of the Chiribaya culture in southern Peru; so much genetic material was recovered that they could reconstruct the genome. They learned that this TB strain was related most closely to a form found only in seals. In South America, it was likely contracted first by hunters who handled contaminated meat. This TB is a different strain from that prevalent today in the Americas, which is more closely related to a later Eurasian strain.
How old is tuberculosis?
In 2014, results of a new DNA study of a tuberculosis genome reconstructed from remains in southern Peru suggest that human tuberculosis is less than 6,000 years old.
How many people died in Bristol in 1790?
Of the 1,571 deaths in the English city of Bristol between 1790 and 1796, 683 were due to tuberculosis. Remote towns, initially isolated from the disease, slowly succumbed. The consumption deaths in the village of Holycross in Shropshire between 1750 and 1759 were one in six (1:6); ten years later, 1:3.
Who discovered the cure for tuberculosis?
The first step in finding a cure was the discovery of the cause of tuberculosis by Robert Koch in 1882. The sanatorium movement that began shortly afterward in Europe, and soon spread to the United States, brought attention to the plight of afflicted persons, and catalyzed public health action.
What is the history of tuberculosis?
A Historical Perspective. Of all achievements in medicine, the successful treatment of tuberculosis has had one of the greatest impacts on society. Tuberculosis was a leading cause of disease and a mortal enemy of humanity for millennia. The first step in finding a cure was the discovery of the cause ...
How long does pyrazinamide treatment last?
Incorporation of pyrazinamide into the first-line regimen led to a further reduction of treatment duration to six months. Treatment of multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis remains a difficult problem requiring lengthy treatment with toxic drugs.
What was the first step in finding a cure for tuberculosis?
The first step in finding a cure was the discovery of the cause of tuberculosis by Robert Koch in 1882.
Is isoniazid safe for tuberculosis?
In 1952, isoniazid opened the modern era of treatment; it was inexpensive, well tolerated, and safe. In the early 1960s, ethambutol was shown to be effective and better tolerated than para-aminosalicylic acid, which it replaced. In the 1970s, rifampin found its place as a keystone in the therapy of tuberculosis.
How many courses of MDR-TB treatment will be donated?
The company signs an agreement with USAID and JSC Pharmstandard to donate 30,000 six-month courses of the treatment over the next four years to be used for MDR-TB treatment worldwide.
What is Johnson and Johnson's commitment to end TB?
Part of Johnson & Johnson’s 10-year commitment to help end TB includes investing in critical innovation work. In July, the company launches the international RESPIRI-TB research consortium, in partnership with Europe’s Innovative Medicines Initiative and nine research institutions, which is aimed at discovering and developing new TB antibiotics.
When will Johnson and Johnson's STREAM study be completed?
Final study results are expected as early as 2023.
How much mortality does tuberculosis have?
The use of antituberculosis drugs has changed tuberculosis from a disease with about a 50% mortality, treated by measures to collapse the affected lung lesions and by rest for the patient, to a condition successfully curable by chemotherapy.
When was the domiciliary treatment center established?
Domiciliary Treatment. In 1956, the Tuberculosis Chemotherapy Center (now the Tuberculosis Research Center) was established in Madras, India, to study whether older, standard treatment in hospital or sanatorium improved the results of chemotherapy ( 26 ).
When was PZA discovered?
With slight modifications, this model is still being used today. PZA, reviewed recently ( 37 ), was discovered in 1952. It is a remarkable drug that does not appear to have a genetic site of action but accumulates within the bacterial cell, where it acidifies its content and damages membranes.
When was the first randomized trial of SM?
After the discovery of SM ( 12) and the proof of its antituberculosis activity in the guinea pig, small uncontrolled studies were undertaken in the United States, but the first clinical trial with a randomized intake in the history of medicine was started in 1946 by the British Medical Research Council ( 13 ).
When was sanocrysin used in animal experiments?
These attempts were extensively reviewed by Hart ( 10 ). He indicated that sanocrysin, a gold salt, was widely used in treatment between 1925 and 1935. A number of different sulphones that had activity in experimental animals were also investigated but were never widely used in treatment.
When did guinea pigs start being tested?
Drug susceptibility testing started in the 1950s with tests in liquid medium, but was later performed on solid medium slopes.
Does SM cure tuberculosis?
In contrast to the results in pulmonary tuberculosis, a parallel study showed that SM was able to cure about 44% of patients with tuberculous meningitis ( 15 ). Drug resistance did not emerge in these patients because the bacterial population was too small to contain resistant mutants.
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
How long does pyrazinamide last?
pyrazinamide (PZA) TB Regimens for Drug-Susceptible TB. Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months (total of 6 to 9 months for treatment). Drug Susceptible TB Disease Treatment Regimens. Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, ...
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
What did Bernheim discover about tuberculosis?
He carried out a number of experiments and found that the simple asprin played a vital role in the life cycle of the tuberculosis germ. On 30th August 1940 Bernheim had his discovery published in the journal Science. As soon as he received some copies he sent one to his friend and colleague Jorgen Lehmann.
What is the role of actinomycetes in TB?
Along with studying fungi he also studied the actinomycetes. Actinomycetes are a group of microbes which can be considered as intermediary between bacteria and fungi. Actinomycetes (shown on a agar plate) have been vital in the history of TB drugs. Waksman had found in his previous studies of the microbiological affect of the soil ...
What was the name of the scientist who wrote about streptomycin?
Waksman was to receive numerous honours as a result of his work on streptomycin and in 1949 his portrait was on the cover of Time magazine. In 1949 Schatz decided to write to Waksman about various matters concerning the streptomycin patent, the royalties, and his various dealings with Merck and Rutgers.
What would happen if you added salicylic acid to tuberculosis?
What it said was that if you added one milligram of salicylic acid (asprin) to tuberculosis bacteria you could stimulate the oxygen uptake of the bacteria by more than one hundred per cent .” 2Ryan, F, “The Forgotten Plague”, Little, Brown and Company, 1992.
When was rifamycin first used?
The rifamycins were discovered in 1957 in Italy when a soil sample from a pine forest on the French Riviera was brought for analysis to the Lepetit Pharmaceuticals research laboratory in Milan, Italy. A research group led by Professor Piero Sensi and Dr Maria Teresa Timbal then discovered a new bacterium. This new species was of considerable scientific interest as it was producing a new class of molecules with antibiotic activity. Rifampin was first used clinically in 1966.
When was streptomycin first isolated?
The first public announcement of the isolation of the antibiotic was made in a paper in January 1944 6Schatz, A., Bugie, E., and Waksman, S. A. “Streptomycin, a Substance Exhibiting Antibiotic Activity against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria”, Proc. Soc. Exper. Biol.
When was actinomycin isolated?
Various preliminary studies of the production of antibiotics by actinomycetes resulted in the isolation of actinomycin in 1940 but it was extremely toxic. 5Waksman, S, “The Conquest of Tuberculosis”, Robert Hale Ltd, 1964 This was followed two years later by streptothricin which was also found to have significant toxicity.
When was TB discovered?
In 1882, Robert Koch's discovery of the tubercule baccilum revealed that TB was not genetic, but rather highly contagious; it was also somewhat preventable through good hygiene.
What was the cure for TB in the 1800s?
By the dawn of the 19th century, tuberculosis—or consumption—had killed one in seven of all people that had ever lived. Throughout much of the 1800s, consumptive patients sought "the cure" in sanatoriums, where it was believed that rest and a healthful climate could change the course of the disease. In 1882, Robert Koch's discovery of the tubercule baccilum revealed that TB was not genetic, but rather highly contagious; it was also somewhat preventable through good hygiene. After some hesitation, the medical community embraced Koch's findings, and the U.S. launched massive public health campaigns to educate the public on tuberculosis prevention and treatment. Browse a gallery of images depicting Americans' fight against one of the deadliest diseases in human history.
How many people died from tuberculosis in the 19th century?
By the beginning of the 19th century, tuberculosis, or "consumption," had killed one in seven of all people that had ever lived. Victims suffered from hacking, bloody coughs, debilitating pain in their lungs, and fatigue. Inspired by Robert Koch's discovery of the tuberculosis bacterium in 1882, Dr. Edward L.
When was the first sanatorium opened?
In 1884, Edward Trudeau opened America's first sanatorium at Saranac Lake, NY, where patients sat outside on the wide sun porches to take the fresh air cure in 1896. Credit: Saranac Lake Free Library. Sanatoriums soon sprang up across the U.S.
How did TB decline in the 1920s?
Through public clinics and better prevention education, TB cases declined sharply in the 1920s and continued to do so throughout the 1930s. Credit: Atlanta History Center. Improved hygiene helped reduce the number of TB cases in the US, though rates continued to climb in poor, crowded neighborhoods.
Why was the parade held on Disease Prevention Day, October 12, 1914?
Credit: Library of Congress. Public health officials used events such as this parade held on Disease Prevention Day, October 12, 1914 to encourage good hygiene.
Where did tuberculosis occur in 1900?
Here, young women listen to a presentation on tuberculosis in New York City , 1900. With increased knowledge of the contagion came increased prejudice. This photo shows a "lungers" camp outside of Phoenix, AZ in September 1903, where TB sufferers lived. TB patients in cities used rooftops and windows to get fresh air.
Origins
Tuberculosis in Early Civilization
- In 2008, evidence for tuberculosis infection was discovered in human remains from the Neolithic era dating from 9,000 years ago, in Atlit Yam, a settlement in the eastern Mediterranean.This finding was confirmed by morphological and molecular methods; to date it is the oldest evidence of tuberculosis infection in humans. Evidence of the infection in humans was also found in a ce…
The East
- Ancient India
The first references to tuberculosis in non-European civilization is found in the Vedas. The oldest of them (Rigveda, 1500 BC) calls the disease yaksma. The Atharvaveda calls it balasa. It is in the Atharvaveda that the first description of scrofula is given. The Sushruta Samhita, written around … - Ancient China
The Classical Chinese word lào 癆 "consumption; tuberculosis" was the common name in traditional Chinese medicine and fèijiéhé 肺結核 (lit. "lung knot kernel") "pulmonary tuberculosis" is the modern medical term. Lao is compounded in names like xulao 虛癆 with "empty; void", láobìn…
Classical Antiquity
- Hippocrates, in Book 1 of his Of the Epidemics, describes the characteristics of the disease: fever, colourless urine, cough resulting in a thick sputa, and loss of thirst and appetite. He notes that most of those affected became delirious before they succumbed to the disease. Hippocrates and many other at the time believed phthisis to be hereditary in nature.Aristotle disagreed, believing t…
Pre-Columbian America
- In South America, reports of a study in August 2014 revealed that TB had likely been spread via seals that contracted it on beaches of Africa, from humans via domesticated animals, and carried it across the Atlantic. A team at the University of Tübingen analyzed tuberculosis DNA in 1,000-year-old skeletons of the Chiribaya culture in southern Peru; so much genetic material was recov…
Europe: Middle Ages and Renaissance
- During the Middle Ages, no significant advances were made regarding tuberculosis. Avicenna and Rhazes continued to consider to believe the disease was both contagious and difficult to treat. Arnaldus de Villa Novadescribed etiopathogenic theory directly related to that of Hippocrates, in which a cold humor dripped from the head into the lungs. In Medieval Hungary, the Inquisition re…
Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries
- Franciscus Sylvius began differentiating between the various forms of tuberculosis (pulmonary, ganglion). He was the first person to recognize that the skin ulcers caused by scrofula resembled tubercles seen in phthisis, noting that "phthisis is the scrofula of the lung" in his book Opera Medica, published posthumously in 1679. Around the same time, Thomas Willis concluded that …
Nineteenth Century
- Epidemic tuberculosis
In the 18th and 19th century, tuberculosis (TB) had become epidemic in Europe, showing a seasonal pattern. In the 18th century, TB had a mortality rate as high as 900 deaths (800–1000) per 100,000 population per year in Western Europe, including in places like London, Stockholm a… - A romantic disease
It was during this century that tuberculosis was dubbed the White Plague, mal de vivre, and mal du siècle. It was seen as a "romantic disease". Individuals with tuberculosis were thought to have heightened sensitivity. The slow progress of the disease allowed for a "good death" as those aff…
Twentieth Century
- Containment
At the beginning of the 20th century, tuberculosis was one of the UK's most urgent health problems. A royal commission was set up in 1901, The Royal Commission Appointed to Inquire into the Relations of Human and Animal Tuberculosis. Its remit was to find out whether tubercul… - Vaccines
The first genuine success in immunizing against tuberculosis was developed from attenuated bovine-strain tuberculosis by Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin in 1906. It was called "BCG" (Bacille Calmette-Guérin). The BCG vaccine was first used on humans in 1921 in France, but it w…
See Also