
Explore
Patients who have osteomalacia can take vitamin D, calcium or phosphate supplements, depending on the individual case. For instance, people with intestinal malabsorption (the intestines cannot absorb nutrients or vitamins properly) may need to take larger quantities of vitamin D and calcium.
What supplements should I take if I have osteomalacia?
Eating a diet rich in vitamin D and calcium and getting sufficient exposure to sunlight can help prevent osteomalacia due to vitamin D deficiency. Bhan A, Rao AD, Bhadada SK, Rao SD.
How is osteomalacia prevented in patients with vitamin D deficiency?
More importantly, osteomalacia can look like weakening of the bones from osteoporosis on bone density testing. In some cases, a bone biopsy will be done to see if bone softening is present. Treatment may involve vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus supplements taken by mouth.
What is osteomalacia and how is it treated?
Because it’s fairly easy for most people to get enough calcium from their diet, a lack of calcium is not a common sole cause of osteomalacia. But it’s still worth knowing which foods are high in this important nutrient.
Can calcium deficiency cause osteomalacia?
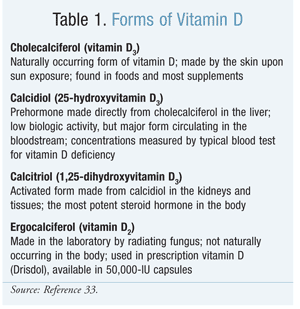
What vitamin helps osteomalacia?
Eating a diet rich in vitamin D and calcium and getting sufficient exposure to sunlight can help prevent osteomalacia due to vitamin D deficiency.
What vitamin is deficiency in osteomalacia?
Vitamin D deficiency accounts for the most common nutritional deficiency among children and adults. Osteomalacia describes a disorder of "bone softening" in adults that is usually due to prolonged deficiency of vitamin D. This results in abnormal osteoid mineralization.
Is there a cure for osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia is treatable, usually with vitamin and/or mineral supplements, and most people can be cured. It is generally treated by administration of vitamin D, calcium and, if needed, also phosphorus. If the osteomalacia is caused by an underlying condition, this will also need to be treated.
Which minerals can help prevent osteomalacia?
Prevention. Osteomalacia resulting from vitamin D deficiency can be prevented by eating adequate dairy products that have been fortified with vitamin D and by getting enough sunlight. If patients suspect their diet may be deficient in vitamin D, they should be instructed about alternate sources of vitamins and minerals ...
What is vitamin K deficiency?
Vitamin K is important for blood clotting, bone health, and more. The main symptom of a vitamin K deficiency is excessive bleeding caused by an inability to form blood clots. According to the Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS) , vitamin K deficiency is very rare in the United States.
What is a vitamin D deficiency called?
Also called: Hypovitaminosis D, Low Vitamin D.
What is the best treatment option for osteomalacia?
If you have osteomalacia – the adult form of rickets that causes soft bones – treatment with supplements will usually cure the condition. However, it may be several months before any bone pain and muscle weakness is relieved. You should continue taking vitamin D supplements regularly to prevent the condition returning.
How can I boost my vitamin D?
Spend time in sunlight. Vitamin D is often referred to as “the sunshine vitamin” because the sun is one of the best sources of this nutrient. ... Consume fatty fish and seafood. ... Eat more mushrooms. ... Include egg yolks in your diet. ... Eat fortified foods. ... Take a supplement. ... Try a UV lamp.
How do you treat soft bones?
Osteomalacia, or "soft bones, " develops because of a lack of vitamin D. Maintaining your levels of vitamin D and calcium is essential for bone health....How is osteomalacia treated?Wearing braces to reduce or prevent bone irregularities.Surgery to correct bone deformities (in severe cases)Adequate exposure to sunlight.
What vitamin D should I take?
The current recommendations suggest consuming 400–800 IU (10–20 mcg) of vitamin D per day. However, people who need more vitamin D can safely consume 1,000–4,000 IU (25–100 mcg) daily. Consuming more than this is not advised, as it is not linked to any extra health benefits.
How much vitamin d3 should I take daily?
The recommended daily amount of vitamin D is 400 international units (IU) for children up to age 12 months, 600 IU for people ages 1 to 70 years, and 800 IU for people over 70 years.
What vitamin helps with bone pain?
Vitamin D is important for keeping bones strong and preventing injuries from falls. Research shows that people with low levels of vitamin D may have more joint pain.
What is the best treatment for osteomalacia?
Other treatments to relieve or correct osteomalacia symptoms may include: Wearing braces to reduce or prevent bone irregularities.
How to diagnose osteomalacia?
How is osteomalacia diagnosed? 1 The most important indicator is low levels of vitamin D, but low levels of calcium or a significant drop in phosphate levels may also indicate osteomalacia. 2 X-rays may be taken to see if there is any evidence of osteomalacia. 3 A bone mineral density scan may be helpful in evaluating the amount of calcium and other minerals present in a patient’s bone segment. These scans are not required to make the diagnosis of osteomalacia. However, they may give important information about a patient’s bone health.
Why do my bones break down so fast?
Osteomalacia is a disease that weakens bones and can cause them to break more easily. It is a disorder of decreased mineralization, which results in bone breaking down faster than it can re-form. It is a condition that occurs in adults. In children, inadequate concentrations of vitamin D may cause rickets.
What are the indicators of osteomalacia?
The most important indicator is low levels of vitamin D, but low levels of calcium or a significant drop in phosphate levels may also indicate osteomalacia. X-rays may be taken to see if there is any evidence of osteomalacia.
Can osteomalacia be diagnosed with a bone biopsy?
These scans are not required to make the diagnosis of osteomalacia. However, they may give important information about a patient’s bone health. Rarely, the doctor may perform a bone biopsy, in which a sample of bone tissue is taken and examined.
How much vitamin D is needed for osteomalacia?
The treatment of osteomalacia secondary to vitamin D deficiency is vitamin D supplementation of 800 to 4,000 units/day; alternatively, 50,000 units weekly for eight weeks may be required. 1 To treat intestinal malabsorption, high-dose therapy of 50,000 to 100,000 units/day ...
How to prevent osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia resulting from vitamin D deficiency can be prevented by eating adequate dairy products that have been fortified with vitamin D and by getting enough sunlight. 10.
What is the role of a pharmacist in osteomalacia?
Pharmacists may play an important role in raising awareness of vitamin D deficiency associated with osteomalacia while appropriately referring patients for evaluation, assisting clinicians and patients with product selection of vitamin D supplements, monitoring for adverse effects and drug interactions, and educating patients and caregivers about bone health and relief from pain and muscle weakness.
What are the causes of osteomalacia?
Causes and Risk Factors of Osteomalacia. Risk factors for osteomalacia include age 50 to 80 years, lactose intolerance with avoidance of vitamin D-fortified milk, and inadequate exposure to the sun. 1,2,9 Risk has been known to be highest in those individuals who have both inadequate dietary intake of vitamin D and minimal exposure to sunlight, ...
What disorders affect the absorption of vitamin D?
Disorders that alter vitamin D metabolism include kidney failure and primary biliary cirrhosis. 2. Surgeries: Surgeries that interfere with the absorption of vitamin D in the GI tract such as the partial or full removal of the stomach (gastrectomy) and removal or bypass of the small intestine. 2.
Is osteomalacia more common in seniors?
Much awareness has been raised regarding the risk of fractures secondary to osteoporosis in seniors. Another condition affecting bones in adults, osteomalacia, is less common than osteoporosis, can be insidious, and may present comorbidly with osteoporosis. 1 Whereas osteoporosis is a weakening of previously constructed bone, ...
Does bicarbonate help with renal tubular acidosis?
When renal tubular acidosis exists with osteomalacia, oral bicarbonate will correct acidosis. 1 Phosphate supplements and vitamin D analogues are often used for the treatment of osteomalacia from Fanconi syndrome in addition to treatment for the underlying disorder. 1. Prior research suggested that vitamin D 3 was a better choice than vitamin D 2.
Why is vitamin D important for osteomalacia?
A lack of vitamin D is the most common cause of osteomalacia. Vitamin D is an important nutrient that helps you absorb calcium in your stomach. Vitamin D also helps maintain calcium and phosphate levels to help your bones form properly. It’s made within the skin from exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays in sunlight.
How long does it take for osteomalacia to heal?
You may see improvements in a few weeks if you increase your intake of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus. Complete healing of the bones takes about 6 months.
How do you know if you have osteomalacia?
There are a few symptoms of osteomalacia. The most common is bones that fracture easily. Another is muscle weakness. This happens because of problems in the areas where muscle attaches to bone. A person with osteomalacia may have a hard time walking or may develop a waddling gait.
Can cancer affect vitamin D?
Certain types of cancer can interfere with vitamin D processing. Kidney and liver disorders can affect the metabolism of vitamin D. A diet that doesn’t include phosphates can cause phosphate depletion, which can also lead to osteomalacia. Drugs for treating seizures — like phenytoin and phenobarbital — can also result in osteomalacia.
Is osteomalacia the same as osteoporosis?
Problems with bone formation or the bone-building process causes osteomalacia. This condition isn’t the same as osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a weakening of living bone that’s already formed and being remodeled.
Can osteomalacia cause bone fractures?
If you don’t treat the cause of your osteomalacia, there are complications. Adults can fracture bones easily such as rib, leg, and spine bones. Also, in children, osteomalacia and rickets often occur together, which can lead to bowing of the legs or premature tooth loss. Symptoms can return if not enough vitamin D is available.
How long does it take to cure osteomalacia?
What treatments are there for osteomalacia? Treatment will cure osteomalacia in most cases, but easing bone pain, muscle weakness and cramps may take several months. If it’s caused by a lack of vitamin D, you will probably need to take vitamin D supplements every day.
What hormone is raised when you have osteomalacia?
Alkaline phosphatase, which is a substance made by the cells that make bone. This is at a raised level in people who have osteomalacia. Parathyroid hormone, produced by the parathyroid gland, is raised as part of the body’s reaction to low vitamin D levels.
What is the purpose of Vitamin D in bone?
The strength of the bone depends on how much of these minerals is laid down. Vitamin D controls levels of calcium and phosphorus in your body.
Why do my bones break easily?
Osteomalacia is the name of a condition where bones become soft and weak. This means they can bend and break more easily than normal. The most common cause is not having enough vitamin D. Rickets is the name of a similar condition that affects children.
How long does it take for osteomalacia to heal?
Most people with osteomalacia will recover with treatment. However, it can take months for bones to recover and for muscles to become strong again. A late diagnosis can make recovery more difficult, especially if bones have fractured.
Why is it important to have calcium in your bones?
Calcium is needed to make bones strong and a lack of calcium can cause osteomalacia. Because it’s fairly easy for most people to get enough calcium from their diet , a lack of calcium is not a common sole cause of osteomalacia. But it’s still worth knowing which foods are high in this important nutrient.
What is the term for the process of replacing old bone cells with new ones?
Old bone cells are continuously being removed and replaced with new cells. This is called bone turnover. Bone has a hard outer shell, called the cortex. Inside the bone there’s a softer and lighter structure, called the matrix. It has a structure a bit like a mesh or honeycomb.
Why does osteomalacia occur?
Osteomalacia is softening of the bones. It most often occurs because of a problem with vitamin D, which helps your body absorb calcium. Your body needs calcium to maintain the strength and hardness of your bones.
What supplements are used for weight loss surgery?
Treatment may involve vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus supplement s taken by mouth. People who cannot absorb nutrients well through the intestines may need larger doses of vitamin D and calcium. This includes people who have some types of weight loss surgery.
Can bone x-rays detect osteomalacia?
Bone x-rays and a bone density test can help detect pseudofractures, bone loss, and bone softening. More importantly, osteomalacia can look like weakening of the bones from osteoporosis on bone dens ity testing. In some cases, a bone biopsy will be done to see if bone softening is present.

Causes and Risk Factors of Osteomalacia
Symptoms and Diagnostic Testing
- During the early stages of osteomalacia, patients may have no symptoms, although some signs may be seen on x-rays or other diagnostic tests (e.g., bone scan, bone biopsy).2 As the condition worsens, symptoms develop (TABLE 1). Blood and urine tests often detect abnormal levels of vitamin D and the minerals calcium and phosphorus in cases of osteomalacia caused by vitami…
Treatment
- The underlying cause of osteomalacia drives the required therapy. The treatment of osteomalacia secondary to vitamin D deficiency is vitamin D supplementation of 800 to 4,000 units/day; alternatively, 50,000 units weekly for eight weeks may be required.1 To treat intestinal malabsorption, high-dose therapy of 50,000 to 100,000 units/day or intramus...
Special Considerations in Seniors
- There is decreased absorption of vitamin D with advancing age.11 Furthermore, research has demonstrated that low serum concentrations of vitamin D result in greater bone loss in geriatric patients who are ill.11 To ensure adequate nutrient intake, nutrient density should be increased since caloric intake decreases with age.11 Because seniors consume less vitamin D and their a…
Vitamin D Adverse Events and Drug Interactions
- When doses of vitamin D do not exceed the physiologic requirements, they are usually tolerated well and nontoxic.3 In overdose, however, vitamin D can lead to weakness, vomiting, headache, somnolence, constipation, and weight loss; ongoing vitamin D administration may result in hypercalcemia, which may manifest by deposition of calcium and phosphate into in the kidneys, …
Prevention
- Osteomalacia resulting from vitamin D deficiency can be prevented by eating adequate dairy products that have been fortified with vitamin D and by getting enough sunlight.10 If patients suspect their diet may be deficient in vitamin D, they should be instructed about alternate sources of vitamins and minerals.9 Exposure to sunlight should be sufficient, but not excessive; 15 minu…
Conclusion
- Pharmacists may play an important role in raising awareness of vitamin D deficiency associated with osteomalacia while appropriately referring patients for evaluation, assisting clinicians and patients with product selection of vitamin D supplements, monitoring for adverse effects and drug interactions, and educating patients and caregivers about bone health and relief from pain and …