Explore
What can you do to manage polycythemia vera?
- Blood withdrawals. The most common treatment for polychythemia vera is having frequent blood withdrawals, using a needle…
- Treatments to reduce itching. If you have bothersome itching, your doctor may prescribe medication, such as…
- Drugs that reduce the number of red blood cells. If phlebotomy alone doesn’t help enough, your doctor may suggest…
What are my treatment options for polycythemia vera?
You may need modifications if you have:
- A kidney stone: Avoid foods high in oxalate. 3
- A gastrointestinal ulcer: Avoid foods and drinks that irritate the ulcer. 5
- Gout: Avoid foods high in purine.
What is the best diet for polycythemia vera?
They may include:
- Blood tests
- Gene tests
- Bone marrow tests
How can you manage polycythemia vera?
Treatment
- Blood withdrawals. The most common treatment for polychythemia vera is having frequent blood withdrawals, using a needle in a vein (phlebotomy).
- Treatments to reduce itching. ...
- Drugs that reduce the number of red blood cells. ...
- Heart medications. ...
What are the different types of polycythemia vera treatment?
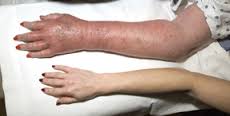
How would polycythemia be treated therapeutic?
Low-risk patients should be treated with phlebotomy and low-dose aspirin. Cytotoxic therapy is indicated in high-risk patients, and the drug of choice is hydroxyurea because of its efficacy in preventing thrombosis and low leukemogenicity.
What is the drug of choice for polycythemia?
Hydroxyurea: The drug of choice for polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia.
Does a hematologist treat polycythemia?
Seeing a hematologist Any hematologist may be able to help you with your PV. But it's a good idea to ask if they've treated anyone else with this particular disease. Most hematologists who treat PV and other blood disorders practice at major medical centers.
What are the first symptoms of polycythemia vera?
What are the symptoms of polycythemia vera?Lack of energy (fatigue) or weakness.Headache.Dizziness.Shortness of breath and trouble breathing while lying down.Vision problems, such as double vision, blurred vision, and blind spots.Inability to concentrate.Night sweats.Face and becomes red and warm (flushed)More items...
Are there any new treatments for polycythemia vera?
Treatment is First FDA-Approved Option Patients Can Take Regardless of Previous Therapies. Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Besremi (ropeginterferon alfa-2b-njft) injection to treat adults with polycythemia vera, a blood disease that causes the overproduction of red blood cells.
How is polycythemia vera 2020 treated?
Cytoreductive therapy is recommended for high-risk ET and PV, but it is not mandatory for intermediate-risk ET. First-line drug of choice for cytoreductive therapy, in both ET and PV, is hydroxyurea and second-line drugs of choice are interferon-α and busulfan.
What is the difference between polycythemia vera and polycythemia?
Polycythemia, also called erythrocytosis, refers to an increase in red blood cell mass, noted on laboratory evaluation as increased hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Polycythemia vera is a subtype of polycythemia and is associated with the overproduction of all 3 cell lines.
How often does polycythemia vera turn into leukemia?
Polycythemia vera transforms to acute leukemia (blast phase) 10 years after diagnosis in about 10% of cases. Patients who progress to the blast phase respond to treatment poorly and have a median survival of only 3 to 6 months after the start of the blast phase.
When is phlebotomy needed for polycythemia?
Patients older than 60 years or with a previous history of thrombosis are considered to be high risk. Patients younger than 60 years and with no prior history of thrombosis are considered low risk. All patients with PV should undergo phlebotomy to keep their hematocrit below 45%.
How fast does polycythemia progress?
One study shows that anywhere from 2% to 14% of the time, polycythemia vera changes into AML within 10 years. In this disease, stem cells in your bone marrow turn into unhealthy blood cells, including white blood cells called myeloblasts. These cells grow out of control, crowding out healthy blood cells.
Does polycythemia turn into leukemia?
In rare cases, polycythemia vera may eventually progress into a form of leukemia known as acute myeloid leukemia.
Does polycythemia vera go away?
Polycythemia vera (PV) doesn't have a cure. However, treatments can help control the disease and its complications. PV is treated with procedures, medicines, and other methods. You may need one or more treatments to manage the disease.
What is the treatment for bone marrow thinning?
Each drug is different, so your doctor will talk with you about side effects and what the latest research shows. Radiation Therapy. This treatment slows red blood cell production in bone marrow, which thins your blood and helps it flow more easily.
Why do you get phlebotomy?
You may get phlebotomy when your doctor first tells you that you have PV. It's a lot like donating blood.
Does hydroxurea help with phlebotomy?
Hydroxyurea is a cancer drug that slows down the growth of new cells in your body. In PV, it lowers the number of red blood cells and platelets, which are cells that help blood clot. If you take this drug, you may not need phlebotomy. Hydroxyurea can also prevent or treat an enlarged spleen -- a complication of PV.
How to diagnose polycythemia vera?
How do doctors diagnose polycythemia vera (PV)? To diagnose PV, your doctor will perform a test called a complete blood count (CBC) to see if your number of red blood cells is higher than normal. Your doctor may also test your blood to look for amounts of a hormone called erythropoietin.
What is the best medicine for PV?
Some people with PV take aspirin every day because it helps thin the blood. Two other drugs used to treat PV are ruxolitininib (Jakafi®), which is used for patients who do not respond to or cannot take hydroxyurea. Pegylated interferon (Pegasis®), is used to treat hepatitis C.
How does phlebotomy work?
By removing iron from the body, the production of red blood cells by the bone marrow slows down. During phlebotomy, a health professional will insert a needle into a vein and drain blood through a tube into a container.
Is there a cure for PV?
There is no cure for PV. People with the condition usually need treatment their entire lives. Regular doctor visits and blood tests can help ensure the disease does not get worse. PV treatment helps you manage the disorder to ease symptoms and avoid complications for a healthier life.
What is the goal of treating secondary polycythemia?
The goal of treating secondary polycythemia is to control its underlying cause, if possible. For example, if the cause is carbon monoxide exposure, the goal is to find the source of the carbon monoxide and fix or remove it.
How to treat PV?
Your doctor also may prescribe ultraviolet light treatment to help relieve your itching. Other ways to reduce itching include: Avoiding hot baths.
How to stop itching after bath?
Other ways to reduce itching include: 1 Avoiding hot baths. Cooler water can limit irritation to your skin. 2 Gently patting yourself dry after bathing. Vigorous rubbing with a towel can irritate your skin. 3 Taking starch baths. Add half a box of starch to a tub of lukewarm water. This can help soothe your skin.
What is the treatment for itching in people with PV?
Researchers are studying other treatments for PV. An experimental treatment for itching involves taking low doses of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). This type of medicine is used to treat depression. In clinical trials, SSRIs reduced itching in people who had PV.
What is the best medicine for bone marrow?
Examples of these medicines include hydroxyurea and interferon-alpha. Hydroxyurea is a medicine generally used to treat cancer. This medicine can reduce the number of red blood cells and platelets in your blood.
What are the goals of PV treatment?
Goals of Treatment. The goals of treating PV are to control symptoms and reduce the risk of complications, especially heart attack and stroke. To do this, PV treatments reduce the number of red blood cells and the level of hemoglobin (an iron-rich protein) in the blood. This brings the thickness of your blood closer to normal.
Does interferon help with PV?
It also can be used to treat PV. Interferon-alpha can prompt your immune system to fight overactive bone marrow cells.
What is the treatment for polycythemia vera?
The primary treatment of polycythemia vera is therapeutic phlebotomy. In therapeutic phlebotomy , blood is removed from the body similar to a blood donation to reduce the number of red blood cells in circulation. Therapeutic phlebotomy is continued on a regular basis to keep the hematocrit (concentration of red blood cells) below 45%, ...
What is polycythemia vera?
Updated on September 24, 2020. Polycythemia vera, a myeloproliferative neoplasm, results from a genetic mutation which leads to the production of too many red blood cells ( erythrocytosis ). The white blood cell and platelet counts may also be elevated. This increase in the number of blood cells (without an increase in the liquid portion of blood) ...
How long does polycythemia vera last?
Fortunately, with treatment, survival increases from six to 18 months to 13 years or more. One of the challenges in treating polycythemia vera is that more than 12 percent of people will transform into myelofibrosis and around 7 percent will develop acute leukemia/ myelodysplastic syndrome . In contrast to most people with essential ...
How does phlebotomy treat polycythemia vera?
Phlebotomy treats polycythemia vera in two ways: by decreasing the number of blood cells by physically removing them from the body and by causing an iron deficiency that limits new red blood cell production.
What is the hematocrit of a phlebotomist?
Therapeutic phlebotomy is continued on a regular basis to keep the hematocrit (concentration of red blood cells) below 45% , though some physicians will use different targets depending on gender (45% for men and 42% for women).
What is the first medication added to therapeutic phlebotomy?
Often the first medication added to therapeutic phlebotomy is oral hydroxyurea.
Does hydroxyurea affect platelets?
It also reduces the production of white blood cells and platelets. Similar to other conditions treated with hydroxyurea, it is started at a low dose and increased until the hematocrit is in the goal range. It is normally well tolerated with few side effects other than the decreased production of blood cells.
How does polycythemia progress?
How Does Polycythemia Vera Progress? Polycythemia vera, also called “PV,” is a chronic blood disorder in which a person’s bone marrow (the spongy tissue located in the center of your bones) makes too many red blood cells. People with PV also make too many white blood cells (the cells that fight infection) and platelets ...
What is PV symptom?
PV symptoms result primarily from an elevated red blood cell count. That said, a high number of platelets and white blood cells also play a role in certain symptoms and complications.
Why do people with PV have blurry vision?
Vision problems ranging from blurry or double vision to transient blindness may occur in PV. They are a result of delayed blood flow to the retina, since the blood of people with PV is thick and moves sluggishly and slowly.
What is the name of the disease where the bone marrow makes too many red blood cells?
Polycythemia vera, also called “PV,” is a chronic blood disorder in which a person’s bone marrow (the spongy tissue located in the center of your bones) makes too many red blood cells.
Is PV curable?
Although PV isn’t curable, there are multiple treatment options available for stalling its progression and managing symptoms for a long time. Understanding why your doctor recommends a specific one is an empowering way to play an active role in your care.
Is there a cure for PV?
Learning you have been diagnosed with PV can be distressing and naturally, you may wonder, "Will I be OK?" Although there is no cure, it’s still important to explore and get treatment . With the right one, you can successfully stall PV’s progression in your body and manage symptoms for a long time.
