
Full Answer
Is there a non-invasive treatment option for small bowel angioectasias?
Novel pharmacotherapy directed at biomarkers could potentially provide a non-invasive treatment option for angioectasias particularly in the elderly where management can be challenging. Keywords: Argon plasma coagulation; capsule endoscopy; double balloon enteroscopy; serum biomarkers; small bowel angioectasias; somatostatin analogues; thalidomide.
What is angioectasia endoscopy?
Congestive enteropathy was also noted at endoscopy. Angioectasia is the most common cause of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. they consist of thin tortuous veins that lack an internal elastic layer. Endoscopy: angioectasias consist of punctate or patchy areas of erythema, 2–10 mm in size.
Is there a way to prevent angiodysplasia?
There doesn’t appear to be any way to prevent angiodysplasia. It’s important that you don’t ignore signs of angiodysplasia. Contact your doctor if you experience unusual fatigue, weakness, dizziness, or rectal bleeding. If left untreated, angiodysplasia can cause severe blood loss. And in cases of extreme anemia, you may need a blood transfusion.
What causes angioectasia in small bowel bleeding?
Small bowel angioectasia in the proximal small bowel seen on capsule endoscopy. The majority of patients with SB bleeding have angioectasias, while other common lesions include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-related enteropathy (NSAID-related diaphragm), Crohn's disease and small bowel tumors.

What is Angioectasia of the jejunum?
Angioectasia is the most common origin of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding (OGIB), constituting 30-40% of the OGIB cases. It consists of dilated, ectatic, tortuous, thin-walled vessels of the mucosa or submucosa, involving small capillaries, veins, and arteries.
What causes intestinal Angioectasia?
Pathogenic factors contributing to the formation of angioectasia are considered to be high intestinal wall tension causing chronic obstruction of submucosal veins with consecutive precapillary dilation[7], mucosal ischemia from chronic hypoxia or hypoperfusion[8,9], and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-related ...
What is the treatment of small intestine bleeding?
The small intestinal ulcers can be treated with endoscopic techniques or surgery in case of recurrent bleeding. Ulcers due to specific aetiology require treatment according to the aetiology. NSAIDs should be stopped in bleeding due to NSAID-induced ulcers.
What is the treatment for angiodysplasia?
Surgical resection is the definitive treatment for angiodysplasia. Partial or complete gastrectomy for the management of gastric angiodysplasia has been reported to be followed by bleeding in as many as 50% of patients. Rebleeding was attributed to other angiodysplastic lesions.
What is Angioectasia mean?
Angioectasia are an acquired vascular malformation associated with advanced age. Pathogenesis of colonic angioectasia formation is multifactorial and commonly attributed to mild chronic venous obstruction and to chronic mucosal hypoxemia resulting in increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression 3 .
Is angiodysplasia serious?
If left untreated, angiodysplasia can cause severe blood loss. And in cases of extreme anemia, you may need a blood transfusion.
Does internal bleeding heal itself?
Some internal bleeding due to trauma stops on its own. If the bleeding continues or is severe, surgery is required to correct it.
How do you stop internal bleeding on blood thinners?
To stop the bleeding:Put a clean towel, cloth, or bandage on the wound.Press on it firmly until the bleeding stops (don't press on something stuck in your skin)Keep it in place with medical tape or your hands.Raise the injury above your heart if you can.
What happens if your intestines are bleeding?
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a symptom of a disorder in your digestive tract. The blood often appears in stool or vomit but isn't always visible, though it may cause the stool to look black or tarry. The level of bleeding can range from mild to severe and can be life-threatening.
Is Angioectasia the same as angiodysplasia?
Background. Angioectasias, also named angiodysplasias in the literature, are vascular malformations that can be found throughout the gastrointestinal tract, with the most common site being the right colon [1, 2]. These lesions may occasionally cause severe bleeding but they can also be found in symptom-free patients.
Can Angioectasia cause anemia?
Intestinal angioectasias (AE) can cause acute, recurrent bleeding or chronic anemia resulting in very frequent hospitalizations and transfusions [3].
Is angiodysplasia chronic condition?
Mortality/morbidity. Bleeding from angiodysplasia is usually self-limited, but it can be chronic, recurrent, or even acute and life threatening. Approximately 90% of bleeding angiodysplasias spontaneously cease bleeding, presumably because of its venous nature.
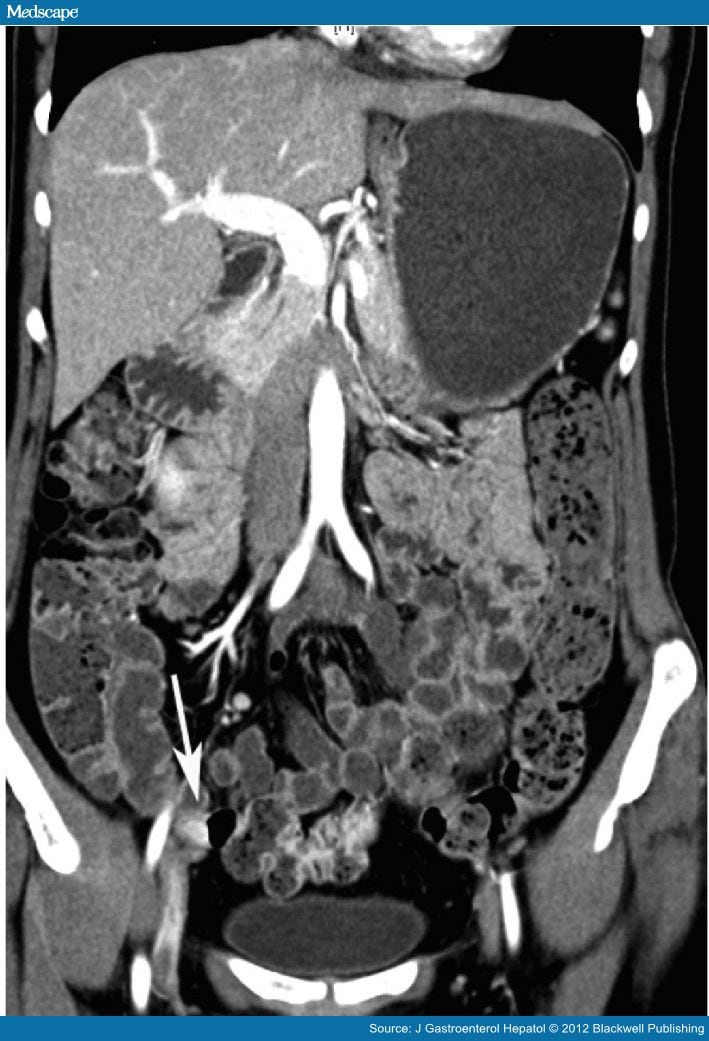
What are causes of SB bleeding?
NSAID-related diaphragm in the distal ileum seen on balloon-assisted enteroscopy.
Who needs evaluation?
Typically, SB endoscopy is pursued in patients with persistent or recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding after a negative bidirectional endoscopy, and in those with unexplained iron deficiency anemia regardless of the results of a fecal occult blood test.
Diagnostic testing
A variety of endoscopic and radiologic tests are available to evaluate the small bowel for bleeding. "Understanding the advantages and limitations of these tests, as well as their diagnostic yield and therapeutic capabilities, can help clinicians determine the most appropriate choice for a given patient," says Dr. Pasha.
Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy (CE) is superior to other diagnostic tests for detection of clinically significant SB findings, making it the first test of choice in the majority of patients with SB bleeding. It provides detailed imaging of the small bowel mucosa, and superior detection of multiple vascular lesions, inflammation and tumors.
Multiphase CT scan (angiography and enterography)
Multiphase CT enterography (CTE) has a higher sensitivity than capsule endoscopy for the detection of small bowel tumors. The administration of a large volume of neutral or negative oral contrast allows adequate SB distension and evaluation of mucosal details, while IV contrast allows optimal visualization of the mesenteric vasculature.
Therapeutic modalities
The primary role of DE is for treatment of SB lesions detected on diagnostic testing. The available DE techniques — balloon-assisted (double-balloon enteroscopy and single-balloon enteroscopy) and spiral enteroscopy — have a comparable diagnostic and therapeutic yield in SB bleeding.
Patient outcomes
Long-term patient outcomes associated with SB bleeding, especially after endoscopic treatment of vascular lesions, are still unknown. Although the recurrence rate of SB bleeding is high, endoscopic treatment typically reduces transfusion requirements.
What causes angiodysplasia in the GI tract?
The cause of angiodysplasia is unknown. But normal spasms occurring in the GI tract may be responsible for the enlargement of blood vessels. This enlargement leads to the development of small pathways between a vein and an artery, which can leak with blood. In addition, age-related weakening of blood vessels may also cause angiodysplasia.
What is an angiodysplasia?
Overview. Angiodysplasia is an abnormality with the blood vessels in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The GI tract includes the mouth, esophagus, small and large intestines, stomach, and anus. This condition causes swollen or enlarged blood vessels, as well as the formation of bleeding lesions in the colon and stomach.
Why is anemia a symptom of angiodysplasia?
Anemia is one symptom of this condition because it causes lesions and bleeding in the GI tract. Anemia is when your red blood cell count is lower than normal. This can cause a reduction in oxygen flow throughout your body and trigger a range of symptoms. You may experience any of the following with angiodysplasia:
How does a doctor treat a bleeding vein?
In this procedure, your doctor uses a thin plastic tube to deliver medicine to a bleeding blood vessel. This medication closes up the blood vessel and stops bleeding. Cauterizing. Once your doctor identifies the site of the bleeding, they can use cauterization to close off a part of the vein and stop the bleeding.
Why is angiodysplasia more common in older people?
In addition, age-related weakening of blood vessels may also cause angiodysplasia. This might explain why the condition is more common in older people. . Other risk factors for angiodysplasia include a history of heart disease, such as aortic stenosis, as well as taking an anticoagulation or blood thinner medication.
Can angiodysplasia cause blood loss?
It’s important that you don’t ignore signs of angiodysplasia. Contact your doctor if you experience unusual fatigue, weakness, dizziness, or rectal bleeding. If left untreated, angiodysplasia can cause severe blood loss. And in cases of extreme anemia, you may need a blood transfusion.
Is outlook good for angiodysplasia?
Outlook for angiodysplasia. The outlook for angiodysplasia is good when treatment successfully controls the bleeding. Once bleeding stops, anemia may resolve itself, at which point you may regain energy. Keep in mind that even with treatment, you could experience bleeding again in the future.
Is GIAD a benign condition?
Gastrointestinal Angiodysplasia (GIAD) is a benign condition caused by vascular malformation, usually in the large, and sometimes, in the small intestine. The topic Gastrointestinal Angioectasia you are seeking is a synonym, or alternative name, or is closely related to the medical condition Gastrointestinal Angiodysplasia. Quick Summary:
Is gastrointestinal angiodysplasia self limiting?
The prognosis of an individual with Gastrointestinal Angiodysplasia is typically excellent with suitable treatment, since in many cases the bleeding is self-limiting. However, the prognosis also depends upon the severity of the condition. Please find comprehensive information on Gastrointestinal Angiodysplasia regarding definition, distribution, ...
What Are Causes of SB bleeding?
Who Needs Evaluation?
Diagnostic Testing
Capsule Endoscopy
Multiphase Ct Scan
Therapeutic Modalities
- Deep enteroscopy (DE): 1. The primary role of DE is for treatment of SB lesions detected on diagnostic testing. The available DE techniques — balloon-assisted (double-balloon enteroscopy and single-balloon enteroscopy) and spiral enteroscopy — have a comparable diagnostic and therapeutic yield in SB bleeding. 2. DE may also be useful for diagnosis ...
Patient Outcomes
For More Information