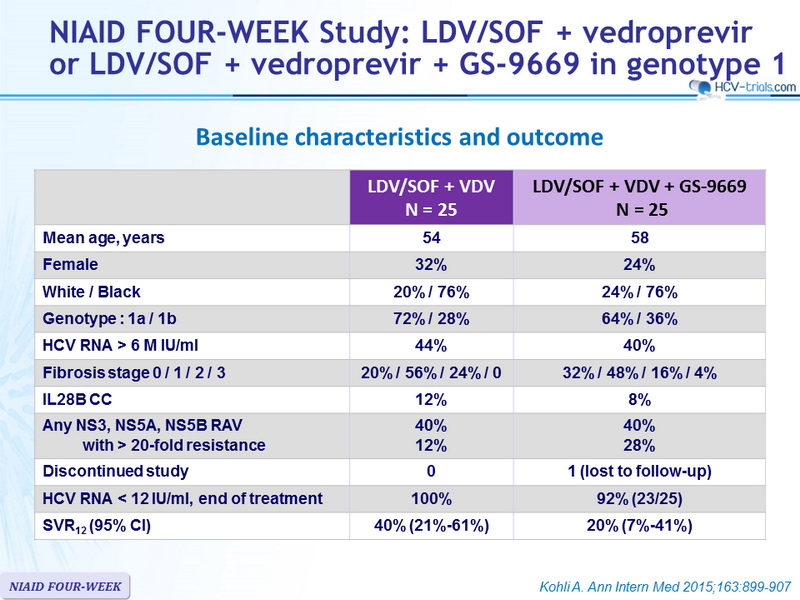
Treatment is usually 8-12 weeks long but can be as much as 16 weeks long in certain situations. Some patients with more damage to their liver may require 24 weeks of treatment, but this is uncommon. The duration depends on the medication, and specific HCV factors in particular patients.
Full Answer
How is hepatitis C (HCV) treated?
Jan 09, 2017 · The available drugs for interferon-free antiviral treatment of hepatitis C include inhibitors of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, NS3/4A protease, and NS5A protein of the hepatitis C virus (HCV), and ribavirin.
When was HCV treatment approved by the FDA?
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection causes liver inflammation that can lead to liver problems, including cancer. People who have chronic hepatitis C need medication to treat it.
What is the success rate of HCV drugs?
Mar 21, 2022 · Genotyping is important in predicting the response to treatment, as well as determining the duration of treatment. 11 HCV is an RNA virus with six known genotypes and more than 50 subtypes. 8, 9, 10 Genotype 1 is the most common HCV genotype in the US and accounts for three-quarters of all HCV infections, and remains the most difficult type to ...
How long does HCV treatment take to work?
HCV Medications. Prescribing Information, Clinical Studies, and Slide Decks. All materials are available for download in their original formats as PDF or PowerPoint. Section Editors. David H. Spach, MD. David H. Spach, MD. Professor of Medicine. Division of Allergy & Infectious Diseases. University of Washington.

What is the cost of HCV treatment?
A 2018 study found that a single pill of one hepatitis C drug cost $1,000. The total was $84,000 for its 12-week course of treatment. Another drug cost $23,600 per month. That's for treatment that could take 6 months to a year.Jun 26, 2020
What are the four drugs used to treat HCV?
Here are the medications available to treat hepatitis C, plus some helpful information about what to expect with their treatment.Ribavirin. ... Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) ... Combination drugs. ... Ledipasvir-sofosbuvir (Harvoni) ... Elbasvir-grazoprevir (Zepatier) ... Sofosbuvir-velpatasvir (Epclusa)More items...
How much do direct-acting antivirals cost?
Conclusions: Within the next 15 years, large-scale manufacture of 2 or 3 drug combinations of HCV DAAs is feasible, with minimum target prices of $100-$250 per 12-week treatment course. These low prices could make widespread access to HCV treatment in low- and middle-income countries a realistic goal.
What is the best treatment of HCV?
Hepatitis C is treated using direct-acting antiviral (DAA) tablets. DAA tablets are the safest and most effective medicines for treating hepatitis C. They're highly effective at clearing the infection in more than 90% of people.
Is Hep C 100 curable?
Hepatitis C is a curable liver infection that results from the hepatitis C virus. Without proper treatment, chronic hepatitis C infections can lead to severe complications, such as liver disease, liver scarring, and liver cancer.Sep 13, 2019
How long is Epclusa treatment?
Epclusa is a two-drug combination administered as a single daily pill containing the viral NS5A inhibitor Velpatasvir and Sofosbuvir. The treatment duration is 12 weeks for all genotypes.
How much is hep C treatment in India?
The generic version of these drugs are available in cities such as Bengaluru Hyderabad and Chennai at the cost of Rs70000 or around $1000 USD for the entire treatment regimen.
Is Hep C curable 2020?
Hepatitis C (hep C) infection used to be a lifelong condition for most people. Up to 50 percent of people may clear the hepatitis C virus (HCV) from their body without treatment. For everyone else, the infection becomes chronic. With advances in hep C treatment, most people can now be cured of HCV.
How much does hep C treatment cost UK?
A 12-week course of treatment with elbasvir-grazoprevir usually costs £36,500 per patient, but the NHS will pay less than this as the company has offered a confidential discount. Taken once daily, the tablet could treat around 4,000 patients in the first year, alongside other options already available for hepatitis C.
Is hep C curable 2021?
Today, chronic HCV is usually curable with oral medications taken every day for two to six months. Still, about half of people with HCV don't know they're infected, mainly because they have no symptoms, which can take decades to appear.Aug 31, 2021
How long is treatment for hep C?
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C? Depending on the drug combination, the specific genotype of hepatitis C that is to be treated, any prior treatment, and whether the person has cirrhosis, the duration of medical therapy may be as few as 8 weeks, or up to 24 weeks. Most regimens are for 12 consecutive weeks.
Can you get hep C twice?
Yes. Having had hep C once does not make you immune from getting it again. You can be reinfected with hep C whether you clear the virus by successful treatment (called a sustained virologic response, or SVR) or by spontaneously clearing it on your own.Apr 15, 2016
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
As a result, people experience better outcomes, fewer side effects and shorter treatment times — some as short as eight weeks.
What is the best treatment for hepatitis C?
Liver transplantation. If you have developed serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection, liver transplantation may be an option. During liver transplantation , the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver.
How old do you have to be to get tested for hepatitis C?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults ages 18 to 79 years be screened for hepatitis C, even those without symptoms or known liver disease. Screening for HCV is especially important if you're at high risk of exposure, including: Anyone who has ever injected or inhaled illicit drugs.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to clear?
The goal of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 weeks after you complete treatment.
How to prevent liver damage?
Avoid medications that may cause liver damage. Review your medications with your doctor, including over-the-counter medications you take as well as herbal preparations and dietary supplements. Your doctor may recommend avoiding certain medications. Help prevent others from coming in contact with your blood.
How to prepare for a liver appointment?
Because appointments can be brief and because there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea to be well prepared. To prepare, try to: Review your medical record. This is particularly important if you are seeing a liver specialist (hepatologist) for the first time after finding out you have hepatitis C.
What to do if you have hepatitis C?
If you receive a diagnosis of hepatitis C, your doctor will likely recommend certain lifestyle changes. These measures will help keep you healthy longer and protect the health of others as well:
What is the best medication for hepatitis C?
A Full List of Hepatitis C Medications: Epclusa, Harvoni, Zepatier, and More. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection causes liver inflammation that can lead to liver problems, including cancer. People who have chronic hepatitis C need medication to treat it. These drugs can help ease symptoms.
Why is it important to treat hepatitis C?
Even if an HCV infection hasn’t caused symptoms yet, it’s still important to treat it. This is because drugs can also lower the risk of complications from hepatitis C, such as dangerous liver problems. HCV has different genetic variations ...
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat cirrhosis?
Epclusa, which contains sofosbuvir and velpatasvir, was approved in 2016. It can be used in combination with ribavirin in people with moderate to severe cirrhosis. Epclusa was the first medication to treat all six HCV genotypes.
What are directed inhibitors used for?
These drugs are used to treat all HCV genotypes. They’re used alone or in combination with other medications. Examples of directed inhibitors include ledipasvir, a component of the combination drug Harvoni and elbasvir, a component of the combination drug Zepatier.
How long does mavyret last?
It contains glecaprevir and pibrentasvir. Mavyret is the first treatment that can be administered for only 8 weeks in people without cirrhosis. Most of the other combination drugs must be administered for a minimum of 12 weeks.
How does ribavirin work?
Ribavirin works by stopping viruses from replicating and spreading. It’s an oral medication that comes as a capsule or tablet and is available in several strengths. It’s always used in combination with other drugs to treat hepatitis C. The most common brand name of ribavirin is Rebetol.
What is a protease inhibitor?
Protease inhibitor antiviral medications (NS3/4A inhibitors) Protease inhibitors work by preventing the spread of infection within the body by stopping viruses from multiplying. Grazoprevir is a protease inhibitor for hepatitis C genotypes 1 and 4.
When was HCV approved?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first of these medications for HCV treatment in 2011. Several more medications have been approved since that time. Most of these individual drugs are effective for specific strains, or genotypes, of HCV.
What is the new drug called for HCV?
Trusted Source. of people who take them, depending on the type of HCV infection and treatment exposure. These new drugs are called direct-acting antivirals (DAAs).
What is the liver infection?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that attacks the liver. Infection with hepatitis C can lead to serious liver disease, including cirrhosis and cancer. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is transmitted by exposure to blood or other bodily fluids that contain HCV.
How many people die from hepatitis C each year?
Americans have chronic hepatitis C. About 19,000 of these people die each year from cirrhosis or liver cancer. Fortunately, recent advancements in the fight against this virus have changed the outlook for people with HCV. New drugs have transformed the disease from one that can, at best, be controlled to one that can be cured for most people who ...
What are the criteria for liver disease?
These criteria may be based on: the severity of liver disease. whether the person avoids alcohol and drug use. whether the drug’s prescribed by a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. the life expectancy of the person seeking treatment. whether less expensive treatments could be used first.
Is generic medicine cheaper than brand name?
It also means there are no generic versions of these drugs yet. Generics are typically much cheaper than brand- name versions. The FDA determines how long this period of exclusivity will last. During this time, the pharmaceutical companies have a lot of freedom in establishing prices.
Does insurance cover cirrhosis of the liver?
Payment restrictions. Based on your insurance provider, some companies will only pay for treatment if you have cirrhosis of the liver or bridging fibrosis , which is a thickening and scarring of the liver.
What is an EUA?
EUA. An Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) allows the FDA to authorize unapproved medical products or unapproved uses of approved medical products to be used in a declared public health emergency when there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives. Pregnancy Category. A.
Is there a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision?
Has a high potential for abuse. Has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States or a currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions. Abuse may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence.
Is fetal risk based on adverse reaction data?
Studies in animals or humans have demonstrated fetal abnormalities and/or there is positive evidence of human fetal risk based on adverse reaction data from investigational or marketing experience, and the risks involved in use in pregnant women clearly outweigh potential benefits. N. FDA has not classified the drug.
Treatment
- Hepatitis C virus is treated with all-oral medications. These pills, called antiviral medications , are usually taken once per day. These antiviral medications are extremely good at attacking the virus and preventing it from multiplying. Antiviral medications were not the original treatment for hepatitis C. Before 2014, the only treatment for hepatitis C was called interferon and ribavirin, ta…
Medical uses
- Ribavirin (without interferon) is still sometimes prescribed to be taken along with the new antiviral medicines, but it has become more and more uncommon that ribavirin is needed at all. Ribavirin has some mild-moderate side effects. Ribavirin is a pill taken twice per day, as 2 or 3 pills in the morning plus 2 or 3 pills at night, depending on the patient's body weight. Most patients do not n…
Mechanism
- In an untreated state, the hepatitis C virus infects the cells of the liver and then continuously lives there, making copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. Antiviral medications can destroy the ability of the virus to reproduce, so the amount of virus in the bloodstream then decreases. The amount of virus in the blood is measured by a viral load (also called HCV RNA).
Prognosis
- Treatment is successful when the viral load drops to undetectable levels, which means the virus cannot be detected in the bloodstream at all. The viral load becomes undetectable during treatment and remains undetected after treatment has ended. If there is still no detectable virus in the blood 12 weeks after the end of the treatment, the treatment was successful. This is called …
Symptoms
- The medications will usually cause a very big drop in the viral load within the first two weeks. Some patients will see their viral load become undetectable very early, such as by the fourth week. For other patients, it can take longer until their viral load becomes undetectable.
Results
- Your provider will meet with you during treatment to review how well you are tolerating treatment and review laboratory results. Laboratory tests help keep tabs on your health, track the viral load, and determine your response to treatment. You will be given specific dates to go get your blood tested at the lab during and after the treatment.
Access
- For more about hepatitis C treatment, see our patient information , contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Hepatitis Toll-Free Information Line at 1-888-4 HEPCDC (1-888-443-7232), or visit the CDC website at http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/index.htm .
Diagnosis
- Screening for hepatitis C
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults ages 18 to 79 years be screened for hepatitis C, even those without symptoms or known liver disease. Screening for HCVis especially important if you're at high risk of exposure, including: 1. Anyone who has ever i… - Other blood tests
If an initial blood test shows that you have hepatitis C, additional blood tests will: 1. Measure the quantity of the hepatitis C virus in your blood (viral load) 2. Identify the genotype of the virus
Treatment
- Antiviral medications
Hepatitis C infection is treated with antiviral medications intended to clear the virus from your body. The goal of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 weeks after you complete treatment. Researchers have recently made significant advances in treatmen… - Liver transplantation
If you have developed serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection, liver transplantation may be an option. During liver transplantation, the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver. Most transplanted livers come from decease…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- If you receive a diagnosis of hepatitis C, your doctor will likely recommend certain lifestyle changes. These measures will help keep you healthy longer and protect the health of others as well: 1. Stop drinking alcohol.Alcohol speeds the progression of liver disease. 2. Avoid medications that may cause liver damage.Review your medications with your doctor, including o…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you may have a risk of hepatitis C, see your family doctor. Once you've been diagnosed with a hepatitis C infection, your doctor may refer you to a specialist in liver diseases (hepatologist) or infectious diseases.