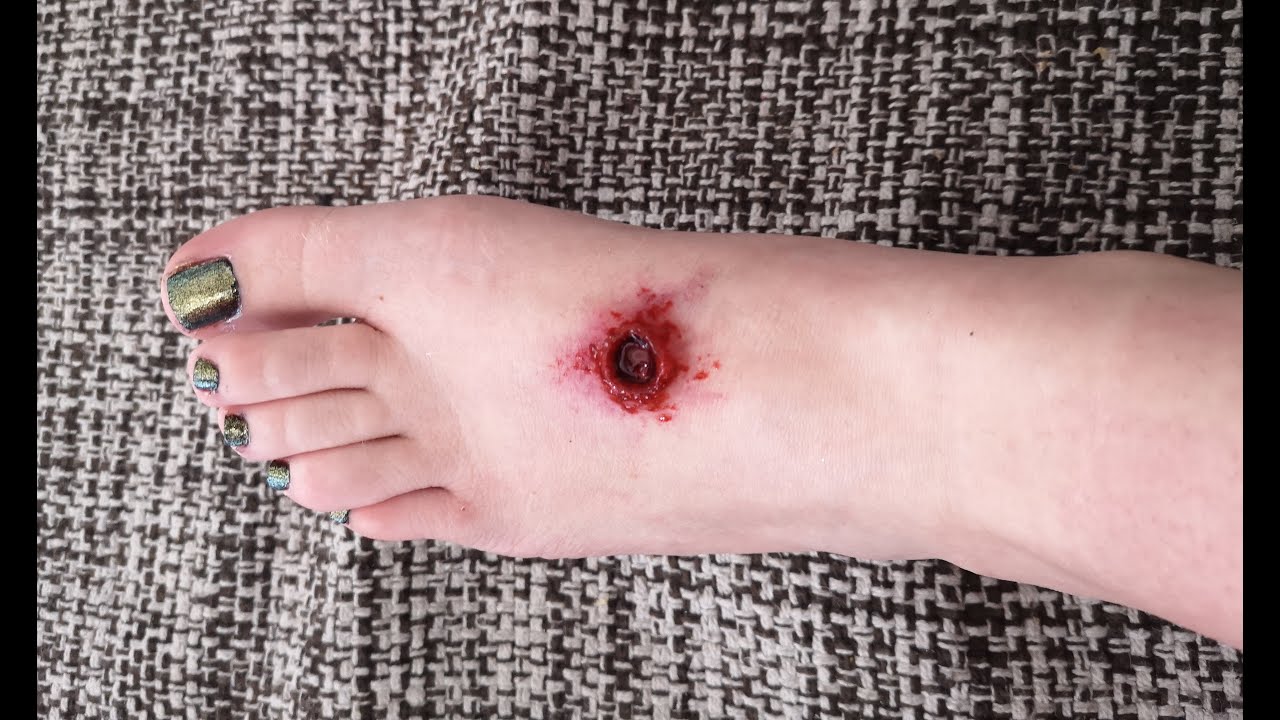
Assessment of Gunshot Wounds of the Foot The initial treatment calls for washing the wound with normal saline followed by application of a sterile gauze dressing. A topical antibacterial agent may be added to the dressing.
Full Answer
What is the initial treatment for a gunshot wound on the foot?
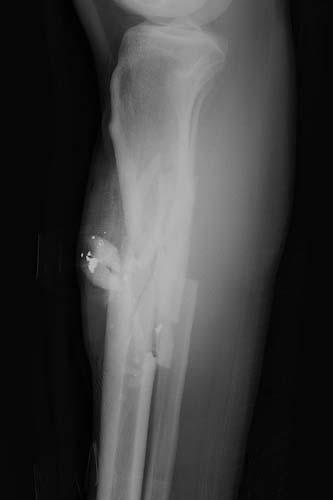
Surgical treatment was performed three hours after trauma and included extensive debridement of damaged soft tissue, removing of the non-viable bone and metal fragments, rocks and other foreign bodies. Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) was applicated in the operating table. The starting therapy was continuously -125 mm Hg of vacuum.
How do you treat a gunshot wound that won't heal?
Adherence to the principles of soft tissue treatment (venous pumps, elevation, prevention of venous congestion or vasoconstriction, protected range of motion and prevention of atrophy) and fracture treatment (stable fixation) are the hallmarks of postoperative care and rehabilitation after gunshot wounds to the foot.
How do you treat a gunshot wound on a dog?
Dec 19, 2021 · Strong pressure on the wound: If blood is coming out of a hole, put a lot of pressure on it. For heavy bleeding, don't be afraid to use your knee and really lean hard on the wound. Dressing: Dressings help the blood clot and seal the wound. Use whatever's available—gauze, towels, a shirt, etc.
What is the treatment for a low velocity gunshot wound?
It is imperative that the physician participating in the care and treatment of foot and ankle trauma appreciate the epidemiology, the unique characteristics, and principles of treatment of gunshot injuries involving the foot and ankle. ... Gunshot wounds of the foot Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003 Mar;(408):86-91. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200303000 ...
What is postoperative care after a gunshot wound?
Adherence to the principles of soft tissue treatment (venous pumps, elevation, prevention of venous congestion or vasoconstriction, protected range of motion and prevention of atrophy) and fracture treatment (stable fixation) are the hallmarks of postoperative care and rehabilitation after gunshot wounds to the foot.
How does a bullet cause vascular injury?
A bullet causes vascular injury either by directly damaging the vessel or indirectly through the effect of cavitation. The suspicion of a possible vascular injury is based on several parameters. The physical examination, which should include an assessment of the pulses and capillary refill, is important in the determination of potential vascular injury. A knowledge of the local vascular anatomy and a knowledge of the entrance and exit wounds of the project are critical in the assessment of vascular injury. Angiography is indicated in following circumstances: (1) in patients with preexisting vascular disease; (2) close proximity of the bullet wound to a significant vascular structure; (3) in the presence of massive tissue injury; (4) diminished or absent pulses; (5) in the presence of an expanding hematoma, uncontrolled ultrasound may be hemorrhage or limb ischemia; (6) detection of a thrill or bruit; and (7) when the bullet exit wound cannot be determined by inspection or radiographs. 1,12,27 In situations where angiography is contraindicated, duplex Doppler ultrasound may be used as an alternative method of analysis of the arterial system.
What is ballistics in physics?
Ballistics. The term ballistics refers to the physics of the projectile as measured by its mass, velocity, and configuration or shape. In large measure these characteristics will influence the tissue damage and characteristics of the wound created by the bullet.
What is nerve injury?
Nerve injury is sustained by direct or indirect forces. Fortunately, most injuries are neuropraxic and usually recover without exploration or repair of the nerve. 23 However, direct laceration or injury to nerve (neurotmesis) generally results in poor outcome associated with a permanent loss of function of the nerve. The potential for long-term nerve injury is highest in patients with high-velocity injuries and shotgun blasts. 10 The risks of reflex sympathetic dystrophy, chronic pain, and late amputation all are potential sequela of extensive neurologic injury caused by high-velocity bullet or shotgun injuries. 10,31
Why is physical examination important?
The physical examination, which should include an assessment of the pulses and capillary refill, is important in the determination of potential vascular injury. A knowledge of the local vascular anatomy and a knowledge of the entrance and exit wounds of the project are critical in the assessment of vascular injury.
What to do when you have a gunshot wound?
If you are ever dealing with a gunshot wound, the key priorities are staying safe, calling for help, stopping the bleeding, and keeping the wound clean. You will need to make some quick decisions, but the more prepared you are, the better the outcome will be.
Is a gunshot wound a puncture wound?
Gunshot wounds are puncture wounds. Don't expect to be able to tell the difference between entrance and exit gunshot wounds. There's a myth that one type is significantly worse than the other. There's no reliable way to tell and it doesn't matter.
How to survive a gunshot wound?
Once safe, call 911 and follow the instructions from the dispatcher. Surviving a gunshot wound depends on how quickly a patient gets to a hospital. Ideally, the patient should be in an ambulance on the way to a hospital within 10 minutes of being shot. 1.
How to stop bleeding from a gunshot wound?
Stopping the bleeding is a crucial part of managing a gunshot wound. 1. Methods for stopping bleeding include: Place strong pressure on the wound: If blood is coming out of a hole, put a lot of pressure on it. For particularly bad bleeding, don't be afraid to use your knee and really lean hard on the wound. Use a dressing : Dressings help the blood ...
What to do if you get shot?
Call 911. If you have been shot or if you're with someone who has been shot, it's vital that you get to a safe place. You can't help anyone if you get hurt. If the person who's been injured can walk or run, take them with you. In the case of an accidental shooting, make sure the gun is secured.
What happens if you get shot in the abdomen?
A gunshot wound to the abdomen can cause severe bleeding, as well as organ damage and abdominal wall damage. 4 A wound that punctures the stomach or intestines can lead to an infection due to leaking of gastrointestinal fluid or feces into the abdominal cavity.
Can you move a limb that has been shot?
A gunshot to a limb is likely to cause a vascular injury, and it may cause nerve damage or broken bones as well. In general, you should avoid moving a limb that has been shot. Preventing blood loss by holding pressure is the best approach you can take while waiting for medical help to arrive.
Who is the expert on gunshot wounds?
Want to know how to treat a gunshot wound? This week, EMS and firearms expert Gary Anderson will be teaching you everything you need to know about how to treat a gunshot wound!
What happens when a bullet hits a bone?
If that happens, and a wobble or tumble is generated, it will send much more energy down the bone and cause more of the hard tissues to break away, and makes the one tissue less stable.
Do solid organs have the same effects as muscle tissue?
Solid organs will suffer the same effects as muscle tissue. For the purposes of this article, let me talk about the unexpected effects of gunshot wounds that do not carve a hole in the organ.
What is a HIPPA?
HIPPA is a law designed to protect patients’ information. Lack of volunteers to receive a gunshot wound to get very awesome pictures. Theft of pictures from other sources. The images we will create will be disturbing to some but remember, no animals were injured making this article.
Abstract and Figures
Civilian gunshot injuries of the foot are not so common in Croatia. They are related with accidents in hunting or weapon cleaning. Gunshot injuries represent a special challenge for surgeon because of specific anatomical relations and biomechanical function of the foot.
References (14)
Debridement is an essential act in the treatment of various wounds, which removes devitalized and colonized necrotic tissue, also poorly healing tissue and all foreign bodies from the wound, in order to enhance the formation of healthy granulation tissue and accelerate the process of wound healing.
What is a gunshot wound?
A gunshot wound is caused when a bullet or other projectile is shot into or through the body. Gunshot wounds can cause serious injury, including: The amount of damage depends on the location of the injury and the speed and type of bullet. Gunshot wounds to the head or body (torso) are likely to cause more damage.
Can you put lotion on a wound?
These can damage the wound tissue and slow your healing. Do not put any lotion, cream, or herbal remedies on or around your wound without asking your provider first.
What are the consequences of a gunshot wound?
Gunshot wounds can cause serious injury, including: Severe bleeding. Damage to tissues and organs. Broken bones. Wound infections. Paralysis. The amount of damage depends on the location of the injury and the speed and type of bullet. Gunshot wounds to the head or body (torso) are likely to cause more damage. ...
Can bullets be removed?
You may have bullet pieces that remain in your body. Often these cannot be removed without causing more damage. Scar tissue will form around these remaining pieces, which may cause ongoing pain or other discomfort. You may have an open wound or a closed wound, depending on your injury.
Can you use alcohol on a wound?
Wash your hands again after cleaning the wound and applying the new dressing. Do not use skin cleansers, alcohol, peroxide, iodine, or soaps with antibacterial chemicals on the wound unless your provider tells you to. These can damage the wound tissue and slow your healing.
Is it normal to be scared of being shot?
You may feel shock, fear for your safety, depression, or anger as a result. These are completely normal feelings for someone who has been through a traumatic event . These feelings are not signs of weakness. You may notice other symptoms as well, such as:
How long does it take for stitches to be removed?
If you have non-dissolvable stitches or staples, your provider will remove them within 3 to 21 days. Do not pull at your stitches or try to remove them on your own.
How to reduce swelling in arm and leg?
Elevate your arm or leg above the level of your heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your arm or leg on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably. Exercise as directed.
How to treat a swollen arm?
Apply ice on the wound area for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain. Elevate your arm or leg above the level of your heart as often as you can.
Can you get an MRI with metal?
Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body. A neurovascular exam may show damage to your blood vessels or nerves and show any problems with your circulation.
Can you get a tetanus shot?
You may be given a tetanus shot. Tetanus is a severe infection caused by bacteria. Tell your healthcare provider if you have had the tetanus vaccine or a tetanus booster within the last 5 years. A blood transfusion may be given if you bleed heavily from your GSW.
What is a tetanus booster?
Tetanus is a severe infection caused by bacteria. Tell your healthcare provider if you have had the tetanus vaccine or a tetanus booster within the last 5 years. A blood transfusion may be given if you bleed heavily from your GSW. IV fluids may be given to prevent dehydration and increase blood flow to major organs.
Why do you need IV fluids?
IV fluids may be given to prevent dehydration and increase blood flow to major organs. An immobilizer, splint, or cast may be applied to your limb to prevent it from moving. It may help your wound heal. Surgery may be needed to repair damage to bones, tendons, ligaments, or major blood vessels in your arm or leg.
How to treat a swollen swollen swollen swollen swolle
Carefully wash the wound with soap and water. Dry the area and put on new, clean bandages as directed. Change your bandages when they get wet or dirty. Monitor your wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus. Apply ice on the wound area for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed .