The most common treatment options for early stage, or localized, prostate cancer include:
- Active Surveillance is the close monitoring of the status of your prostate cancer through regular office visits and...
- Surgery usually involves a radical prostatectomy, which is the removal of the entire prostate by a surgeon.
- Radiation therapy uses radiation to destroy the cancer...
What are some examples of local therapy used in cancer?
The most common treatment options for early stage, or localized, prostate cancer include: Active Surveillance is the close monitoring of the status of your prostate cancer through regular office visits and... Surgery usually involves a radical prostatectomy, which is the removal of the entire ...
What are the treatment options for localized prostate cancer?
4 rows · Jun 15, 2018 · Treatment of localized cancer can be curative, but the risk of death from screening-detected ...
What are some examples of cancer staging systems?
If there is cancer in the lymph nodes, or the tumor is large, postoperative therapy may include: Chemotherapy and targeted therapy (trastuzumab). Hormone therapy, such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitor therapy, for tumors that are also hormone receptor positive. Antibody-drug conjugate therapy ...
What is active surveillance for colon cancer?
Sep 30, 2021 · The other type of localized treatment for breast cancer is radiation therapy. This is done by a cancer specialist called a radiation oncologist. Radiation directs energy beams towards a specific area to intentionally damage and kill cells that are multiplying quickly, like cancer cells. Because radiation specifically targets replicating DNA, it ...

What does it mean if cancer is localized?
Is chemotherapy a localized treatment?
Is radiation treatment localized?
What are the three modes of treatment for cancers?
What is local chemotherapy?
How is regional chemotherapy given?
Is radiation localized or systemic?
Is radiation therapy systemic or local?
What is worse chemo or radiation?
What is tumor therapy?
What cancers can be cured?
- Prostate Cancer.
- Thyroid Cancer.
- Testicular Cancer.
- Melanoma.
- Breast Cancer -- Early Stage.
Are there chemotherapy alternatives?
What are the factors used to determine the treatment of cancer?
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines use four main factors to stratify risk of disease progression or recurrence and to determine the recommended treatment: clinical stage, pathologic grade, prostate-specific antigen level, and comorbidity-adjusted life expectancy.
What is the best treatment for prostate cancer?
Radical prostatectomy or external beam radiation therapy should be considered for patients with high-risk localized prostate cancer regardless of comorbidity-adjusted life expectancy.
How to detect prostate cancer?
Preventive Services Task Force recommended against PSA screening for prostate cancer in 2012 and is in the process of updating this topic. 16 The only method for diagnosing prostate cancer is a prostate biopsy. 17 Using the standard 12-core biopsy, less than 1% of the prostate is sampled and can miss a tumor in 20% of cases. Saturation biopsy using 24 cores increases the likelihood of identifying a tumor but may increase complications. The use of magnetic resonance imaging may improve the ability to identify clinically significant lesions. 18
How long does a person live after prostate cancer treatment?
22 Prostate cancer is usually slow growing, and the survival benefit of treatment may present only after 10 years.
How many radiation oncologists recommend surgery for prostate cancer?
A survey found that for the same hypothetical patient, 93% of urologists would recommend surgery, and 72% of radiation oncologists would recommend radiation therapy. 11 In a survey of men with newly diagnosed prostate cancer, more than one-half significantly overestimated the survival benefit of treatment; patient education, income, and health literacy did not affect the results. 12 Although these patients had been counseled by their urologists and had already elected treatment or observation, more than one-half incorrectly answered most of an 18-item questionnaire designed to test knowledge about treatment options. This questionnaire ( https://www.aafp.org/afp/2011/0815/p413.html#afp20110815p413-f1) can be used to identify patients who need further counseling. 13
How does prostate cancer progress?
Prostate cancer progression may be indicated by an increase in the pathologic grade, a significant rise in serum prostate-specific antigen level, or an abnormality on digital rectal examination. Prostate cancer is the third most common cause of cancer-related death in U.S. men, with an estimated 161,000 cases and 26,700 deaths in 2017.
What is brachytherapy for cancer?
Brachytherapy is an option for patients with low-risk disease and some patients with intermediate- risk disease. Active surveillance is an option for patients with low-risk and very low-risk disease. With active surveillance, patients are closely followed and undergo invasive treatments only if the cancer progresses.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Preoperative systemic therapy. Systemic therapy is the use of drugs that can enter the bloodstream and reach cancer cells throughout the body. Preoperative systemic therapy is given to shrink the tumor before surgery.
What is the procedure to remove cancer from lymph nodes?
Breast-conserving surgery and sentinel lymph node biopsy. If cancer is found in the lymph nodes, a lymph node dissection may be done.
What is the best treatment for a premenopausal woman with a tumor?
Chemotherapy. Hormone therapy, such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitor therapy, for women who cannot have chemotherapy. In premenopausal women with hormone receptor positive tumors, preoperative therapy may include: A clinical trial of hormone therapy, such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitor therapy.
What is aromatase inhibitor therapy?
Aromatase inhibitor therapy and treatment to stop or lessen how much estrogen is made by the ovaries. Drug therapy, surgery to remove the ovaries, or radiation therapy to the ovaries may be used. In postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive tumors, no more treatment may be needed or postoperative therapy may include: ...
What is preoperative therapy for triple negative tumors?
In women with HER2/neu negative tumors or triple negative tumors, preoperative therapy may include: Chemotherapy. A clinical trial of a new chemotherapy regimen. A clinical trial of monoclonal antibody therapy. For patients with triple-negative or HER2-positive disease, the response to preoperative therapy may be used as a guide in choosing ...
Why do women get radiation therapy?
For women who had breast-conserving surgery, radiation therapy is given to the whole breast to lessen the chance the cancer will come back. Radiation therapy may also be given to lymph nodes in the area.
What is systemic therapy?
Systemic therapy is the use of drugs that can enter the bloodstream and reach cancer cells throughout the body. Postoperative systemic therapy is given to lessen the chance the cancer will come back after surgery to remove the tumor. Postoperative systemic therapy is given depending on whether:
What factors determine my treatment options?
There are several factors that determine which treatments are best for someone who has been diagnosed with breast cancer. These are factors specific to the individual as well as features of their particular breast cancer.
Localized treatments for breast cancer
Localized treatments directly target the breast tumor and surrounding tissue. There are two types of localized treatments: surgery to remove the cancer and radiation therapy to kill any microscopic cancer cells left behind after surgery.
Systemic therapies for breast cancer
The goal of systemic therapy is to administer medication to the whole body in order to reach cancer cells that may have spread outside of the breast or the nearby lymph nodes. These wandering cells are called micrometastases. They’re too small for lab or imaging tests to detect.
Is breast cancer treatment painful?
Breast cancer tumors usually aren’t painful (but sometimes they can be). It’s more common to experience discomfort from some of the treatments for breast cancer. But there are many ways to treat these symptoms:
The bottom line
There are many different treatments for breast cancer. And the right treatment for you depends on a lot of personal and cancer-related factors. But what’s most important are your desired treatment goals. Some people want to be as aggressive as possible.
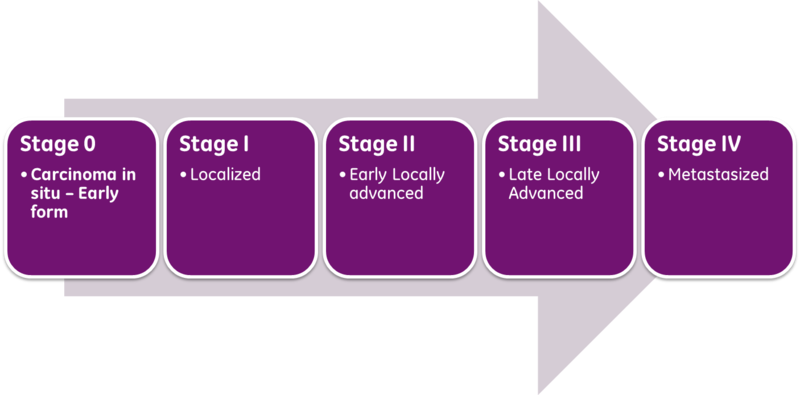
What are some examples of cancers with different staging systems?
Examples of cancers with different staging systems include brain and spinal cord tumors and blood cancers. In the TNM system: The T refers to the size and extent of the main tumor. The main tumor is usually called the primary tumor. The N refers to the the number of nearby lymph nodes that have cancer.
What is stage IV cancer?
Stage IV. The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body. Another staging system that is used for all types of cancer groups the cancer into one of five main categories. This staging system is more often used by cancer registries than by doctors.
What is tumor grade?
Tumor grade, which refers to how abnormal the cancer cells look and how likely the tumor is to grow and spread
What does the N mean in cancer?
The N refers to the the number of nearby lymph nodes that have cancer.
What is CIS in cancer?
Also called carcinoma in situ, or CIS. CIS is not cancer, but it may become cancer. Stage I, Stage II, and Stage III. Cancer is present. The higher the number, the larger the cancer tumor and the more it has spread into nearby tissues. Stage IV. The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
How many stages of cancer are there in TNM?
The TNM system helps describe cancer in great detail. But, for many cancers, the TNM combinations are grouped into five less -detailed stages. When talking about your cancer, your doctor or nurse may describe it as one of these stages:
Does cancer stage change?
New information about how a cancer has changed over time gets added on to the original stage. So, the stage doesn't change, even though the cancer might.
What is localized prostate cancer?
Understanding Localized Cancer. Early stage, or localized, prostate cancer refers to cancer that is still confined to the prostate, either Stage I or Stage II. Early stage prostate cancer may be easier to cure and treatment is done with the aim to cure the cancer. If you have been diagnosed with a later stage ...
Why do doctors recommend aggressive treatment for prostate cancer?
If you have high risk prostate cancer, most likely your doctor will suggest an aggressive course of treatment because you are at high risk for the disease to spread throughout your body. These genomic tests look at the genetic markers of the cancer cells to tell us how the cancer may behave.
What are the risk categories for prostate cancer?
Early stage prostate cancer is found only in the prostate gland and has not spread beyond the prostate to nearby tissue or to another part of the body. This risk group is determined by a combination of the PSA level, Gleason score, and DRE results.
What is the Gleason score for prostate cancer?
Today almost all men with prostate cancer have a Gleason Score of between 6 and 10, a number that is generated by adding the two most common patterns seen within the tumor.
Why do you need an AS test for prostate cancer?
These tests may be helpful when making a treatment choice if you have low risk prostate cancer because you might be a good candidate for Active Surveillance ( AS). AS is a way of closely monitoring your cancer that may allow you to avoid treatment, if possible, or to give treatment if the cancer progresses while it is stil localized, if necessary.
What does stage 1 mean in prostate cancer?
The stage tells you the location and how large (in relation to the prostate) the tumor is. Early stage prostate cancer is found only in the prostate. Stage I or Stage T1 means the cancer is small, may be too small to feel by the doctor and only in the prostate. Stage II or Stage T2 means the cancer is larger, only in the prostate ...
Can prostate cancer spread?
Low-risk prostat e cancer are unlikely to grow or spread for many years