Is there a cure for erythroblastosis fetalis?
After birth, treatment may include: blood transfusion intravenous fluids oxygen or mechanical breathing machine exchange transfusion to replace the baby’s damaged blood with fresh blood
What is the treatment for a Rh negative mother?
Jun 30, 2021 · RhoGAM should be administered at 28 weeks since it has a half-life of about 12 weeks and covers the mother until term or 40 weeks, and postpartum if the neonate is Rh-positive. A standard dose of RhoGAM (0.3 mg) will eradicate 15 mL of fetal RBCs. This dose is adequate for a routine pregnancy.
What are the possible complications of erythroblastosis fetalis?
Jun 01, 2017 · Phototherapy: This is also called light therapy and is used to treat jaundice. The light treatment helps to convert the... Immunoglobulin: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) to neutralize maternal anti-D antibodies. These can be administered...
What blood groups increase the risk of erythroblastosis fetalis?
Dec 23, 2020 · How it can be treated? If a baby experiences erythroblastosis fetalis in the womb, they may be given intrauterine blood transfusions to minimize anemia. When the child’s lungs and heart mature enough for delivery, a physician might advise delivering the infant early. After a baby is born, additional blood transfusions might be required.

What is erythroblastosis fetalis and its treatment?
What is the treatment for Rh incompatibility?
What is the main reason for erythroblastosis fetalis?
What is erythroblastosis fetalis What is the cause who is at risk How is it treated?
Why are RhoGAM injections given?
How is RhoGAM administered?
Under what conditions is erythroblastosis fetalis possible?
Why do I need an anti d injection?
What happens if mother is Rh positive and baby is Rh-negative?
What causes erythroblastosis fetalis?
There are two main causes of erythroblastosis fetalis: Rh incompatibility and ABO incompatibility. Both causes are associated with blood type. There are four blood types: In addition, blood can be either Rh positive or Rh negative. For example, if you’re type A and Rh positive, you have A antigens and Rh factor antigens on the surface of your RBCs.
What type of blood type mismatch can cause antibodies against her baby's blood cells?
Another type of blood type mismatch that can cause maternal antibodies against her baby’s blood cells is ABO incompatibility. This occurs when the mother’s blood type of A, B, or O isn’t compatible with the baby’s. This condition is almost always less harmful or threatening to the baby than Rh incompatibility.
What is it called when fluid accumulates in the lungs?
Babies can also experience a condition known as hydrops fetalis, where fluid starts to accumulate in spaces where fluid is normally not present. This includes spaces in the: abdomen. heart. lungs. This symptom can be harmful because the extra fluid places pressure on the heart and affects its ability to pump.
What is rh incompatibility?
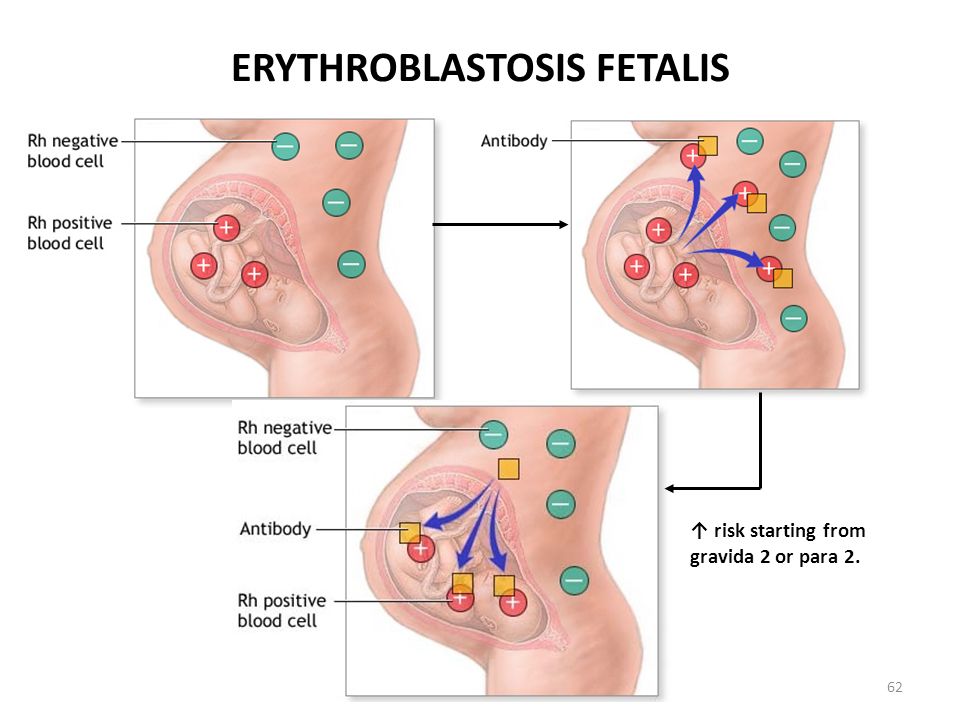
Rh incompatibility. Rh incompatibility occurs when a Rh-negative mother is impregnated by a Rh-positive father. The result can be a Rh-positive baby. In such a case, your baby’s Rh antigens will be perceived as foreign invaders, the way viruses or bacteria are perceived.
Can Rh antigens be foreign invaders?
In such a case, your baby’s Rh antigens will be perceived as foreign invaders, the way viruses or bacteria are perceived. Your blood cells attack the baby’s as a protective mechanism that can end up harming the child. If you’re pregnant with your first baby, Rh incompatibility isn’t as much of a concern.
When is a father's blood test done?
If the father’s blood type is Rh negative, no further testing is needed. However, if the father’s blood type is Rh positive or their blood type isn’t known, your blood may be tested again between 18 to 20 weeks of pregnancy, and again at 26 to 27 weeks. You’ll also receive treatment to prevent erythroblastosis fetalis.
Why is my baby jaundiced after birth?
If your baby is jaundiced after birth, but Rh incompatibility isn’t a concern, the baby may be experiencing problems due to ABO incompatibility. ABO incompatibility occurs most frequently when a mother with an O blood type gives birth to a baby who has an A, B, or AB blood type. Because O blood types may produce both A and B antibodies, the mother’s blood can attack the baby’s. However, these symptoms are generally much milder than a Rh incompatibility. ABO incompatibility can be detected via a blood test known as a Coombs test. This test, along with a test to determine the baby’s blood type, is performed after the baby is born. It can indicate why the baby may appear jaundiced or anemic. These tests are usually done for all babies whose mothers have type O blood.
What is an exchange transfusion?
An exchange transfusion is a procedure that removes the antibodies that are attacking RBCs and some of the bilirubin. Small portions of your baby's blood will be removed and replaced with donor blood.
What is bilirubin in babies?
Bilirubin is made when RBCs break down. It is usually removed from the body through bowel movements. A high bilirubin level in your baby can be a sign of erythroblastosis fetalis. Your baby may need more blood tests after he or she is born. Amniocentesis is a procedure done during pregnancy.
What are the three blood types?
A, B, and O are the 3 major blood types. Erythroblastosis fetalis is most common when the mother's blood type is O and the baby's blood type is A or B. The differences in blood type causes your immune system to react by making antibodies. The antibodies can cross over to your baby through the placenta.
What happens to a baby before birth?
Before your baby is born: Fast heart rate. Larger than normal organs, such as the heart, liver, or spleen. Swelling of your baby's body. After your baby is born: Pale skin caused by anemia. Jaundice (yellowing of your baby's skin or the whites of his or her eyes)
Why is my baby's skin yellow?
Swelling of your baby's body. After your baby is born: Pale skin caused by anemia. Jaundice (yellowing of your baby's skin or the whites of his or her eyes) Small red or brown spots, or purple patches on your baby's skin. Swelling of your baby's body.
What is the purpose of blood tests?
Blood tests are used to check your blood type and Rh type, and to look for antibodies. Providers may want to test the blood of the baby's father for ABO and Rh type. Your baby's blood type, RBCs, Rh type, and bilirubin levels may also be checked. Bilirubin is made when RBCs break down. It is usually removed from the body through bowel movements. ...
How to take a fluid sample?
Healthcare providers take a fluid sample by putting a needle through your skin into your uterus (womb). The sample will then be sent to a lab for tests.
Erythroblastosis Fetalis Definition
Erythroblastosis Fetalis is a hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) that occurs when the system of a Rh- mother produces antibodies to an antigen in the blood of a Rh+ fetus. here is how to medically define Erythroblastosis Fetalis:
What Causes Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN)?
Erythroblastosis Fetalis or Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn is caused when the blood types of a mother and baby are incompatible.
Erythroblastosis Fetalis Prevention
Erythroblastosis Fetalis is very preventable. Erythroblastosis Fetalis prevention is easy. Today, nearly all women with Rh-negative blood are identified in early pregnancy through blood tests. If a mother is Rh-negative and has not been sensitized, she is usually given a drug called Rh immunoglobulin, or RhoGAM.
Erythroblastosis Fetalis Diagnosis
Erythroblastosis Fetalis can be diagnosed during pregnancy or after the baby is born. Tests conducted during pregnancy may include:
Erythroblastosis Fetalis Treatment
Erythroblastosis Fetalis can be treated during pregnancy or after the baby is born. Treatment during#N#pregnancy may include:
What are the symptoms of erythroblastosis fetalis?
The major symptoms of erythroblastosis fetalis are briefly discussed below: Jaundice: This occurs due to the deposition of bilirubin (breakdown product of hemoglobin from RBC) in the skin and the whites of the eyes. This imparts a yellowish color to these structures. Hemolytic Anemia: This occurs due to the destruction of RBCs.
What blood groups are associated with erythroblastosis?
These blood groups include Kell, Duffy, Kidd, Lutheran, Diego, Xg, P, Ee, Cc and MNS.
What is the term for a newborn with hemolytic disease?
Erythroblastosis fetalis, also called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), usually occurs in the fetus, but can also occur in the neonate (erythroblastosis neonatorum). It is a type of anemia in which the red blood cells (RBC) of the fetus are destroyed by maternal antibodies in an immune response targeted against the fetus.
What is Rh incompatibility?
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn – An Example of Rh Incompatibility. The Rh system of blood grouping is based on the presence or absence of the Rh factor on the surface of RBC. This factor is an inherited protein antigen that was first discovered in rhesus monkeys, hence called “Rh” based on the first two letters of the word “ rh esus”.
What is the blood group of ABO?
The ABO system is another system of blood grouping discovered by Karl Landsteiner, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the year 1930. This system is based on the presence or absence of the A and B protein antigens on the surface of RBC. When only the A antigen is present, the blood group is A. When only the B antigen is present, the blood group is B. When both A and B antigens are present, the blood group is AB. If both A or B are absent, the blood group is O. ABO incompatibility disease is almost exclusively limited to fetuses with A or B antigens whose mothers have blood group O. Approximately one-third of fetuses have the mother’s antibodies in their circulation, but only a small percentage develop symptoms of ABO incompatibility disease. ABO incompatibility is considered to be less harmful to the fetus than Rh incompatibility.
Who discovered the ABO system?
The ABO system is another system of blood grouping discovered by Karl Landsteiner, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the year 1930. This system is based on the presence or absence of the A and B protein antigens on the surface of RBC.
Can a baby have jaundice after birth?
In another scenario, the baby may develop jaundice after birth, in spite of the fact that there is no Rh incompatibility. Under these circumstances, the symptoms can be attributed to ABO incompatibility. However, the symptoms are much milder than in case of Rh incompatibility.
How to get blood to a baby?
This is done by placing a needle through the mother's uterus and into the abdominal cavity of the fetus or directly into the vein in the umbilical cord. It may be necessary to give a sedative medication to keep the baby from moving.
What is an exchange transfusion?
The exchange transfusion helps increase the red blood cell count and lower the levels of bilirubin. An exchange transfusion is done by alternating giving and withdrawing blood in small amounts through a vein or artery.
Why is anemia dangerous for babies?
This makes the baby anemic. Anemia is dangerous because it limits the ability of the blood to carry oxygen to the baby's organs and tissues. As a result: The baby's body responds to the hemolysis by trying to make more red blood cells very quickly in the bone marrow and the liver and spleen.
Why does bilirubin cause yellowing?
This is called hyperbilirubinemia. Because bilirubin has a pigment or coloring, it causes a yellowing of the baby's skin and tissues. This is called jaundice.
What is severe anemia?
Severe anemia with enlargement of the liver and spleen. When these organs and the bone marrow cannot compensate for the fast destruction of red blood cells, severe anemia results and other organs are affected. Hydrops fetalis. This occurs as the baby's organs are unable to handle the anemia.
What is the color of amniotic fluid?
With amniocentesis, the amniotic fluid may have a yellow coloring and contain bilirubin. Ultrasound of the fetus shows enlarged liver, spleen, or heart and fluid buildup in the fetus's abdomen, around the lungs, or in the scalp. After birth, symptoms may include: A pale coloring may be evident, due to anemia.
How long does it take for a baby to turn yellow?
The baby may not look yellow immediately after birth, but jaundice can develop quickly, usually within 24 to 36 hours.