Treatment for colon cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. Symptoms of colon cancer may include blood in your stool (rectal bleeding), abdominal pain or cramps, change in bowel habits (including diarrhea or constipation), unexplained weight loss, and weakness or fatigue.
Full Answer
What is the treatment for rectal cancer?
Treatment for rectal cancer is based largely on the stage (extent) of the cancer, although other factors can also be important. People with rectal cancers that have not spread to distant sites are usually treated with surgery. Treatment with radiation and chemotherapy (chemo) may also be used before or after surgery.
What should I know about my treatment options for colorectal cancer?
If you’ve been diagnosed with colorectal cancer, your cancer care team will discuss your treatment options with you. It’s important that you think carefully about each of your choices. Weigh the benefits of each treatment option against the possible risks and side effects. Local treatments treat the tumor without affecting the rest of the body.
What does it mean when rectal cancer returns?
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. It may come back near the area of the initial rectal tumor (locally) or in distant organs, like the lungs or liver. If the cancer does recur, it's usually in the first 2 to 3 years after surgery, but it can also recur much later.
How long will I need a colostomy for rectal cancer?
You will need it for the rest of your life. If the rectal cancer has spread into nearby organs, more surgery is needed. The doctor may take out the rectum and nearby organs, like the bladder, prostate, or uterus, if the cancer has spread to those organs. You will need a colostomy after that surgery.

What happens after rectal cancer treatment?
When you wake up after surgery, you will have some pain and will need pain medicines for a few days. For the first couple of days, you may not be able to eat or you may be allowed limited liquids, as the rectum needs some time to recover. Most people are able to eat solid food again in a few days.
How many rounds of chemo is normal for rectal cancer?
You usually have chemotherapy every 2 to 3 weeks depending on what drugs you have. Each 2 to 3 week period is called a cycle. You may have up to 8 cycles of chemotherapy.
How long is neoadjuvant chemotherapy for rectal cancer?
The protocol for neoadjuvant therapy involved 5 Gy of radiotherapy per day for five days which was followed by TME surgery. Patients were regularly followed up every three months for one year and annually thereafter for at least two years. The overall rate of local recurrence was found to be 5.3%.
Is rectal cancer hard to treat?
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Rectal cancer is curable, especially when detected early through screening methods like colonoscopy.
Is rectal cancer worse than colon cancer?
The prognosis of rectal cancer was not worse than that of colon cancer. Local advanced colorectal cancer had a poorer prognosis than local regional lymph node metastasis.
Can cancer spread while on chemo?
While chemotherapy is one of the oldest and most successful ways of treating cancer, it doesn't always work. So, yes, cancer can spread during chemotherapy. Spreading could mean the tumor keeps growing, or that the original tumor shrinks, but cancer metastasizes, forming tumors in other areas of the body.
What is total neoadjuvant therapy in rectal cancer?
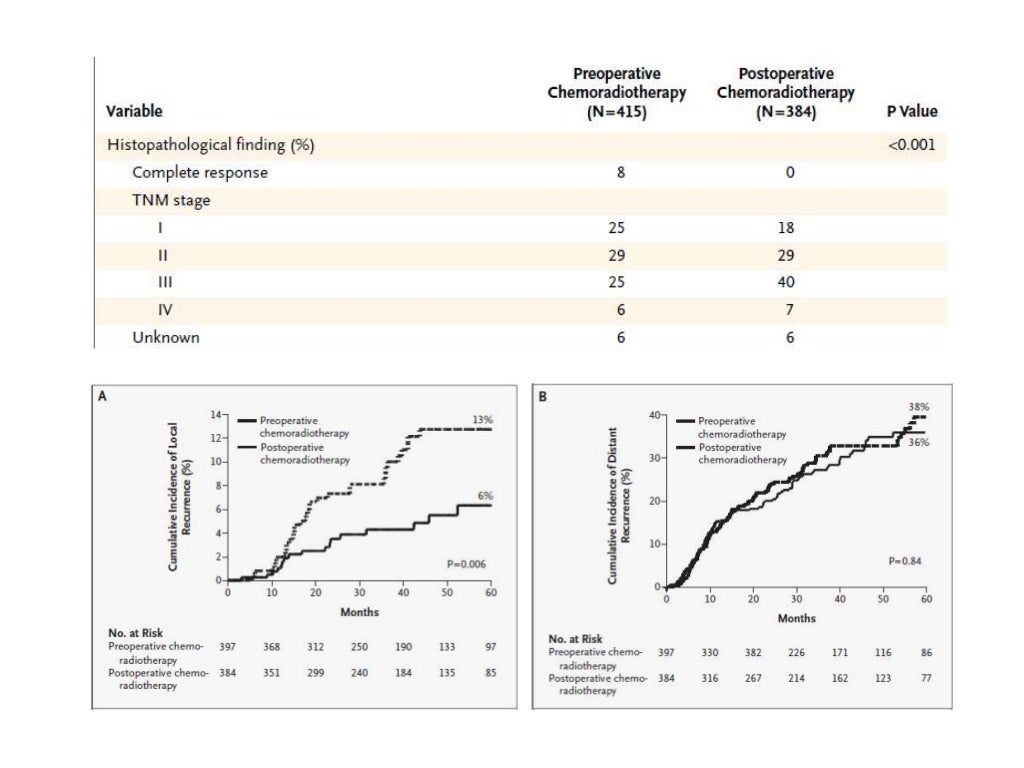
Background: Total neoadjuvant therapy (TNT) is a novel approach for locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC), which attempts to deliver both systemic chemotherapy and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy prior to surgery. However, its efficacy and safety remain controversial in randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Are we already in the era of total neoadjuvant treatment for rectal cancer?
Therefore, in the institutions where adjuvant chemotherapy has been the standard of care to date, the answer to the question of whether or not we are already in the era of total neoadjuvant treatment for rectal cancer is: yes, we are.
What neoadjuvant chemotherapy means?
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment where chemotherapy drugs are administered before surgical extraction of the tumor. Your doctor may recommend neoadjuvant chemotherapy to shrink the breast cancer tumor to give him or her more surgical options for your care.
How long does it take for rectal cancer to metastasize?
But if a tumor develops into a carcinoma with the ability to metastasize, it will progress to metastasis quickly. This transformation occurs within about two years, before another mutation can develop.
How quickly does rectal cancer progress?
In most cases, colon and rectal cancers develop slowly over many years. Most of these cancers begin as a growth of tissue called a polyp in the inner lining of the colon or rectum. Usually polyps bulge into the colon or rectum; some are flat.
Is a 5 cm rectal tumor large?
In stage IIA, the tumor is larger than 2 centimeters but not larger than 5 centimeters. In stage IIB, the tumor is larger than 5 centimeters.
Treating Stage 0 Rectal Cancer
Stage 0 rectal cancers have not grown beyond the inner lining of the rectum. Removing or destroying the cancer is typically all that's needed. You...
Treating Stage I Rectal Cancer
Stage I rectal cancers have grown into deeper layers of the rectal wall but have not spread outside the rectum itself.This stage includes cancers t...
Treating Stage II Rectal Cancer
Many stage II rectal cancers have grown through the wall of the rectum and might extend into nearby tissues. They have not spread to the lymph node...
Treating Stage III Rectal Cancer
Stage III rectal cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.Most people with stage III rectal cancer will be trea...
Treating Stage IV Rectal Cancer
Stage IV rectal cancers have spread to distant organs and tissues such as the liver or lungs. Treatment options for stage IV disease depend to some...
Treating Recurrent Rectal Cancer
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. It may come back near the area of the initial rectal tumor (locally) or in di...
Treating Stage 0 Colon Cancer
Since stage 0 colon cancers have not grown beyond the inner lining of the colon, surgery to take out the cancer is often the only treatment needed....
Treating Stage I Colon Cancer
Stage I colon cancers have grown deeper into the layers of the colon wall, but they have not spread outside the colon wall itself or into the nearb...
Treating Stage II Colon Cancer
Many stage II colon cancers have grown through the wall of the colon, and maybe into nearby tissue, but they have not spread to the lymph nodes.Sur...
Treating Stage III Colon Cancer
Stage III colon cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but they have not yet spread to other parts of the body.Surgery to remove the section of...
Treating Stage IV Colon Cancer
Stage IV colon cancers have spread from the colon to distant organs and tissues. Colon cancer most often spreads to the liver, but it can also spre...
Treating Recurrent Colon Cancer
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. The recurrence may be local (near the area of the initial tumor), or it may b...
How is colorectal cancer treated?
Colorectal cancer can also be treated using drugs, which can be given by mouth or directly into the bloodstream. These are called systemic treatments because they can reach cancer cells throughout almost all the body. Depending on the type of colorectal cancer, different types of drugs might be used, such as: Chemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer.
What is local treatment for colorectal cancer?
Local treatments treat the tumor without affecting the rest of the body. These treatments are more likely to be useful for earlier stage cancers (smaller cancers that haven't spread), but they might also be used in some other situations. Types of local treatments used for colorectal cancer include:
What kind of doctor treats colorectal cancer?
These doctors could include: A gastroenterologist: a doctor who treats disorders of the gastrointestinal (GI or digestive) tract. A surgical oncologist (oncologic surgeon): a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer.
What is the difference between a radiation oncologist and a cancer oncologist?
A colorectal surgeon: a doctor who uses surgery to treat diseases of the colon and rectum. A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy ...
Why is communicating with your cancer team important?
Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life. Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, ...
Why is it important to discuss treatment options with your doctor?
Making treatment decisions. It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. It’s also very important to ask questions if there's anything you’re not sure about.
What is a medical oncologist?
A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, psychologists, nutritionists, social workers, and other health professionals.
What is the cancer in the colon?
The cancer had blocked (obstructed) the colon. The cancer caused a perforation (hole) in the wall of the colon.
What is stage 1 colon cancer?
Stage I colon cancers have grown deeper into the layers of the colon wall, but they have not spread outside the colon wall itself or into the nearby lymph nodes. Stage I includes cancers that were part of a polyp. If the polyp is removed completely during colonoscopy, with no cancer cells at the edges (margins) ...
Where does stage IV colon cancer spread?
Stage IV colon cancers have spread from the colon to distant organs and tissues. Colon cancer most often spreads to the liver, but it can also spread to other places like the lungs, brain, peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity), or to distant lymph nodes. In most cases surgery is unlikely to cure these cancers.
What does it mean when cancer comes back?
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. The recurrence may be local (near the area of the initial tumor), or it may be in distant organs.
Does stage 3 colon cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Stage III colon cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but they have not yet spread to other parts of the body. Surgery to remove the section of the colon with the cancer (partial colectomy) along with nearby lymph nodes, followed by adjuvant chemo is the standard treatment for this stage. For chemo, either the FOLFOX (5-FU, leucovorin, ...
Can colon cancer spread to lymph nodes?
Many stage II colon cancers have grown through the wall of the colon, and maybe into nearby tissue, but they have not spread to the lymph nodes. Surgery to remove the section of the colon containing the cancer (partial colectomy) along with nearby lymph nodes may be the only treatment needed. But your doctor may recommend adjuvant chemotherapy ...
Can you get rid of liver cancer with chemo?
For tumors in the liver, another option may be to destroy them with ablation or embolization. If the cancer has spread too much to try to cure it with surgery, chemo is the main treatment. Surgery might still be needed if the cancer is blocking the colon or is likely to do so.
What is the best treatment for colorectal cancer?
You may need several treatments or a combination that includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy to have the best results.
How long does it take for cancer to come back?
But in about 35% to 40% of people who get surgery with or without chemotherapy, the cancer may come back within 3 to 5 years of treatment. If this happens, it could be in the colon or rectum, or in another part of the body, such as the liver and lungs.
What to ask when you are selected for a trial?
If you’re selected for a trial, ask about risks and side effects so you can decide if you want to move forward. Palliative care. If you have pain, nausea, or other side effects from your colon cancer or treatments for it, ask your doctor about this option.
Does cancer come back if it is in the liver?
Spread to other organs. If the cancer was also in other organs, such as the liver or lungs, it’s more likely to come back. Quality of the surgery. This is most important for rectal cancers, where surgery can be difficult.
Can cancer make you sick?
Stopping treatment. Many cancer treatments are tough to endure. They can make you feel exhausted, nauseated, or sick in other ways. If you’ve dealt with side effects through several treatments but haven’t improved, you may decide that it isn’t worth trying other treatments that show even less promise.
What is the procedure to remove rectal cancer?
If the rectal cancer is more advanced and close to the anus, surgery will be done to take out the cancer and make an opening on your belly to get rid of body waste (poop). This is called a colostomy. You will need it for the rest of your life. If the rectal cancer has spread into nearby organs, more surgery is needed.
What is the best treatment for colon cancer?
If you have side effects, talk to your cancer care team so they can help. Targeted therapy. Targeted therapy drugs may be used for certain types of colon or rectum cancer. These drugs affect mainly cancer cells and not normal cells in the body.
What test is used to check for cancer?
If signs are pointing to cancer, more tests will be done. Here are some of the tests you may need: Colonoscopy : A colonoscopy is a test where a thin tube with a light on the end (called a colonoscope) is put through the anus, into the rectum and colon to look closely at the inside.
What organs do you need to have a colostomy for?
The doctor may take out the rectum and nearby organs, like the bladder, prostate, or uterus, if the cancer has spread to those organs. You will need a colostomy after that surgery. If the bladder is removed, an opening to collect urine or pee (called a urostomy) is needed, too.
What is the stage of cancer?
It also tells if the cancer has spread to nearby organs or to organs farther away. Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread.
How do you know if you have cancer?
This is the best way to know if you have cancer. Gene and protein tests: The cancer cells in the biopsy tissue might be tested for genes or proteins such as KRAS, BRAF, MMR and MSI. Knowing which genes or proteins your cancer has can help the doctor decide if treatments like targeted therapy or immunotherapy might help.
What is clinical research?
Clinical trials are research studies that test new drugs or other treatments in people. They compare standard treatments with others that may be better. Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. They are the best way for doctors to find better ways to treat cancer. If your doctor can find one that’s studying the kind of cancer you have, it’s up to you if you want to take part. And if you do sign up for a clinical trial, you can always stop at any time.
What to do if you have advanced colorectal cancer?
What You Can Do. Many people with advanced colorectal cancer have common concerns. Here are some tips that may help: Stay ahead of pain. Not everyone will hurt from the disease or its treatments. But if you do, you don’t have to just grin and bear it. Talk to your doctor if you're feeling it.
What is the best treatment for colon cancer?
But once the disease spreads, it’s often not an option. For advanced colorectal cancer, the best treatments are ones that travel through your bloodstream, such as chemotherapy .
How does cancer help you live longer?
It may even help you live longer. Stay connected. Cancer and your treatment can feel lonely sometimes. You may feel like no one really understands what you’re going through. It helps to reach out to others, whether it’s your friends, a counselor, or a support group of other people with colorectal cancer.
How do you feel when you have a tumor?
The ones you have depend on the size of the tumor and where it has spread. Cancer in your liver may make you sick to your stomach and make your skin yellow or itchy. Tumors in your lungs can make it harder to breathe.
How to shrink a tumor?
You may need a new drug or treatment to shrink your tumor. It may also help to add a pain specialist to your cancer care team. Other things can help, too, like massage and hot and cold packs. Stay active. When you get enough rest and exercise, you can boost your mood and feel less tired. It may even help you live longer.
Is there a cure for colorectal cancer?
Although it’s outside your colon or rectum, it's still colorectal cancer, and doctors treat it with drugs for that disease. For most people, there's no cure. But treatments can help you feel better and live longer. Scientists are also researching and testing many new therapies.
Can you use your body's immune system to destroy cancer cells?
Some use your body's own immune system to find and destroy cancer cells. This may be an option if other drugs don't help or stop working. Your doctor can tell you more about new cancer treatments that may be right for you.
