Medication
What is immunotherapy?
- Monoclonal antibody therapy. This therapy helps your body produce antibodies that typically fight infection.
- CAR T-cell therapy. This is a newer type of therapy that uses your body’s own T cells, a type of white blood cell, to help fight leukemia.
- Donor lymphocyte infusion. ...
- Interferon. ...
Procedures
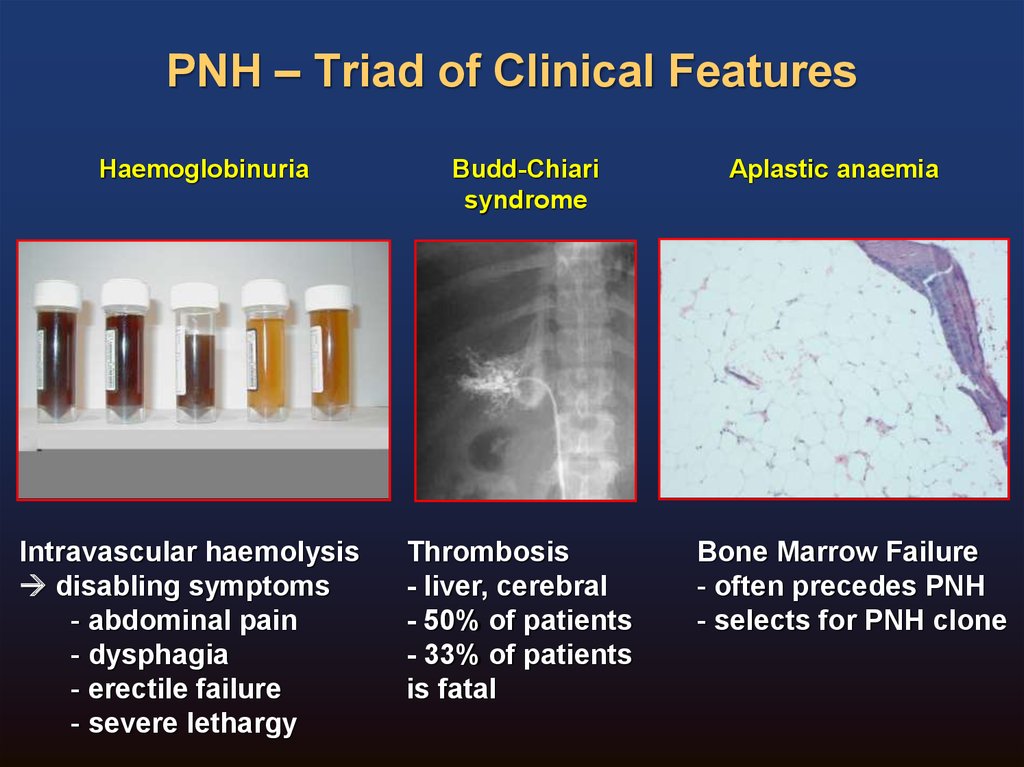
Leukemia treatment choices depend on the type of leukemia, certain features of the leukemia cells, the extent of the disease, and prior history of treatment, as well as the age and health of the patient. Most people with leukemia are treated with chemotherapy. Some also may have radiation therapy and/or bone marrow transplantation.
Therapy
Leukemia Symptoms
- swollen lymph nodes (neck, underarm, groin or stomach)
- enlarged spleen or liver
- frequent infections
- fever
- pale skin tone
- night sweats
- fatigue (feeling very tired)
- unplanned weight loss (10% of body weight over 6 months)
- bone or joint pain and/or tenderness
- easy bruising or bleeding
Nutrition
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects your blood cells and bone marrow. As with other types of cancer, there’s currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience ...
What are the different ways to cure leukemia?
What would be the most likely treatment for leukemia?
How to cure leukemia naturally?
Is there a known treatment and cure for leukemia?

Can leukemia be treated successfully?
As with other types of cancer, there's currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience remission, a state after diagnosis and treatment in which the cancer is no longer detected in the body. However, the cancer may recur due to cells that remain in your body.
How long is treatment for leukemia?
The total treatment usually takes about 2 years, with the maintenance phase taking up most of this time. Treatment may be more or less intense, depending on the subtype of ALL and other prognostic factors.
What is the new treatment for leukemia?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved two new treatments for some adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML): enasidenib (Idhifa®), a drug that targets aberrant forms of the IDH2 protein; and liposomal cytarabine-daunorubicin CPX-351 (Vyxeos™), a two-drug chemotherapy combination encapsulated ...
What is the main cause of leukemia?
Some scientists believe that leukemia results from an as-of-yet undetermined combination of genetic and environmental factors that can lead to mutations in the cells that make up the bone marrow. These mutations, known as leukemic changes, cause the cells to grow and divide very rapidly.
Can leukemia lead to death?
Leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma are expected to cause the deaths of an estimated 57,750 people in the US in 2021. These diseases are expected to account for 9.5 percent of the deaths from cancer in 2021, based on the estimated total of 608,570 cancer deaths.
What is the best medicine for leukemia?
A medicine called imatinib is now the main treatment for CML. It's usually given soon after a diagnosis is made to slow the progression of the cancer and stop it reaching an advanced phase. Imatinib works by reducing the production of abnormal white blood cells. It's taken as a tablet once a day.
What were your first symptoms of leukemia?
Common leukemia signs and symptoms include:Fever or chills.Persistent fatigue, weakness.Frequent or severe infections.Losing weight without trying.Swollen lymph nodes, enlarged liver or spleen.Easy bleeding or bruising.Recurrent nosebleeds.Tiny red spots in your skin (petechiae)More items...
What are the 4 main types of leukemia?
There are 4 main types of leukemia, based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic: Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML) Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML) Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)
What exams would be Performed?
As mentioned, your doctor will be requiring to perform series of exams to come up with the best treatment plan. Some of these exams may be anything from the following:
Treatment of Leukemia
Keep in mind that the treatment procedure for leukemia would be dictated by a number of different factors. Your doctor will be determining your options for leukemia treatment based on overall health and age, type of leukemia that you have and whether it began spreading in several parts of your body.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
Chemotherapy (drug treatment to destroy leukemia cells) is the mainstay of leukemia treatment, and may incorporate multiple types of drugs. Radiation and surgery are contemplated only for cases in which leukemia cells have collected in definitive areas.
How many drugs are given for leukemia?
Depending on the type of leukemia, you may receive a single drug or a combination of two or more drugs. The medications may be prescribed as pills, or as fluids administered through a needle or tube inserted into a vein; through a tube inserted in the chest; or through injection into the cerebrospinal fluid.
How does radiation kill leukemia?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill leukemia cells by damaging the genetic material they contain . This treatment can be used adjunctively to chemotherapy to control disease or eradicate local areas of disease. Some patients receive targeted radiation from a large machine aimed at the spleen, brain or other parts of the body where leukemia cells have collected. This type of therapy takes place five days a week for several weeks. Others may receive radiation directed to the whole body. These sessions are given once or twice a day for a few days, usually before a stem cell transplant.
What is the drug used for minimal residual leukemia?
Dose-intensive, curative chemotherapy for minimal residual leukemia. Pioneered clinical trials of the drug tipifarnib, known by its trade name Zarnestra, which blocks an enzyme called farnesyltransferase, which modifies certain cellular proteins so that they can attach to cellular membranes or other structures.
How long does radiation therapy last?
This type of therapy takes place five days a week for several weeks. Others may receive radiation directed to the whole body.
What organ is removed to help fight infection?
In some cases of CLL, for example, doctors may recommend surgery to remove the spleen, an organ located in the abdomen behind the ribs that removes and destroys old red blood cells and helps fight infection. The procedure, called a splenectomy, is helpful if the spleen is destroying red blood cells and platelets.
Where are clinical trials being conducted for leukemia?
Doctors at some medical centers including the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center are conducting clinical trials to test novel vaccines for leukemia.
What is HPSCT?
A bone marrow transplant, or HPSCT, is the process of replacing blood cells in the body. To do this, healthy blood stem cells are injected into the body. These stem cells travel to the bone marrow where they replace the current stem cells called hematopoietic stem cells.
How is it done?
Receiving stem cells is similar to receiving a blood transfusion. A needle may be inserted into a large vein in your arm, or you may have a central venous catheter placed in a blood vessel in the right side of your chest and the stems cells will flow into your heart.
What are the side effects and risks?
Complications may occur, but not everyone will experience them. Complications may include:
What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy uses strong drugs or chemicals, sometimes in combination, to damage or kill cancer cells. This treatment is systemic, which means chemotherapy drugs attack cancer cells, which tend to be fast-growing. However, these drugs can also affect healthy cells.
How is it given?
Chemotherapy can be given orally as a pill, capsule, or liquid, but most of the time, the drugs are given intravenously, through a catheter or central line. This is a port-like device attached to one of your veins that allows you to receive intravenous drugs.
Which types of leukemia may be treated with this?
All four main types of leukemia may be treated with chemotherapy. In ALL, AML, and CLL, it’s the first and main treatment. For CML, targeted therapies are typically used first, followed by chemotherapy.
What are the side effects and risks?
As with any medical treatment, there are side effects with chemotherapy depending on the drug used, dosage, and how long you take it.
What is the treatment for acute myeloid leukemia?
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) A typical chemotherapy regimen for most types of AML includes: Ara-C (Cytarabine) An anthracycline, like Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) or Daunorubicin. If anthracyclines cannot be tolerated, Fludara (Fludarabine) or Etoposide may be used. Sometimes, Cladribine.
How does chemotherapy help with leukemia?
Chemotherapy works by directly killing or damaging rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells, in your body.
What is the goal of consolidation therapy?
The goal of consolidation therapy, also known as post-remission therapy, is to destroy any remaining cancer cells and make sure leukemia will not relapse. Consolidation may include chemotherapy or a stem cell transplant.
What is a BTK inhibitor?
BTK inhibitors block the activity of a certain type of tyrosine kinase that cancer cells need to grow and stay alive. BTK inhibitors are used to treat CLL/SLL and some types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), a type of blood cancer closely related to leukemia. The two BTK inhibitors currently used are Imbruvica (Ibrutinib) and Calquence (Acalabrutinib).
What are the different types of leukemia?
The four main types of leukemia are: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML, also known as chronic myelogenous leukemia) Each of these types has many subtypes, and some are also classified by stage.
How does chemotherapy work?
Most chemotherapy drugs work by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from growing or causing them to die. Chemotherapy drugs are often combined into regimens. Here are a few of the most common chemotherapy regimens used in the four major types of leukemia.
What are the phases of leukemia?
These phases of leukemia treatment may include induction therapy, consolidation therapy, and maintenance therapy.
What is the best treatment for CML?
Targeted therapy drugs are the main treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), but some patients might also need other treatments. Targeted Therapies for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Interferon Therapy for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Chemotherapy for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Radiation Therapy for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Why is communicating with your cancer team important?
Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life. Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, ...
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What kind of doctor treats blood disorders?
These doctors could include: A hematologist: a doctor who treats blood disorders. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, nutrition specialists, social workers, and other health professionals.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
Traditionally, leukemia is primarily treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Stem cell transplants may also be used in conjunction with chemotherapy, particularly in children. Immunotherapy and targeted therapies are newer treatments for certain types of leukemia.
How does immunotherapy help with leukemia?
Depending on the type of immunotherapy, treatment may help: boost your T-cells (T-cell transfer therapy) preserve the integrity of immune cells by helping prevent them from responding too strongly to leukemia cells ( immune checkpoint inhibitors)
What are the treatments for cancer?
For this reason, standard treatments tend to include: chemotherapy (sometimes with stem cell transplant) radiation therapy. Due to the risk of lifelong side effects, researchers are looking into other options, such as targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
How does targeted therapy work?
As the name suggests, this treatment approach works by targeting genes or proteins that may be helping cancerous cells grow.
What is car T cell therapy?
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a newer type of immunotherapy for childhood ALL. Your body already has T-cells, but when you have cancer, they may not work as they should. With CAR T-cell therapy, some T-cells are removed and genetically modified with receptors to fight cancer more effectively.
What is the survival rate for leukemia?
The overall 5-year survival rate for leukemia is estimated at 63.7 percent. Trusted Source. . As new, earlier treatments have emerged, the death rate for this type of cancer is also declining. In 2020, leukemia made up only 3.8 percent.
Is CLL faster than HCL?
Both CLL and HCL progress slower than any other types of leukemia. To prevent side effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, a doctor may try targeted therapies first. Another option may include “watchful waiting” to see how initial treatments work before attempting more aggressive treatments.
.jpg/300px-17_lores.jpg(felineleukemia).jpg)
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment