Full Answer
What is secondary settling in wastewater treatment?
Oct 28, 2021 · So the question is what substances remain in wastewater after effective secondary treatment. Okay, as we know, secondary treatment and removes soluble organic matter that escapes primary treatment with the help of micro organisms. Secondary treatment of wastewater lowers the P. O. D. By about 90%. Beauty is a mayor of is a measure of amount of …
What are the types of solids present in sewage?
ltem 17 Part A What substances remain in wastewater after effective secondary treatment? chlorides nitrates sulfates V phosphates O heavy metals organic molecules Submit My Answers Give Up Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining
What is the role of organic solids in biological wastewater treatment?
Feb 08, 2019 · Which of the following demonstrate the environmental advantages of secondary and tertiary treatment of wastewater? a) secondary treatment lowers the bod of wastewater making is safe to return to the environment. b) tertiary treatment removes excess nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus which can cause algae growth.
What are the available options in the biological treatment processes of sewage?
Feb 08, 2019 · Derek works in a municipal wastewater treatment plant where he oversees the process of biological treatment. which stage of municipal wastewater treatment does derek oversee? a. preliminary treatment b. primary treatment c. secondary treatment d. …

Secondary Treatment Definition
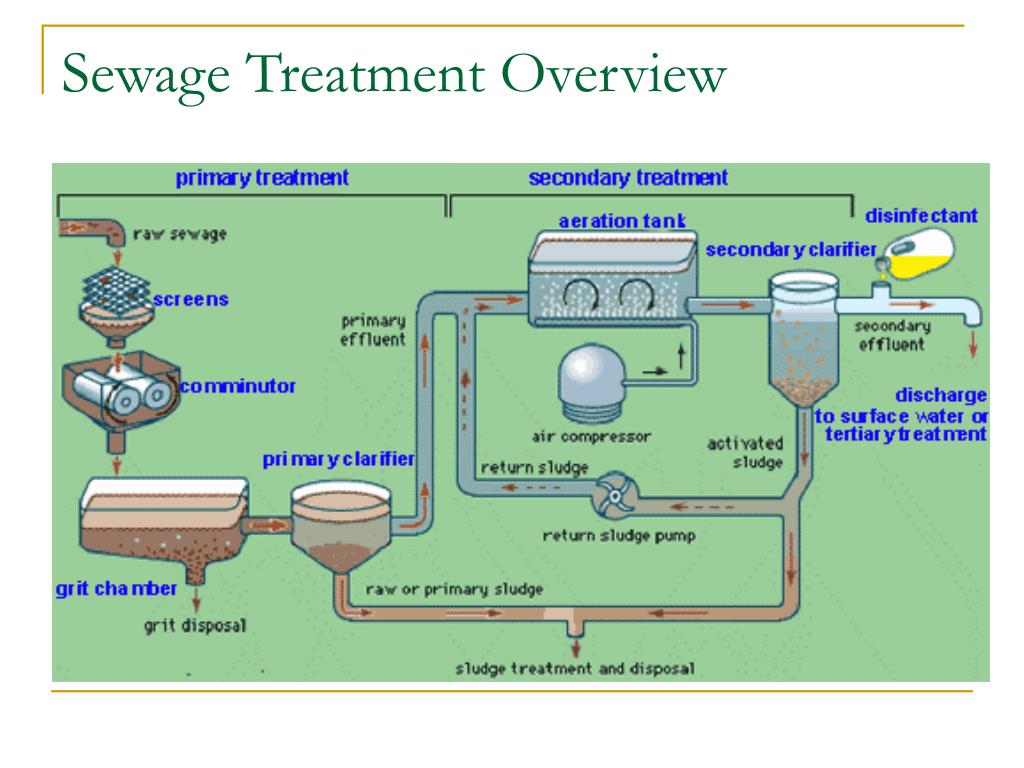
Secondary treatment of wastewater is a process that follows the primary treatment of sewage.
Objectives of Secondary Treatment
The objectives of secondary treatment are to remove the remaining suspended solids, BOD, and COD from the wastewater. It is done to reduce the primary clarifier load and improve the quality of the effluent discharged from the treatment plant.
What are the Stages of Wastewater Treatment?
The stages of wastewater treatment are collection, pre-treatment, primary treatment, secondary treatment, tertiary treatment, disposal, and reuse.
What is The Secondary Treatment of Wastewater?
This article will tell you about the second stage in the wastewater treatment process.
How Does Secondary Treatment Work
Secondary treatment is treating wastewater in a municipal water system that removes most contaminants from wastewater by reducing their levels to acceptably low levels.
What are The Alternative Types of Secondary Biological Processes?
There are a few different types of alternative secondary biological processes, and these include aerobic and anaerobic processes.
Conclusion
The secondary wastewater treatment process is more complicated than the primary wastewater treatment process. It is necessary to remove the remaining pollutants from the wastewater. The method includes various other activities that can remove the remaining impurities.
What are the two types of solids in sewage?
SOLIDS IN SEWAGE. The solids present in the sewage are of two types viz., Organic solids, and. Inorganic solids. Organic solids are the substances derived from living things like produces from plant and animal. Examples of organic solids are carbohydrate, protein, and fat.
What is secondary treatment?
The secondary treatment is designed to remove soluble organics from the wastewater. Secondary treatment consists of a biological process and secondary settling is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage such as are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent.
What is activated sludge?
The activated sludge process (ASP) is an aerobic biological wastewater treatment process that uses microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, to speed up decomposition of organic matter requiring oxygen for treatment.
What is the only thing to be provided for the respiration of aerobic organisms?
The organic solids present in the wastewater serve as food for the aerobic microorganisms. The only thing to be provided is the DO , which is essential for the respiration of the aerobic organisms.
What are the end products of anaerobic and aerobic processes?
Under aerobic conditions, if completely oxidized, organic matter is transformed into non-hazardous products. But an anaerobic process can produce methane (CH 4 ), which is explosive, and ammonia (NH 3) and hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S), which are toxic.
What are the two types of biological processes?
TYPES OF BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES. There are two types of biological treatment process; aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic process means that oxygen is present for the microbes for respiration. Anaerobic process means that the process proceeds in the absence of DO.
What do aerobic bacteria use for respiration?
Aerobic bacteria use dissolved oxygen (DO) from the water bodies for their respiration. They oxidize organic matter under aerobic conditions. The end products of the decomposition are water, CO 2 and Cell tissues. Anaerobic bacteria use oxygen derived from chemical substances for their respiration.
