What STDs stay in your body even after treatment? However, there are still four incurable STDs: hepatitis Inflammatory condition of the liver.Hepatitis
Chlamydia Infection
A common sexually transmitted infection caused by bacteria.
- hepatitis B.
- herpes.
- HIV.
- HPV.
Which STDs stay in your system permanently?
Jan 14, 2019 · Bacterial STDs are curable, while viral STDs aren’t. Common bacterial STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Alternatively, common viral STDs are herpes, HIV, HPV, and hepatitis. Herpes, HIV, and chronic cases of hepatitis will remain in your system permanently after contraction. However, HPV usually won’t.
Do STDs come back after treatment?
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and trichomoniasis can all be treated and cured reasonably easily with antibiotics. However, having your STD treated is not a guarantee that it will never come back. One or more of these can be in play in cases where someone gets treatment for an STD, only to realize they have it again.
Can I get rid of my STD?
Jul 26, 2018 · The eight most common STDs are: syphilis hepatitis B gonorrhea herpes simplex virus chlamydia HIV trichomoniasis human papillomavirus (HPV)
Do you know which STDs are curable?
Nov 25, 2021 · In fact, many people become infected with STDs over and over again. This is because they have unprotected sex with partners who have untreated STDs. What STDs stay in your body even after treatment? However, there are still four incurable STDs: hepatitis B. herpes. HIV. HPV. Can chlamydia come back on it’s own after being treated? Nope!

Which STDs stays in the body for life?
Can STD stay after treatment?
Can STD stay in your body for years?
What STDs that Cannot be cured?
How long can chlamydia stay in your body?
How do you know if chlamydia is gone after treatment?
What happens if you have gonorrhea for too long?
How long can gonorrhea stay dormant?
Can STI stay dormant?
What are the 4 new STDs?
- Neisseria meningitidis. N. ...
- Mycoplasma genitalium. M. ...
- Shigella flexneri. Shigellosis (or Shigella dysentery) is passed on by direct or indirect contact with human faeces. ...
- Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
Does syphilis stay in your body forever?
Which is worse gonorrhea or chlamydia?
Can STDs be cured?
However, there are still four incurable STDs: hepatitis B. herpes. HIV. HPV. Even though these infections can’t be cured, they can be managed with treatment and medication.
Do you show symptoms of STDs?
With most STDs, you may not show any signs or symptoms. For this reason, it’s very important to get tested for STDs on a regular basis for your own safety, the safety of your partner (s), and general public health. The best treatment for STDs will always be prevention.
How common are STDs?
STDs are extremely common. In fact, 20 million new cases are reported in the United States each year, with 50 percent of these cases generally affecting people between the ages of 15 and 24. The good news is that most STDs are curable and even those without a cure can be effectively managed or minimized with treatment.
How many STDs are incurable?
Incurable STDs. Most STDs are curable through the use of antibiotics or antiviral medications. However, there are still four incurable STDs: hepatitis B. herpes. HIV. HPV. Even though these infections can’t be cured, they can be managed with treatment and medication.
What to do if you have hepatitis B?
If you have hepatitis B, your best option is to speak to your doctor about checking your liver and your medication options to lessen symptoms. Immune system modulators and antiviral medications can help slow the virus’s damage to your liver.
How does herpes spread?
are estimated to have herpes worldwide. Herpes is spread through skin-to-skin contact. Many people with herpes may not know they have it because they show no symptoms. However, when there are symptoms, they come in the form of painful sores around the genitals or anus.
What is the treatment for HIV?
The main treatment for HIV is called antiretroviral therapy. These drugs reduce the amount of HIV in the blood to undetectable levels.
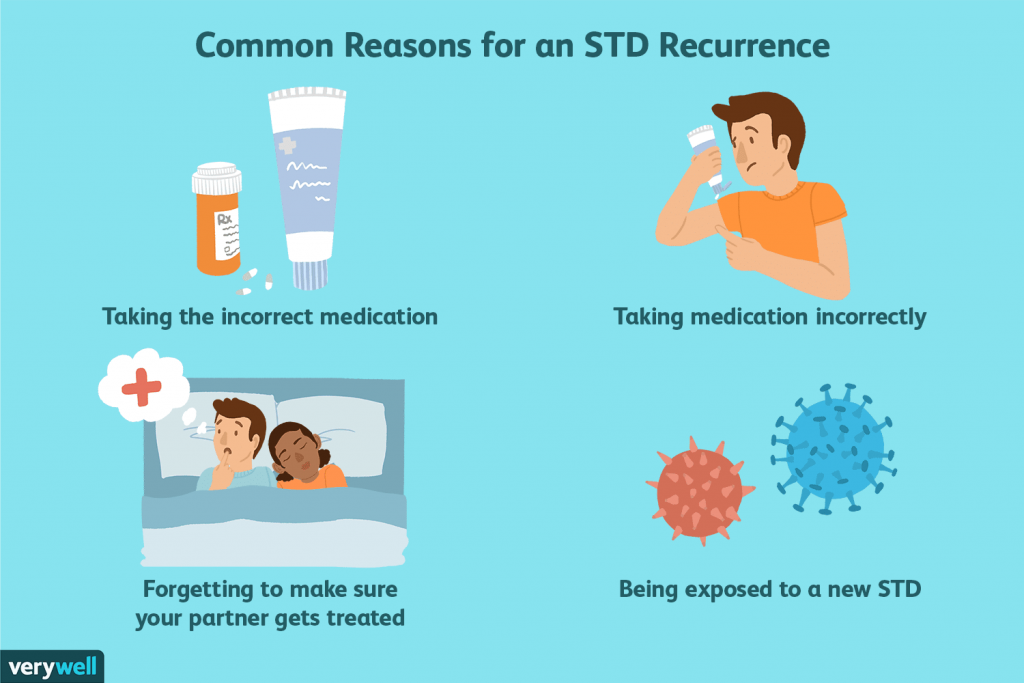
Can you get a STD back?
While it's important that you find treatment for your STD, having your STD treated is not a guarantee that it will never come back. You have to use your medication as directed, and you also have to be careful about prevention so you won't get re-infected. Verywell / Cindy Chung.
How to prevent STDs?
Fortunately, most of the STDs that are curable with antibiotics are also preventable by practicing safe sex. Using condoms, dental dams, and other barriers to make your sex life safer is an effective way to prevent bacterial STDs. However, it's important to use them consistently—for vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse.
Can gonorrhea come back in 2021?
Updated on January 18, 2021. Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and trichomoniasis can all be treated, and often cured, with antibiotics. While it's important that you find treatment for your STD, having your STD treated is not a guarantee that it will never come back. You have to use your medication as directed, and you also have to be careful about ...
Can STDs be caused by the same pathogens?
Not all STDs are caused by the same pathogens (infectious organisms). Different illnesses require different treatments. That's why it's so important for your healthcare provider to correctly identify what's causing your infection. That's also why you can't just take any random antibiotic and hope it's going to work.
Can you finish antibiotics before STD?
That's true even if you feel better before you're done. Failing to finish your antibiotic course as directed might keep your STD from being cured and it might also make it far more difficult to treat your STD next time due to antibiotic resistance. The Role of Antibiotics in Treating Infections.
Can antibiotics keep a STD from being cured?
Failing to finish your antibiotic course as directed might keep your STD from being cured and it might also make it far more difficult to treat your STD next time due to antibiotic resistance. The Role of Antibiotics in Treating Infections.
What to do if you have a STD?
If you've been treated for an STD and don't want to get another one, the best thing that you can do is change your behaviors to decrease your risk. That means consistently practicing safe sex and always talking to new partners about STD risk before having sex.
Can chlamydia return after treatment?
But new research shows that oftentimes chlamydia can return with a vengeance, even after treatment.
Can chlamydia return after antibiotics?
Chlamydia Can Return, Even After Antibiotic Treatment, Because It Survives In The Stomach. It's possible to be re-infected with chlamydia even after antibiotic treatment. Image courtesy of Shutterstock. Chlamydia, the most common sexually transmitted infection and often a symptom-less one, can usually be treated with antibiotics effectively.
Can chlamydia re-infect a person?
Research out of the Arkansas Children’s Research Institute has found that if chlamydia survives in the person’s stomach, even after it has been cleared away from the genitals by antibiotics, it can re-infect the person.
What is the most common sex-transmitted infection?
Chlamydia, which is already the most commonly reported sexually transmitted infection in the U.S. and Europe, is also the most common to be re-infected. About 26 percent of infected people end up getting the disease again, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Why is chlamydia so good at hiding?
Because chlamydia can be dormant for years without being symptomatic, infected persons may easily transmit the disease to sexual partners without knowing. Its ability to lie dormant may also be a reason why it’s so good at hiding in the digestive system despite its eradication elsewhere.
What is the most recognized biological property of chlamydial species?
The authors write in their introduction that the most recognized biological property of chlamydial species is “their ability to remain associated with their host over long periods of time, often in an apparent … latent state and in the presence of an immune response.”.
