Naturally, they face special treatment for their criminal actions compared to their adult counterparts. Even if the juvenile in question committed the same crime that an adult did, the justice system treats them vastly different than adults.
Full Answer
Should juveniles be treated differently than adults?
Effective adolescent treatment approaches include multisystemic therapy, multidimensional family therapy, and functional family therapy. These interventions show promise in strengthening families and decreasing juvenile substance abuse and delinquent behavior.
What does juvenile justice court do for minors?
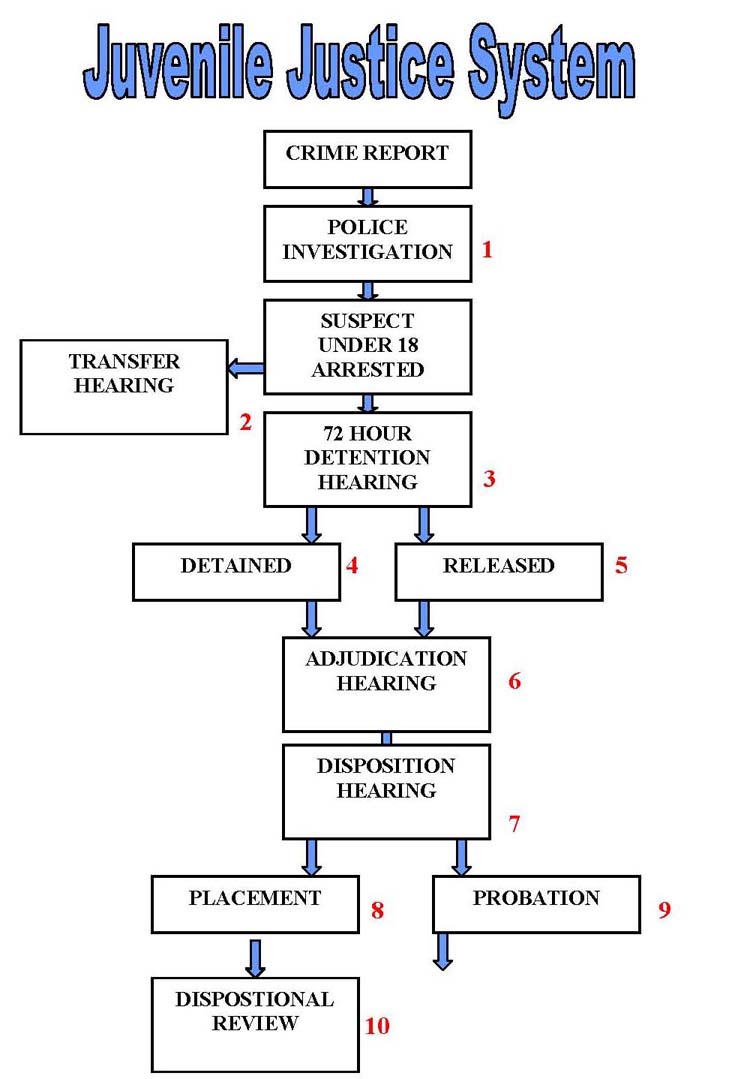
Oct 15, 2020 · For a juvenile crime, the juvenile receives a “disposition,” which is the final decision of how the court will handle the case. Jury Trial: While adults have the right to trial by jury, juveniles do not. Instead, a judge hears their case then …
What is the most effective treatment for juvenile substance abusers?
the law allows a juvenile court to hold a transfer hearing to place a juvenile matter on the regular criminal docket if the child is at least age 14 and charged with (1) a class a felony other than murder or (2) a serious juvenile offense designated as a class b or c felony, if the child has been previously adjudicated delinquent as a result of a …
Are juvenile drug courts effective?
Accession Number: 029939 "As an alternative to traditional juvenile courts, juvenile drug courts attempt to provide substance abuse treatment, sanctions, and incentives to rehabilitate nonviolent drug-involved youth, empower families to support them in …

What is the treatment of juveniles?
Effective adolescent treatment approaches include multisystemic therapy, multidimensional family therapy, and functional family therapy. These interventions show promise in strengthening families and decreasing juvenile substance abuse and delinquent behavior.Apr 18, 2014
How are juveniles treated differently in the courts than adults?
As you can see, the difference in terminology between adult and juvenile court indicates that juvenile offenders are often treated more leniently. This is because there is a strong inclination to rehabilitate juveniles, instead of merely to punish them. Adults are punished for their crimes.Jan 15, 2020
What type of punishments are given to juveniles?
The most common penalties for minors convicted of a juvenile crime include informal probation, court ordered treatment or counseling, placement in foster care, enrollment in a juvenile offender school, or commitment to a state juvenile detention center.Jun 3, 2021
Why is the treatment of juveniles individualized?
Research suggests that appropriately diverting a juvenile out of the court system is more effective at reducing their likelihood of re-offending than criminal prosecution. Using individually designed and community-based programs to reform troubled youth achieves better outcomes.Nov 7, 2016
Should juveniles be treated as adults in the criminal justice system?
A summary of six studies found that there was greater overall recidivism for juveniles prosecuted in adult court than juveniles whose crimes “matched” in juvenile court. Id. Juveniles in adult court also recidivated sooner and more frequently.Oct 3, 2016
Why should we treat juveniles as adults?
Juveniles should be tried as adults because it helps to show them that there are consequences for their actions. Today's court systems are outdated and minors commit crimes because they know they will get off easy.Mar 6, 2020
What is the most commonly used sentence for juvenile offenders?
Incarceration in a public facility is the most common formal sentence for juvenile offenders. Juveniles do not have the protection of the Miranda decision: they do not have the right to remain silent during police interrogation. Acts such as truancy and running away from home are considered status offenses.
What is the most common sentence given to juveniles?
ProbationProbation is perhaps the most common penalty in the juvenile justice system. Judges have considerable discretion to set the terms of probation. These may be specific to the circumstances of the case.Oct 18, 2021
What are the three main disposition options available to the juvenile court judge?
There are several disposition options available to a juvenile court judge, including sending the minor home on probation, custody in a probation camp, placement in a foster home or commitment to the Division of Juvenile Justice.
What is therapeutic intervention for juveniles?
Given the prevalence of sexual offending by juveniles, and the potential links between sexually abusive behavior during adolescence or childhood and sexual offending later in life, therapeutic interventions for juveniles have become a staple of sex offender management practice in jurisdictions across the country.
Which study found that incarcerated juveniles who received intensive treatment in a self-contained housing unit of
Waite and colleagues (2005) found that incarcerated juveniles who received intensive treatment in a self-contained housing unit of the correctional facility had better recidivism outcomes than incarcerated juveniles who received less intensive treatment and who remained in the facility's general population.
How many treated subjects recidivated for every 100 untreated subjects?
Walker and his colleagues reported a treatment effect size of 0.37, meaning that only 37 treated study subjects recidivated for every 100 untreated study subjects who recidivated.
What is the most reliable evidence for a criminology intervention?
In the field of criminology, there is general agreement that certain types of single studies–namely, well-designed and executed experiments, or randomized controlled trials (RCTs) –provide the most trustworthy evidence about an intervention's effectiveness (Sherman et al., 1998; MacKenzie, 2006; Farrington & Welsh, 2007). 1
How much does sex offender treatment reduce recidivism?
The researchers found that sex offender treatment programs for juveniles reduced recidivism, on average, by 9.7 percent. In addition, the treatment programs produced a net return on investment of more than $23,000 per program participant, or about $1.70 in benefits per participant for every $1 spent.
What is crime control based on?
While there is growing interest in crime control strategies that are based on scientific evidence, determining what works is not an easy task. It is not uncommon for studies of the same phenomena to produce ambiguous or even conflicting results, and there are many examples of empirical evidence misleading crime control policy and practice because shortcomings in the quality of the research were overlooked (see, for example, Sherman, 2003, and McCord, 2003). The importance of basing conclusions about what works on highly trustworthy and credible evidence cannot be overstated, and both the quality and consistency of the research evidence has to be considered.
Is a juvenile more impulsive than an adult?
Juveniles are generally more impulsive and less aware of the consequences of their behavior than adults. And while a few sexually abusive behaviors in youth are compulsive and reflective of a recurrent pattern of social deviance, others may be more isolated and not indicative of a long-term behavior pattern.
What is a juvenile in court?
Typically, a juvenile is a defendant under the age of 18, who the court system does not consider an adult yet. They usually go home under supervision until their court date when they have been charged with a crime. For adults, they typically spend this time in a holding facility.
What is a juvenile case petition?
A petition is the charging document the state files in juvenile court. Adjudication: When a court tries an adult offender for a crime and finds them guilty, they convict the offender of that crime.
How does juvenile criminal process differ from adult criminal process?
From the terms used to the treatment offenders face, the juvenile criminal process differs from that for adults. Typically, the penalties juveniles face are significantly less severe than the punishment for adults. Because the juvenile criminal process is so different, it pays to have the aid of an experienced juvenile crime attorney on your side.
What is a juvenile offenders sentence?
Youthful offenders are typically teens between 15-17 who committed serious crimes. If convicted, they will begin their sentence in the juvenile system. If they turn 18 while serving their sentence, they might transfer to an adult holding facility to complete their sentence.
What crimes do juveniles commit?
Each case will vary depending on a number of factors. However, these are some of the most frequent offenses juveniles frequently make: Larceny (theft) Burglary.
What is the final decision of how the court will handle the case?
For a juvenile crime, the juvenile receives a “disposition,” which is the final decision of how the court will handle the case. Jury Trial: While adults have the right to trial by jury, juveniles do not. Instead, a judge hears their case then decides if they are guilty of a delinquent act.
How does juvenile justice differ from adult justice?
From who hears your case to the leniency of the punishment, juvenile defendants face a much different procedure than adults. The criminal process is complicated as is, but when it involves a juvenile, it becomes even more complicated.
What are the felony classes in the United States?
There are currently seven statutory class A felonies: all forms of murder, including capital, arson, and felony; first degree kidnapping;
Can a juvenile be tried as an adult?
JUVENILES TRIED AS ADULTS. Under the law, a juvenile's age at the time he commits an offense, the specific nature of the offense, and his prior record determine if he can be tried as an adult. Juveniles under age 14 are not treated as adult offenders regardless of the crime or the circumstances surrounding it.
Can a juvenile be sentenced to probation?
A youthful offender's sentenced may range from probation to commitment to a state institution for the maximum term authorized by law. JUVENILE DELINQUENT. A child in Juvenile Court is never convicted of a crime but can be adjudged a delinquent for the commission of a delinquent act.
What is a juvenile drug court?
Juvenile Drug Courts: A Process, Outcome, and Impact Evaluation. "As an alternative to traditional juvenile courts, juvenile drug courts attempt to provide substance abuse treatment, sanctions, and incentives to rehabilitate nonviolent drug-involved youth, empower families to support them in this process, and prevent recidivism.
Do juvenile drug courts have recidivism?
The results from this multi-site study does not support the efficacy of juvenile drug courts. In fact, juveniles who were drug court participants had higher recidivism rates than youth on probation. Based on the process evaluation, recommendations are provided for improving juvenile drug courts.
How long does the juvenile court program last?
The program lasts 1 year. The judge will make a decision about the minor’s case but will delay the sentence for 1 year. During that year, the minor will go to Court every other week so the Court can see how they are doing. When the minor goes to Court every other week, the team looks at: How the minor is doing.
What is a drug treatment court?
What is Drug Treatment Court? The Drug Treatment Court is a special process that closely supervises minors who are addicted to drugs. The Court is made up of a team of people from the DA’s Office, the Public Defender’s Office, Juvenile Probation, the Bureau of Drug and Alcohol Service and other agencies.
What happens if a minor goes to mental health court?
If the minor wants to go to Mental Health Court, they have to admit the charges are true. Then, the minor will go on probation and will be strictly supervised. The minor must also get individualized treatment and rehabilitation services. Most minors return home and get services.
Why do minors go back to juvenile court?
Some minors go back to Juvenile Justice Court over and over because of their mental problem. A survey found that on one day, 215 out of 303 minors in Juvenile Hall were already getting some kind of mental health services. Half of them needed medicine for their conditions.
What does probation do?
Probation makes a report. Probation will put their findings in the report to tell the judge if education and treatment can help the minor. Probation also has to say which programs the minors will need to be involved in.
What happens if a minor starts taking drugs again?
If the minor is motivated. The team knows it’s hard to stay sober. They will support the minor for making an effort and will provide the treatment recovery services the minor needs. But, the team will also hold the minor responsible if he or she isn't motivated.
How often do probation officers meet with the court?
Everyone who works with the Domestic Violence/Family Violence Court gets special training. Probation officers, DAs, Public defenders, and Judges meet once a month to make new procedures and change old ones.
Juvenile Court
The Juvenile court is a division of the superior court. It handles three types of cases: Justice, status offense, and child abuse and neglect.
Our Mission is to
Accurately maintain all Juvenile court records in a confidential manner. Facilitate access to appropriate court records for public, inter-office agencies, and court use in an efficient manner.
Juvenile Cases
These offenses concern noncriminal behaviors that are illegal because of the child's age. These behaviors are not illegal for adults. For example, typical status offenses are truancy (cutting school) and running away from home.
The Court's Authority
The juvenile court has broad authority in juvenile cases. It can remove children from their homes, order their placement with relatives or in foster care or group homes, terminate parental rights, create new parental rights, and join various agencies to provide needed services.
Legal Help
Given that these decisions are so serious and affect fundamental rights, it is very important that if a juvenile case involves you or your child, you can add consult an attorney who can advise you more specifically about the court process as it relates to the case.
Your Right to an Attorney
The child in a Juvenile Justice case has a right to an attorney; a parent in an abuse and neglect case has a right to an attorney; and if a child in an abuse and neglect case would benefit from appointment of an attorney, the court will appoint one.
Center for Families, Children & the Courts
The Judicial Council/Administrative Office of the Courts' Center for Families, Children & the Courts was established to maximize the effectiveness of court services for children and families, implement innovative court-related programs for them, and promote those services in the legal community and to the public.
What punishments do judges consider?
These punishments might include: Probation. Minor fines. Community service.
What are the most common behaviors of teenagers?
Based on these factors, teenagers are more likely than adults to: Engage in risky or dangerous behavior . Get into physical or verbal fights. Get into accidents, such as car accidents. Misread the emotions of others and social cues.
Why should juveniles serve time in prison?
Juveniles should serve the appropriate time for the crime they commit because there are possibilities that they may repeat their actions.
What percentage of juvenile arrests are non index crimes?
In excess of 66 percent of every juvenile arrest is for non-index crimes, which include rape, robbery, aggravated assault, burglary, and motor vehicle theft (3). When it comes to acting out in a violent way, age is the one factor that should not justify a person’s behavior.
What age should a juror decide if a person is guilty?
The age of the suspect is the last thing that should cross a juror’s mind when deciding whether a person is guilty and if they are younger than 18, whether they should be tried as an adult. Youth who commit adult crimes should serve adult time.
How would the adult system affect adolescent wrongdoing?
This would beneficially affect adolescent wrongdoing by giving more stronger punishments, greater prevention from acting again, and longer incarceration (2).
Can a 15 year old and a 45 year old commit the same crime?
If a 15-year-old and a 45-year-old committed the same crime, there is no reason for them to be treated differently. Linda Collier states that “ Children who knowingly engage in adult conduct and adult crimes should automatically be subject to adult rules and adult prison time” (63).
Is it dangerous to be a juvenile?
Juveniles are definite dangers to society after they commit a crime. Some people do not expect someone under the age of 18 to commit heinous crimes, but it happens every day and should not be looked upon. Those people who commit such heinous crimes are dangerous while in prison and outside of prison if they get out.
Should adolescent be tried in adult court?
If an adolescent has a past criminal history or is arrested for violent crimes, they ought to be tried in an adult court. Adult prisons and jails are about imprisonment and brutal sentences, while juvenile courts focus mainly on rehabilitation (abcnews.go.com).
What rights do children have in criminal court?
It was the first time that the Supreme Court held that children facing delinquency prosecution have many of the same legal rights as adults in criminal court, including the right to an attorney, the right to remain silent, the right to notice of the charges, and the right to a full hearing on the merits of the case. More….
Why are juveniles so vulnerable?
Second, juveniles are more vulnerable and susceptible to negative influences and outside pressures, including peer pressure.
Which amendment did not guarantee the right to trial by jury?
Pennsylvania, 403 U.S. 528 (1971). The United States Supreme Court held that the Due Process Clause of the 14 th Amendment did not guarantee the right to trial by jury in the adjudicative phase of a state juvenile court delinquency proceeding. Were a jury—a major formality in the criminal process—imposed on juvenile trials, ...

Introduction
- Sex offenders have received considerable attention in recent years from both policymakers and the public. This is due at least in part to the profound impact that sex crimes have on victims and the larger community. While most perpetrators of sex crimes are adults, a significant percentage of sexual offenders are under age 18. Given the prevalence of sexual offending by juveniles, and …
Issues to Consider
- While there is growing interest in crime control strategies that are based on scientific evidence, determining what works is not an easy task. It is not uncommon for studies of the same phenomena to produce ambiguous or even conflicting results, and there are many examples of empirical evidence misleading crime control policy and practice because shortcomings in the qu…
Summary of Research Findings
- Findings From Single Studies
Several single studies examining the effectiveness of treatment programs for juveniles who sexually offend have been undertaken in recent years, and these studies have consistently found at least modest treatment effects on both sexual and nonsexual recidivism. Worling and Curwe… - Findings From Synthesis Research
One of the most frequently cited studies of the effectiveness of juvenile treatment was conducted by Reitzel and Carbonell (2006). Their meta-analysis included 9 studies and a combined sample of 2,986 juvenile subjects, making it one of the largest studies of treatment effectiveness for juveni…
Summary
- Given the prevalence of sexual offending by juveniles, therapeutic interventions for juveniles who sexually offend have become a staple of sex offender management practice in jurisdictions across the country. Indeed, the number of treatment programs for juveniles who commit sexual offenses has increased over the past 30 years, and the nature of treatment itself has changed a…