If the ranula is small, it may subside without any treatment. But if the size of the ranula is large, it may require treatment. In such cases, if the ranula is left untreated, it can cause complications.
Full Answer
Can a ranula go away on its own?
If a ranula is suspected as there is a 2-3 inch diameter soft swelling under the tongue or chin medical attention with the child’s medical provider should be obtained. If the diagnosis is felt to be a ranula based upon their examination and imaging tests treatment can then be sought from specialists such as interventional radiologists or surgeons.
What is the best treatment for a ranula?
He argues that modified marsupialization with packing reduces recurrence 10% to 12%. 23 The packing is felt to eradicate ranulas while decreasing the risk of injury to Wharton’s duct and the lingual nerve. 24 Baurmash 24 supports this conservative approach because sublingual gland removal is more invasive and may be inappropriate treatment when the diagnosis of ranula is …
What is the size of a normal ranula?
Small, simple ranulas that don’t cause problems may not require treatment. Some cysts may disappear on their own. Treatment is necessary, however, for enlarged simple ranulas, especially when swelling interferes with swallowing or speaking, and for most plunging ranulas.
What are the complication rates for plunging Ranulas?
Small ranulas that don’t cause problems may not require treatment. Some cysts disappear on their own. But treatment is necessary for enlarged …

How to tell if you have a ranula?
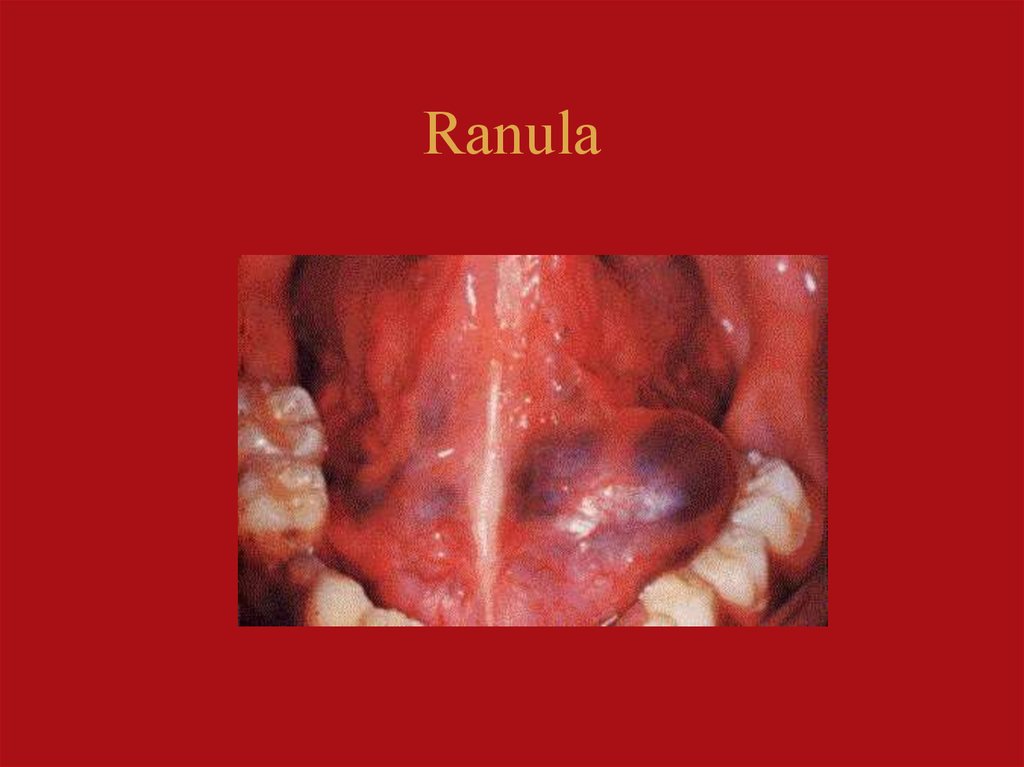
Symptoms of a ranula. A clear or bluish bubble-like growth on the floor of the mouth is the main symptom of a ranula. Since they don’t typically cause pain, they may go unnoticed until the cyst grows in size. Then it may cause problems with speech, swallowing and, occasionally, breathing if it grows large enough to press on the trachea (windpipe).
What is a simple ranula?
A simple (or oral) ranula is when the cyst stays in the floor of the mouth, underneath the tongue. A plunging (or diving) ranula is when the cyst grows down under the mouth and into the neck. It is rarer than a simple ranula and may occur along with a simple ranula.
How to treat ranula cyst?
There are a few ways the ranula can be treated: 1 Incision or needle aspiration: Depending on its size, your doctor can make an incision and drain the cyst to decrease swelling or use a needle to withdraw the fluid. These treatments are often temporary and the cyst reappears in about two-thirds of the time because the underlying damage still exists. 2 Marsupialization: The surgeon makes a slit in the cyst and sutures the edges to maintain an opening. This procedure allows the cyst to drain freely. 3 Surgery: This involves removal of the cyst and the damaged sublingual gland. Removing the cyst alone may not resolve the issue since the problem originates in the gland. If your doctor removed just the cyst and preserves the gland, a new cyst may develop.
Can a ranula form without a cause?
Sometimes a ranula forms without a known cause. Other times, trauma to the mouth, from oral surgery, getting hit in the face or biting the lower lip, can start one. There are two types of ranulas. A simple (or oral) ranula is when the cyst stays in the floor of the mouth, underneath the tongue.
What is a ranula in the mouth?
There are two types of ranulas. A simple (or oral) ranula is when the cyst stays in the floor of the mouth, underneath the tongue. A plunging (or diving) ranula is when the cyst grows down under the mouth and into the neck.
What is a plunging ranula?
A plunging (or diving) ranula is when the cyst grows down under the mouth and into the neck. It is rarer than a simple ranula and may occur along with a simple ranula. Ranulas are one of the most common salivary gland disorders.
What doctor will examine a ranula?
Diagnosis of a ranula. A pediatric otolaryngologist, a physician who specializes in the ears, nose and throat (ENT), will examine the child. Depending on the location and type of problem, the doctor may press on (palpitate) the child’s neck or look inside their mouth, pushing on the floor of the oral cavity.
Can a ranula be enlarged?
But you should see a doctor for an enlarged ranula since there’s the risk of the lesion rupturing. You’ll know the ranula is enlarged if it impairs eating, swallowing, speech, or breathing. Some doctors can make a diagnosis based on the appearance and location of the cyst.
What does it mean when you have a ranula?
A clear or bluish translucent growth on the floor of the mouth is the main symptom of a ranula. They don’t typically cause pain, so you may not notice it until the cyst increases in size. If you have a simple ranula, swelling is confined to the sublingual gland. This is the smallest of the three paired salivary glands around the throat and mouth.
Can a ranula cause pain?
They don’t typically cause pain, so you may not notice it until the cyst increases in size. If you have a simple ranula, swelling is confined to the sublingual gland. This is the smallest of the three paired salivary glands around the throat and mouth. Another type of ranula is a diving or plunging ranula, which occurs when a simple ranula ruptures.
What happens if you plunge your ranula?
A plunging ranula can produce additional symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, difficulty speaking, and tracheal compression.
Can you remove a ranula cyst?
Removing the cyst alone may not resolve the issue since the problem originates in the gland. If your doctor preserves the gland, a new cyst may develop. Another treatment option for a ranula is marsupialization. This is when your doctor cuts a slit in the cyst and sutures the edges.
Can ranula cysts disappear on their own?
Some cysts disappear on their own. But treatment is necessary for enlarged ranulas, especially when swelling interferes with swallowing or speaking. Depending on its size, your doctor can make an incision and drain the cyst to decrease swelling. Even if this treatment works, fluid may accumulate again.
Ranula
A ranula (Latin word rana, meaning frog) describes a blue, translucent swelling in the floor of the mouth, reminiscent of the underbelly of a frog.
Ranula Investigations
MRI is the most sensitive imaging study to evaluate the sublingual gland and its pathologic states.
Medical Treatment
A recent though small study evaluated the effectiveness of orally administered Nickel Gluconate-Mercurius Heel-Potentised Swine Organ Preparations D10/D30/D200, a homo-toxicological agent.
Surgical Treatment
Marsupialisation : Simple marsupialisation is the oldest and most widely reported treatment for ranulæ . It involves ‘unroofing’ the cyst and tacking the edges of the cyst to adjacent tissue.
Outcome and Prognosis
The overall risk for recurrence when the sublingual gland is not excised has been reported to be in excess of 50%.