What happens to viral load when HIV is not treated?
Shortly after contracting HIV, the viral load will drop as the immune system starts to fight the virus. Without treatment, the viral load will rise again as the virus starts to destroy specific immune system cells known as CD4 cells.
How can I prevent HIV?
HIV Treatment as Prevention 1 Taking HIV Medication to Stay Healthy and Prevent Transmission. 2 Keep Taking Your HIV Medication to Stay Undetectable. 3 Talk with Your HIV Health Care Provider. Talk with your health care provider about the benefits... 4 Talk to Your Partner. TasP can be used alone or in conjunction...
Does undetectable viral load mean HIV is cured?
Having an undetectable viral load doesn’t mean a person’s cured, because HIV can still hide in other parts of the immune system. Rather, it means the medication they’re taking is effective at suppressing the growth of the virus. Ongoing suppression can only be achieved by continuing to take this medication.
How does daily antiretroviral therapy treat HIV infection?
Daily antiretroviral therapy can reduce the amount of HIV in the blood to levels that are undetectable with standard tests. Staying on treatment is crucial to keep the virus suppressed.

How long does it take to reduce HIV viral load?
When a person living with HIV begins an antiretroviral treatment regimen, their viral load drops. For almost everyone who starts taking their HIV medication daily as prescribed, viral load will drop to an undetectable level in six months or less.
What is an ideal viral load for HIV?
A lower HIV viral load is below 10,000 copies. The virus probably isn't actively reproducing as fast, and damage to your immune system may be slowed, but this is not optimal. A viral load that can't be detected -- less than 20 copies -- is always the goal of HIV treatment.
What is considered a low viral load for HIV?
A lower HIV viral load is below 10,000 copies per milliliter of blood. The virus probably isn't actively reproducing as fast and damage to the immune system may be slowed, but this is not optimal. An undetectable HIV viral load is generally considered to be less than 20 copies per milliliter of blood.
Is a viral load of 40 good?
A viral load of 40 is excellent. This means that you're undetectable, and that you can't transmit HIV through sexual intercourse. It also means that there will be less risk to your baby. You're already doing the best thing possible by being on ARVs and adhering to them.
What is low viral load?
Viral load refers to the amount of virus in an infected person's blood. This is expressed as the number of viral particles in each milliliter of blood. Higher viral load can have different implications for different viruses but typically means the infection is progressing.
What does a viral load of 50 mean?
When copies of HIV cannot be detected by standard viral load tests, an HIV-positive person is said to have an “undetectable viral load.” For most tests used clinically today, this means fewer than 50 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood (<50 copies/mL). Reaching an undetectable viral load is a key goal of ART.
When is a viral load high?
Viral load refers to the amount of virus that can be detected in an infected person. High viral loads are concerning because they can mean the person is more infectious.
What does a viral load of 60 mean?
People with an undetectable viral load sometimes experience what are called 'blips' in their viral load. Their viral load increases from undetectable to a low but detectable level before becoming undetectable again on the next test. For example, your viral load may temporarily rise to 60 copies/ml or 150 copies/ml.
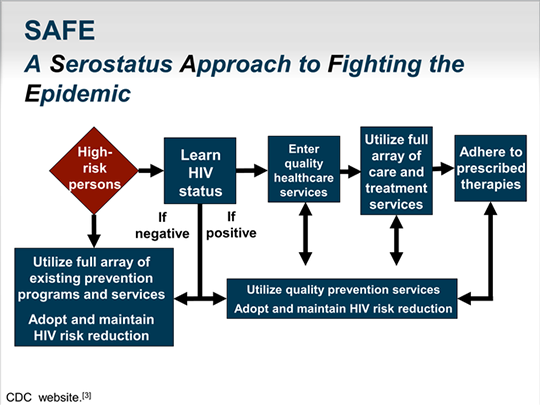
What are the prevention strategies for HIV?
These prevention strategies could include condoms and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV-negative partners.
What are the reasons for poor retention in HIV care?
Poor retention in HIV care is more common in people who have substance use disorders, serious mental health problems, unmet socioeconomic needs such as housing, food, or transportation, limited financial resources or health insurance, or schedules that complicate adherence to HIV medication.
How can a local health department help HIV patients?
Local or state health department or local community-based organizations can help providers and HIV medical clinics by integrating their existing prevention services within the HIV care clinic to provide the support services patients need to improve engagement and adherence in HIV care.
How to prepare for HIV?
Prepare patients for situations or changes in routine that could trigger nonadherence or short-term interruption, such as side effects, illicit drug use, or running out of HIV medication. Encourage patients to keep one or two days worth of medication on hand in case of emergency to avoid missed doses.
Is ART good for HIV?
There are many benefits to ART, including improved health and reduced risk of HIV transmission – but adherence is key! The success of ART is contingent on adherence to achieve and maintain viral suppression. Data show, however, that not all HIV-positive individuals on ART are virally suppressed, while even fewer maintain viral suppression over time.
What happens to the viral load after HIV diagnosis?
Shortly after contracting HIV, the viral load will drop as the immune system starts to fight the virus. Without treatment, the viral load will rise again as the virus starts to destroy specific immune system cells known as CD4 cells.
Why do doctors use viral load?
Doctors initially use the viral load to check the status of HIV after diagnosis, then to monitor the success of HIV treatments. When a person contracts HIV the virus replicates in their blood. The more copies of the virus there are, the higher a person’s viral load. If there is a high number of copies in the blood, ...
What does it mean when a person has a higher number of CD4 cells?
Higher numbers of CD4 cells indicate that the person’s immune system is stronger and better able to fight off infections. When the viral load reaches less than 200 copies/ml of blood, doctors consider that HIV is undetectable.
What does it mean when a person has an undetectable viral load?
. An undetectable viral load means that a person has effectively zero risk of sexually transmitting the virus to an HIV-negative partner.
What is antiretroviral therapy?
Antiretroviral therapy aims to reduce a person’s viral load to undetectable levels. This is known as viral suppression. After starting antiretroviral therapy, a person’s HIV viral load tests will come back with low numbers. When this occurs, the treatment is working, and HIV is no longer progressing.
What does it mean when you have a viral load test?
When doctors say a person has detectable levels of HIV in a viral load test, it means there is a significant amount of HIV in their blood. This level will vary based on the stage of the condition and the stage of treatment. On first diagnosis of HIV, a person’s viral load is typically high.
How does HIV affect CD4 cells?
HIV hijacks the cellular machinery of CD4 cells to reproduce and shed more HIV, which means the viral load increases . As the HIV viral load increases, the number of healthy CD4 cells decreases as they are destroyed creating HIV copies . Treatment aims to produce a low viral load and a high CD4 count.
How does antiretroviral treatment help HIV?
Taking antiretroviral treatment daily as directed to achieve and maintain durably undetectable status stops HIV infection from progressing, helping people living with HIV stay healthy and live longer, while offering the benefit of preventing sexual transmission.
How long does it take for HIV to be undetectable?
A person is considered to have a “durably undetectable” viral load if their viral load remains undetectable for at least six months after their first undetectable test result.
How long does it take for HIV to transmit?
There is effectively no risk of sexual transmission of HIV when the partner living with HIV has achieved an undetectable viral load and then maintained it for at least six months. Most people living with HIV who start taking antiretroviral therapy daily as prescribed achieve an undetectable viral load within one to six months after beginning treatment.
Why is staying on treatment important?
Staying on treatment is crucial to keep the virus suppressed. NIAID-supported research has demonstrated that achieving and maintaining a “durably undetectable” viral load (the amount of HIV in the blood) not only preserves the health of the person living with HIV, but also prevents sexual transmission of the virus to an HIV-negative partner.
What is PREP in HIV?
Research shows that adhering to treatment often can improve with support from loving relationships and from the community. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), in which an HIV-negative person takes antiretroviral medication to prevent infection, can be part of the conversation. Learn more about PrEP.
Does HIV prevent STIs?
Neither HIV treatment nor PrEP prevents other sexually transmitted infections, or STIs. Ways to reduce the risk of STIs include having both partners tested, limiting the number of sexual partners and using condoms. Vaccines are available to prevent some STIs, including hepatitis B and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Can antiretroviral drugs reduce HIV?
Development of antiretroviral drugs to treat HIV has turned what was once an almost always fatal infection into a manageable chronic condition. Daily antiretroviral therapy can reduce the amount of HIV in the blood to levels that are undetectable with standard tests.
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV Medication to Stay Healthy and Prevent Transmission. If you have HIV, it is important to start treatment with HIV medication (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) as soon as possible after your diagnosis. If taken every day, exactly as prescribed, HIV medication can reduce the amount of HIV in your blood (also called the viral load) ...
What is it called when your viral load is low?
If your viral load is so low that it doesn’t show up in a standard lab test, this is called having an undetectable viral load . People living with HIV can get and keep an undetectable viral load by taking HIV medication every day, exactly as prescribed.
Why is it called viral suppression?
It is called viral suppression because HIV medication prevents the virus from growing in your body and keeps the virus very low or “suppressed.”. Viral suppression helps keep you healthy and prevents illness.
How long does it take for HIV to be undetectable?
Almost everyone who takes HIV medication daily as prescribed can achieve an undetectable viral load, usually within 6 months after starting treatment. There are important health benefits to getting the viral load as low as possible. People living with HIV who know their status, take HIV medication daily as prescribed, ...
Can HIV go back up?
So, you need to keep taking your HIV medication daily as prescribed. When your viral load stays undetectable, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. If you stop taking HIV medication, your viral load will quickly go back up.
Can HIV be transmitted to HIV-negative people?
People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
Does TasP work for HIV?
People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. TasP works when a person living with HIV takes HIV medication exactly as prescribed and has regular follow-up care, ...
How to stay healthy with HIV?
Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load is the best thing you can do to stay healthy. Helps protect your partners. If you take HIV medication every day, exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking your HIV medication daily is also important because skipping doses makes it easier for HIV to change form, causing your medication to stop working. This is called drug resistance. HIV can become resistant to your medication and to similar medications that you have not yet taken.
What is it called when HIV is low?
Allows the HIV medication to reduce the amount of HIV in your body (also called the viral load) to a very low level. This is called viral suppression. If the viral load is so low that it doesn’t show up in a standard lab test, this is called having an undetectable viral load.
How does HIV medication work?
Taking your HIV medication daily as prescribed provides many benefits. Among them, it: 1 Allows the HIV medication to reduce the amount of HIV in your body (also called the viral load) to a very low level. This is called viral suppression. If the viral load is so low that it doesn’t show up in a standard lab test, this is called having an undetectable viral load. Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load is the best thing you can do to stay healthy. 2 Helps protect your partners. If you take HIV medication every day, exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. This is called Treatment as Prevention
Does ART reduce viral load?
Yes, antiretroviral therapy (ART) reduces your viral load, ideally to an undetectable level. If your viral load goes down after starting ART, then the treatment is working, and you should continue to take your medicine as prescribed.
Can you get sick from taking HIV medication?
Taking your HIV medication every day, exactly the way your health care provider tells you to will help keep your viral load low and your CD4 cell count high. If you skip doses, even now and then, you are giving HIV the chance to multiply rapidly. This could weaken your immune system, and you could become sick.
When was viral load reduction updated?
This link is to an early study describing the two-phase viral load reductions. This answer was updated in July 2020 from a question first posted on 15 September 2012.
How long does it take for a viral load to be undetectable?
Good adherence – not missing doses. UK and US guidelines recommend that your viral load should be undetectable within three months. However, many people achieve this within the first month, especailly if they are using an integrase inhibitor. Some people take longer, especially if their viral load is very high when they start treatment.
How long does HIV live in the first phase?
The first phase is very rapid – referred to in some studies as being the first few days and in others as within the first two weeks. This is where the actively infected CD4 cells are targeted. CD4 cells infected with HIV only live for a few days and when you start treatment this virus and these cells are quickly reduced.
How long does the second phase of a viral infection last?
In people with very high viral loads when they start treatment, this second phase may continue for longer until viral load becomes undetectable .

Art Initiation
Art Adherence and Viral Suppression
- There are many benefits to ART, including improved health and reduced risk of HIV transmission – but adherence is key! The success of ART is contingent on adherence to achieve and maintain viral suppression. Data show, however, that not all HIV-positive individuals on ART are virally suppressed, while even fewer maintain viral suppression over time. According to CDC’s national …
Viral Load Monitoring
- Plasma HIV RNA viral load should be measured regularly to confirm initial and sustained response to ART. Most patients taking ART as prescribed achieve viral suppression within six months. The frequency of viral load testing depends on several factors. Current guidelines recommend viral load monitoring as follows: 16 1. With initiation of ART (before initiation and within 2 to 4 weeks …
Regular, Ongoing Care
- Keeping patients in regular care improves their health and reduces their risk of HIV transmission to others. The benefits of ongoing care can include addressing and supporting ART adherence, maintaining decreased viral load and increased CD4 count, lowering rates of progression to AIDS, decreasing rates of hospitalization, and improving overall hea...
Coinfections
- STD preventive services are an essential component of HIV prevention and care. Providers should engage patients in regular conversations about STDs, including review of sexual history and STD sympt...
- People with HIV are also at risk for a variety of opportunistic infections such as TB and hepatitis virus. These risks can be reduced by viral suppression and a number of other preve…
- STD preventive services are an essential component of HIV prevention and care. Providers should engage patients in regular conversations about STDs, including review of sexual history and STD sympt...
- People with HIV are also at risk for a variety of opportunistic infections such as TB and hepatitis virus. These risks can be reduced by viral suppression and a number of other prevention behaviors.