
What is radioisotope therapy for cancer?
Radioisotope therapy uses radioactive liquid (known as radioisotopes or radionuclides) to destroy cancer cells. The liquid can be given: as an injection into a vein. Cancer cells take in the radioisotope more than normal cells do. This means they get a higher dose of radioactivity. This eventually destroys the cancer cells.
What is internal radiotherapy and how does it work?
Internal radiotherapy is treatment with a radioactive material that is put inside the body to treat cancer. There are different types of internal radiotherapy. We have information about the following types: selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT).
What are the different uses of radioactive isotopes?
Nuclear medicine uses radioactive isotopes in a variety of ways. One of the more common uses is as a tracer in which a radioisotope, such as technetium-99m, is taken orally or is injected or is inhaled into the body. The radioisotope then circulates through the body or is taken up only by certain tissues.
What is the first radioisotope used in medicine?
The first radioisotope used extensively in nuclear medicine is I-131, which was discovered by Glenn Seaborg in 1937. At the first time I-131 is used as an indicator of the function of the thyroid gland by detecting the emitted beam, with a Geiger enumerator placed near the thyroid gland.

What type of radiation is used in internal radiotherapy?
Brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy that is often used to treat cancers of the head and neck, breast, cervix, prostate, and eye. Brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy in which seeds, ribbons, or capsules that contain a radiation source are placed in your body, in or near the tumor.
What radioactive isotope is used in brachytherapy?
Currently, the isotope most commonly used for temporary brachytherapy is iridium (Ir)-192, which provides a higher dose of radiation than the iodine (I)-125 and palladium (Pd)-103 permanent implants.
What are radioactive isotopes used to treat?
In radiotherapy, radioisotopes typically are employed to destroy diseased cells. Radiotherapy commonly is used to treat cancer and other conditions involving abnormal tissue growth, such as hyperthyroidism.
Can radiation therapy be administered internally?
Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy) allows a higher dose of radiation in a smaller area than might be possible with external radiation treatment. It uses a radiation source that's usually sealed in a small holder called an implant.
What isotope is used in external radiotherapy?
By implanting radioactive sources directly into the tumor it is possible to deliver high-dose radiation to small tumors. The isotopes most commonly used in IRT are iridium-192 or iodine-125. Iridium (half-life 74 days), usually in the form of a wire, is used as a removable source.
Why Ir-192 is used in brachytherapy?
Low-dose rate (LDR) brachytherapy places radioactive materials inside the body for extended periods of time, but the high energy of the source used in HDR brachytherapy (usually Iridium-192) means that doctors can deliver equivalent doses of radiation in a much shorter amount of time.
What is radioactive iodine-131 used for medically?
I-131 is used in medicine to diagnose and treat cancers of the thyroid gland. Where does it come from? I-131 is produced commercially for medical and industrial uses through nuclear fission. It also is a byproduct of nuclear fission processes in nuclear reactors and weapons testing.
What radioactive isotope is used as an internal treatment for thyroid cancers?
Because of this, radioactive iodine (RAI, also called I-131) can be used to treat thyroid cancer. The RAI collects mainly in thyroid cells, where the radiation can destroy the thyroid gland and any other thyroid cells (including cancer cells) that take up iodine, with little effect on the rest of your body.
Why is cobalt used for external radiotherapy instead of a radioisotope that produces alpha radiation?
The main reason for its wide use in radiotherapy is that it has a longer half-life, 5.27 years, than many other gamma emitters. However this half life still requires cobalt sources to be replaced about every 5 years.
How is internal radiotherapy performed?
Brachytherapy, also called internal radiation therapy, places radioactive material directly inside or next to the tumor. It uses a higher total dose of radiation to treat a smaller area than external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) which directs high-energy x-ray beams at a tumor from outside the body.
What is the difference between internal and external radiation therapy?
During external-beam radiation therapy, the patient does not give off any radiation after treatment sessions. Any radiation remains in the the treatment room. However, internal radiation therapy causes the patient to give off radiation.
What is the difference between external radiotherapy and internal radiotherapy?
The two main types of radiotherapy are: External radiotherapy – where the radiation comes from a machine outside the body. Internal radiotherapy – where the radiation comes from implants or liquids placed inside the body.
What is the best isotope for implants?
Iridium-192 used in the form of pins (epingles), wires, or seeds preloaded in a plastic ribbon have the advantage of being suitable for afterloading techniques, and thus is used commonly for temporary implants. Iodine-125 may be substituted and is the isotope of choice for permanent implants.
What is surface mold radiotherapy?
Surface mold radiotherapy can be used as a primary treatment for select initial or recurrent superficial lesions of the hard palate, lower gingiva, and floor of the mouth. An impression is usually made of the surface to be irradiated and a mold in the form of a partial dental plate is made of dental plaster.
What is brachytherapy in a body?
Brachytherapy that involves placement of sources directly into the tissues, usually via needles, is termed interstitial therapy . Treatment that involves placement of sources in a body cavity (e.g., uterus, bronchus, or esophagus) is termed intracavitary therapy. The use of sources placed in a surface applicator to treat superficial targets is termed mold therapy.
What is interstitial therapy?
Insertion of radioactive needles into a tumour is termed ‘interstitial therapy’. The first use of the technique in the treatment of rectal cancer was by Binkley (1938), who combined the technique with external irradiation for 3 weeks. After an interval of 2 weeks, interstitial therapy was commenced using radium or radon needles. Binkley treated a variety of growths, many of them so advanced that they were beyond any form of therapy. His greatest success was achieved in 18 patients who had small tumours, but were considered to be high surgical risks; 15 of them were alive and well for periods varying from 15 months to 10 years. Ruff et al (1961), from the Mayo Clinic, also reported the destruction of tumours by this technique in 10 of 96 patients treated. This method of therapy was largely abandoned because of the difficulty with dosimetry and safety experienced using radium and radon. With the introduction of new radioisotopes—particularly iridium-192—these difficulties have been overcome. Papillon advocated the use of the technique when small remnants of tumour remain after contact irradiation ( Papillon, 1982 ). It can also be used for the treatment of recurrence after local excision ( Kozlova and Popova, 1977 ).
What is the treatment of a surface applicator?
The use of sources placed in a surface applicator to treat superficial targets is termed mold therapy .
How long does iodine last?
Iridium (half-life 74 days), usually in the form of a wire, is used as a removable source. Iodine seeds (half-life 60 days) are implanted individually or as linear sources and, depending on their activity, can be employed as either temporary or permanent implants.
How is radiation delivered?
Radiation can be delivered by insertion of radiation sources directly into the tumor; this is described as interstitial radiotherapy (IRT) or brachytherapy. Radiation can also be delivered in the form of radioactive colloid (yttrium or chromic phosphate) or radiolabeled antibody into cystic cavities or solid tumors.
What is the most common radioisotope used in nuclear medicine?
The most common radioisotope used in diagnosis is technetium-99 (Tc-99), with some 40 million procedures per year, accounting for about 80% of all nuclear medicine procedures and 85% of diagnostic scans in nuclear medicine worldwide. In developed countries (about one-quarter of world population) the frequency of diagnostic nuclear medicine is 1.9% ...
What is radioisotopes used for in medicine?
(Updated April 2021) Nuclear medicine uses radiation to provide diagnostic information about the functioning of a person's specific organs, or to treat them. Diagnostic procedures using radioisotopes are now routine.
How many people use radioisotopes in a year?
There is widespread awareness of the use of radiation and radioisotopes in medicine, particularly for diagnosis (identification) and therapy (treatment) of various medical conditions. In developed countries (a quarter of the world population) about one person in 50 uses diagnostic nuclear medicine each year, and the frequency ...
Why are radioisotopes important?
In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body.
How many hospitals use radioactive tracer?
Five Nobel Laureates have been closely involved with the use of radioactive tracers in medicine. Over 10,000 hospitals worldwide use radioisotopes in medicine, and about 90% of the procedures are for diagnosis.
What organs absorb iodine?
Doctors and chemists have identified a number of chemicals which are absorbed by specific organs. The thyroid, for example, takes up iodine, whilst the brain consumes quantities of glucose. With this knowledge, radiopharmacists are able to attach various radioisotopes to biologically active substances. Once a radioactive form of one of these substances enters the body, it is incorporated into the normal biological processes and excreted in the usual ways.
How many nuclear procedures are performed annually?
Over 40 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed each year, and demand for radioisotopes is increasing at up to 5% annually. Sterilization of medical equipment is also an important use of radioisotopes.
How is radioactive isotope used in nuclear medicine?
One of the more common uses is as a tracer in which a radioisotope, such as technetium-99m, is taken orally or is injected or is inhaled into the body. The radioisotope then circulates through the body or is taken up only by certain tissues.
What is the purpose of radioisotopes?
Therapeutic applications of radioisotopes typically are intended to destroy the targeted cells. This approach forms the basis of radiotherapy, which is commonly used to treat cancer and other conditions involving abnormal tissue growth, such as hyperthyroidism.
When were radioisotopes discovered?
The use of radioisotopes in the fields of nuclear medicine and radiotherapy has advanced significantly since the discovery of artificial radioisotopes in the first decades of the 1900s. Artificial radioisotopes are produced from stable elements that are bombarded with neutrons.
Why do people have internal radiotherapy?
This is because internal radiotherapy delivers radiation from inside the body, close to the cancer, so affects fewer healthy cells.
What is radioactive liquid treatment?
Radioactive liquid treatment (radioisotopes or radionuclides) You have radioactive liquid treatment as a drink, capsule or injection. The radioactive part of the liquid is called an isotope. It may be attached to another substance, which is designed to take the isotope into the tumour.
What type of cancer is brachytherapy?
Doctors use brachytherapy to treat several different types of cancer, most commonly: 1 prostate cancer 2 cervical cancer 3 womb cancer
What is the radioactive part of phosphorus?
The radioactive part of the liquid is called an isotope. It may be attached to another substance, which is designed to take the isotope into the tumour.
What is radioactive material called?
The radioactive material is called a source and is sealed inside a holder called an implant. The implants may be seeds, wires or discs. The implant is left inside the body for a certain time. This might be for: several minutes.
How to plan brachytherapy?
To plan your brachytherapy, you have a scan, such as a CT or an ultrasound scan. Your doctor uses the scans to work out how much radiation you need and where to put the radioactive source (implants).
Where is brachytherapy put?
With brachytherapy, a small radioactive material is put into your body, into or very close to the cancer. Or in the area where the cancer was removed.
How does radioisotope therapy work?
Radioisotope therapy. Radioisotope therapy uses radioactive liquid (known as radioisotopes or radionuclides) to destroy cancer cells. The liquid can be given: by mouth as a drink or capsules. as an injection into a vein. Cancer cells take in the radioisotope more than normal cells do.
What is internal radiation therapy?
Internal radiotherapy is treatment with a radioactive material that is put inside the body to treat cancer. There are different types of internal radiotherapy. We have information about the following types: selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT).
What is brachytherapy?
Brachytherapy. Brachytherapy uses radioactive implants such as seeds, pellets, wires or plates that are put near or inside the tumour. The radioactivity only affects tissue that is very close to the implant. This means the tumour is treated, but healthy areas around it get much less radiotherapy. Areas of the body that are further away are not ...
What is SIRT in cancer?
Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) is a type of internal radiotherapy that uses radioactive beads. It is used to treat some types of liver cancer. For example, it may be used to treat cancer that spreads to the liver from the bowel. SIRT is not widely available and is not always funded by the NHS.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Internal radiotherapy . Internal radiotherapy is treatment with a radioactive material that is put inside the body to treat cancer.
What radioisotopes are used to treat metastatic bone cancer?
Strontium-89 and Samarium-153. These radioisotopes can be used to treat some types of cancer that have spread to the bones ( metastatic bone cancer ). This treatment can help reduce bone pain and improve quality of life. You can usually go home soon after having this treatment.
Do cancer cells take radioisotopes?
Cancer cells take in the radioisotope more than normal cells do. This means they get a higher dose of radioactivity. This eventually destroys the cancer cells. Your team will tell you how you will have your treatment and any possible side effects.
What is the radiation used for thyroid cancer?
The radiation dose used here is much stronger than the one used in radioiodine scans, which are described in Tests for Thyroid Cancer. This treatment can be used to ablate (destroy) any thyroid tissue not removed by surgery or to treat some types of thyroid cancer that have spread to lymph nodes and other parts of the body.
What to do if you have any questions about the possible risks and benefits of your treatment?
Talk to your health care team if you have any questions about the possible risks and benefits of your treatment.
How to treat RAI?
For RAI therapy to be most effective, you must have a high level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) in the blood. This hormone is what makes thyroid tissue (and cancer cells) take up radioactive iodine. If your thyroid has been removed, there are a couple of ways to raise TSH levels before being treated with RAI: 1 One way is to stop taking thyroid hormone pills for several weeks. This causes very low thyroid hormone levels (hypothyroidism), which makes the pituitary gland to release more TSH. This intentional hypothyroidism is temporary, but it often causes symptoms like tiredness, depression, weight gain, constipation, muscle aches, and reduced concentration. 2 Another way is to get an injection (shot) of thyrotropin (Thyrogen), which can make withholding thyroid hormone for a long period of time unnecessary. This drug is given daily for 2 days, followed by RAI on the 3 rd day.
How long after radiation therapy can you go home?
Depending on the dose of radioiodine used and where you are being treated, you might need to be in the hospital for a few days after treatment, staying in a special isolation room to prevent others from being exposed to radiation. Some people may not need to be hospitalized. Once you are allowed to go home after treatment, you will be given instructions on how to protect others from radiation exposure and how long you need to take these precautions. These instructions may vary slightly by treatment center. Be sure you understand the instructions before you leave the hospital.
Can radiation cause irregular periods?
Radioactive iodine may also affect a woman’ s ovaries, and some women may have irregular periods for up to a year after treatment.
Can iodine therapy be used for thyroid cancer?
Discuss your risks and benefits of RAI therapy with your doctor. Radioactive iodine therapy cannot be used to treat anaplastic (undifferentiated) and medullary thyroid carcinomas because these types of cancer do not take up iodine.
What is internal radiation therapy?
Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy) allows a higher dose of radiation in a smaller area than might be possible with external radiation treatment. It uses a radiation source that’s usually sealed in a small holder called an implant. Different types of implants may be called pellets, seeds, ribbons, wires, needles, capsules, balloons, or tubes. No matter which type of implant is used, it is placed in your body, very close to or inside the tumor. This way the radiation harms as few normal cells as possible.
Where is the radioactive source placed in the body?
This way the radiation harms as few normal cells as possible. During intracavitary radiation, the radioactive source is placed in a body cavity (space) , such as the rectum or uterus. With interstitial radiation, the implants are placed in or near the tumor, but not in a body cavity.
How are implants placed in the body?
The implant procedure is usually done in a hospital operating room designed to keep the radiation inside the room. You’ll get anesthesia, which may be either general (where drugs are used to put you into a deep sleep so that you don’t feel pain) or local (where part of your body is numbed).
What is the term for radiation in the body?
Internal radiation is also called brachytherapy . A radioactive implant is put inside the body in or near the tumor. Getting the implant placed is usually a painless procedure. Depending on your type of cancer and treatment plan, you might get a temporary or a permanent implant.
How long does brachytherapy last?
The source is removed after 10 to 20 minutes. This may be repeated twice a day over a few days, or once a day over the course of a few weeks.
How long does it take for radiation to go away from implants?
Over a few weeks to months, permanent implants will slowly stop giving off radiation. The radiation usually doesn’t travel much farther than the area being treated, so the chances that others could be exposed to radiation is very small. Still, your health care team might ask you to take certain precautions such as staying away from small children and pregnant women, especially right after you get the implants.
Can you leave radioactive material in your body?
The radioactive material is not left in your body. The applicator might be left in place between treatments, or it might be put in before each treatment. People getting HDR sometimes stay in the hospital if it involves multiple day treatments and if the applicator is left in place.
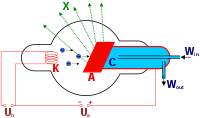
Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis, Nuclear Imaging
- Radioisotopes are an essential part of medical diagnostic procedures. In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can be used for imaging to study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body. In using radiopharmaceuticals for diagnosis, a radioactive dose is given to the patient and the activity in t…
Nuclear Medicine Therapy
- The uses of radioisotopes in therapy are comparatively few, but nevertheless important. Cancerous growths are sensitive to damage by radiation. For this reason, some cancerous growths can be controlled or eliminated by irradiating the area containing the growth. This may be called radiosurgery. External irradiation (sometimes called teletherapy) can be carried out using …
Sterilization
- Many medical products today are sterilized by gamma rays from a Co-60 source, a technique which generally is much cheaper and more effective than steam heat sterilization. The disposable syringe is an example of a product sterilized by gamma rays. Because it is a 'cold' process radiation can be used to sterilize a range of heat-sensitive items such...
Supply of Radioisotopes
- The main world isotope suppliers are Curium (France & USA), MDS Nordion (Canada), IRE (Europe), NTP (South Africa), JSC Isotope (Russia), and ANM(ANSTO Australia). Most medical radioisotopes made in nuclear reactors are sourced from relatively few research reactors, including: 1. HFR at Petten in Netherlands (supplied via IRE and Curium). …
Notes & References
- OECD Nuclear Energy Agency, A Supply & Demand Update of the Mo-99 Market (August 2012) OECD-NEA, The Supply of Medical Radioisotopes: An Economic Diagnosis and Possible Solutions (2019) International Atomic Energy Agency, Feasibility of Producing Molybdenum-99 on a Small Scale Using Fission of Low Enriched Uranium or Neutron Activation of Natural Molybdenum, Tec…