What is the procedure to correct for otosclerosis?
What is the procedure to correct for otosclerosis? Surgery — Surgery can be a highly effective treatment for otosclerosis. The procedure is called a “stapedectomy” (or “stapedotomy”). The procedure is intended to “bypass” the fixed part of the stapes bone by removing it, and replacing it with a new, mobile, prosthetic bone.
What are the treatment options for otosclerosis?
- DIAGNOSIS. Diagnosing otosclerosis is usually done through one of two tests. The first is an audiometric hearing test conducted by a hearing health provider like an audiologist or ENT.
- TREATMENT
- Treatment for hearing loss resulting from otosclerosis is contingent, in part, upon the length and severity of the condition. ...
What is the cure for hearing loss due to otosclerosis?
Your provider may talk to you about:
- Monitoring: If your otosclerosis is mild, your doctor may take a watch-and-wait approach and test your hearing regularly. ...
- Devices: Hearing aids cannot cure otosclerosis, but they can improve the hearing loss you experience because of it.
- Surgery: If your hearing loss is serious or gets worse, your doctor may recommend a surgery called a stapedectomy. ...
How is severe otosclerosis treated?
Treatment of otosclerosis. The treatment of otosclerosis can be divided into two areas: the use of hearing aids and surgery of the stapes. Hearing aids help people who are suffering from conductive deafness, including otosclerosis. However, a hearing aid will not cure the deafness.
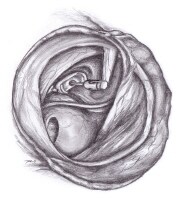
Which surgical procedure is used to restore hearing in cases of otosclerosis?
A stapedectomy is surgery to treat hearing loss caused by otosclerosis. This condition affects your hearing by damaging your stape, a tiny U-shaped bone in your middle ear. Your stape helps you hear by sending sound waves from your middle ear to your inner ear.
What is a stapedectomy procedure?
A stapedectomy (say "stay-puh-DEK-tuh-mee") is surgery to remove a small bone, called the stapes, from the middle ear. The middle ear contains three bones: the stapes (say "STAY-peez"), the incus, and the malleus. These bones help with hearing.
Is a stapedectomy used to treat otosclerosis?
Importance Otosclerosis can be managed through surgical treatment, such as stapedectomy, or through hearing amplification with hearing aids.
What is the difference between stapedectomy and stapedotomy?
Compared to a stapedectomy, a stapedotomy includes the use of a laser to make a precise hole (fenestration) in the stapes footplate. While a stapedectomy typically removes the entire stapes footplate and has it replaced with a micro prosthesis.
What material is used in a stapedectomy?
The materials evolved from Teflon, metal, to plastic, and most recently to gold and titanium. While initially the diameter of the pistons used was 0.8 and 0.6 mm, from the 1970s onwards, it has been becoming even smaller in order to ease the procedure and reduce the risk of inner ear damage.
What is a Mastoidectomy procedure?
A mastoidectomy is surgery to remove cells in the hollow, air-filled spaces in the skull behind the ear within the mastoid bone. These cells are called mastoid air cells.
What is a Tympanotomy procedure?
Tympanostomy (Ear Tubes) Tympanoplasty is surgery to place ear tubes. Ear tubes are small, hollow cylinders inserted into your eardrum. They're often used in children or adults who have chronic middle ear infections or infections that have resisted treatment.
What myringotomy means?
A myringotomy is a procedure to create a hole in the ear drum to allow fluid that is trapped in the middle ear to drain out. The fluid may be blood, pus and/or water. In many cases, a small tube is inserted into the hole in the ear drum to help maintain drainage.
Why is Tympanoplasty done?
Tympanoplasty is the surgical procedure performed to repair a perforated TM, with or without reconstruction of the ossicles (ossiculoplasty), with the aim of preventing reinfection and restoring hearing ability.
When does taste return after stapedectomy?
Conclusion: The incidence of taste disturbance after stapes surgery is high (61.9%), whereas the majority (94.8%) recovers within 1 year.
Are you put to sleep for stapedectomy?
You will be kept comfortable and safe by your anesthesia provider. The anesthesia may make you sleep. Or it may just numb the area being worked on. The surgery will take about 1 to 2 hours.
What can go wrong with stapedectomy?
Hearing loss: There is a slight chance of hearing loss in the inner ear. This loss can be complete and permanent. Dizziness: Some patients experience dizziness that resolves itself within a day of surgery. It is not likely for dizziness to be a persistent problem.
How does otosclerosis affect the ears?
Otosclerosis begins in one ear and affects both the ears later in life. Hearing loss starts with low frequency and then later shifts to high frequency. Most patients who have Otosclerosis notice head noise ( tinnitus) to some degree. This usually gets worse when the affected patient is nervous or fatigued.
What is the term for the abnormal growth of the bone near the middle ear?
Otosclerosis refers to an abnormal growth of the bone situated near the middle ear which can result to hearing loss. This is generally an inherited disorder. The primary form of loss of hearing in Otosclerosis is CHL or conductive hearing loss. In such cases, the sound reaches the ear drum but is not completely transferred via the middle ear, ...
Why is my ear frozen?
A frozen stapes bone is either caused due to conductive hearing loss or a mechanical ear injury. Stapedectomy is performed under general or local anesthesia. A small incision is made just behind the ear to remove fat or muscle tissue for use in the procedure.
How to cure conductive hearing loss?
In this procedure, conductive hearing loss can be cured by removing all or just a part of the middle ear bones behind the stapes (eardrum). It is then replaced with a prosthesis as a substitute. This surgery is very effective to help improve the symptoms of otosclerosis.
What is the best test for hearing loss?
A special imaging test can be used which is called a temporal bone CT scan to look for the cause of hearing loss. The stapes prosthesis generally allows vibrations to pass from your eardrum to your inner ear fluids. This corrects the conductive hearing loss and improves the symptoms of Otosclerosis.
How long does it take to get hearing after ear surgery?
Maximum hearing can be obtained in six to seven months after the surgery. The amount of hearing improvement largely depends on how well the ear can heal. In most of the patients, the ear heals perfectly, while in some patients only partial hearing can be achieved. In such cases, re-operation is advisable.
How long does it take to see improvement after hearing surgery?
Hearing improvement might or might not be noticeable right after the surgery, but you can gradually see the improvement in a month. If hearing suddenly improves right after the surgery, it can decrease due to swelling in the ear. Maximum hearing can be obtained in six to seven months after the surgery.
How to treat otosclerosis?
Mild otosclerosis can be treated with a hearing aid that amplifies sound, but surgery is often required. In a procedure known as a stapedectomy, a surgeon inserts a prosthetic device into the middle ear to bypass the abnormal bone and permit sound waves to travel to the inner ear and restore hearing.
What is otosclerosis in the middle ear?
Otosclerosis is a term derived from oto, meaning “of the ear,” and sclerosis, meaning “abnormal hardening of body tissue.”. The condition is caused by abnormal bone remodeling in the middle ear. Bone remodeling is a lifelong process in which bone tissue renews itself by replacing old tissue with new. In otosclerosis, abnormal remodeling disrupts ...
What is bone remodeling?
Bone remodeling is a lifelong process in which bone tissue renews itself by replacing old tissue with new. In otosclerosis, abnormal remodeling disrupts the ability of sound to travel from the middle ear to the inner ear. Otosclerosis affects more than three million Americans. Many cases of otosclerosis are thought to be inherited.
Why is it so difficult to study the inner ear?
The complicated architecture of the inner ear makes it difficult for scientists to study this part of the body. Because researchers can’t remove and analyze a sample of the inner ear from someone who has otosclerosis (or other hearing disorders), they must study ear bone samples from cadavers donated for research.
What is the name of the doctor who diagnoses otosclerosis?
Otosclerosis is diagnosed by health care providers who specialize in hearing. These include an otolaryngologist (commonly called an ENT, because they are doctors who specialize in diseases of the ears, nose, throat, and neck), an otologist (a doctor who specializes in diseases of the ears), or an audiologist ...
What causes hair cells to tilt?
The bristly structures of the hair cells then bump up against an overlying membrane, which causes the bristles to tilt to one side and open pore-like channels. Certain chemicals then rush in, creating an electrical signal that is carried by the auditory nerve to the brain. The end result is a recognizable sound.
Can otosclerosis cause tinnitus?
Many people with otosc lerosis first notice that they are unable to hear low-pitched sounds or can’t hear a whisper. Some people may also experience dizziness, balance problems, or tinnitus. Tinnitus is a ringing, roaring, buzzing, or hissing in the ears or head that sometimes occurs with hearing loss.
How to diagnose otosclerosis?
Diagnosing otosclerosis is usually done through one of two tests. The first is an audiometric hearing test conducted by a hearing health provider like an audiologist or ENT. The second is an imaging test called a temporal-bone CT, which can also be used to diagnose other types of hearing loss. The CT scan is rarely performed if a patient presents ...
Why does otosclerosis occur?
Otosclerosis is a mysterious condition in which the formation of bone, usually within the middle ear , impedes hearing and causes hearing loss. Although it is not known why this abnormal bone growth occurs, there are factors like pregnancy, virus, and genetics thought to contribute to its likelihood. Treatment and surgeries for otosclerosis varies and can depend on the severity of the condition and other underlying problems.
What is total stapedectomy?
Total Stapedectomy --Total removal of the stapes bone and insertion of a micro prosthesis. Total stapedectomy surgery requires removal of all of the nonfunctioning stapes bones (small bone in the middle ear) and replacing it with a prosthetic device that allows sound to be transferred into the inner ear.
How long has otosclerosis been around?
Surgical treatments for otosclerosis have been around for over a hundred years. Originally the limited knowledge of middle ear functions meant that often these surgeries developed complications or were not successful at all. A wealth of new information, advanced equipment, and medical techniques now mean that 9 out of 10 people who undergo surgery for otosclerosis obtain a successful return of hearing. Note: Not all patients are candidates for surgery. People with Meniere's disease or who still retain enough of an air-bone gap are not typically operated upon.
Can a CT scan be performed on a patient with hearing loss?
The CT scan is rarely performed if a patient presents with typical conductive or middle ear hearing loss. Diagnosis becomes less sure with sensorineural or mixed hearing loss making the CT necessary.
Can hearing aids cure otosclerosis?
Hearing aids —Although hearing aids cannot cure otosclerosis, they can help treat the largest symptom--hearing loss. There are many options today for improving hearing with hearing aids. Technology can help correct hearing loss due to otosclerosis, and may even provide the least invasive and risky solution.
Can fluoride be used after surgery?
Often a fluoride treatment will be given in conjunction with another treatment, a hearing aid or as after surgery care instructions. Hormone Inhibition --A less known preventative treatment is to regulate female hormones thought to play a part in the worsening of this condition. Hearing aids —Although hearing aids cannot cure otosclerosis, ...
What is otosclerosis?
Otosclerosis is a complex and progressive disease of pathological bone remodeling that affects the otic capsule of the temporal bone, result ing in hearing loss. Although traditional diagnostic methods are still used, improvements in technology and research have paved the way for additional diagnostic techniques and advancements.
What tests are used for otosclerosis?
Clinicians can perform a number of screenings that may aid in audiometric referral for patients with otosclerosis, including questionnaires, tuning fork tests, whisper-voice test, and audioscope ( Table 1 ).
What is the purpose of a stapes surgery?
Stapes surgery restores the mechanical transmission of sound through the middle ear, correcting conductive hearing loss. It does not correct sensorineural hearing loss secondary to otosclerotic extension into the cochlea. Stapes surgery is a minimally invasive one-day procedure performed under general anesthesia; more recently, some surgeons have begun to perform stapes surgery under local anesthesia. 6 The two variations of the surgery are:
What is otosclerosis hearing loss?
Patients with otosclerosis present with progressive hearing loss that is worse in lower tones and/or frequencies. For example, patients often report difficulty hearing male voices or vowel sounds in words. About 50% of patients also have tinnitus. 4 Only 10% of patients report vertigo, which is not present unless otosclerosis has extended to the inner ear, affecting the semicircular canals responsible for balance. 2 Otosclerosis is found bilaterally in 80% of patients; however, patients often present with unilateral involvement early in the disease. 6
How much bone remodeling occurs in the otic capsule?
Normal bone remodeling occurs at a rate of 10% per year throughout skeletal regions; however, a normal otic capsule has very little bone remodeling—only 0.13% per year. 2 In patients with otosclerosis, bone remodeling within the otic capsule is increased, leading to accumulation of bone deposits that damage audiologic structures and worsen normal sound transmission. The extent of aberrant bone remodeling in the otic capsule directly correlates to the abnormal audiologic findings.
What is the transitional phase of osteoclasts?
The otospongiosis phase, which represents an increase in both osteoclast activity and microvascularity. 4. The transitional phase, which begins with deposits of spongy bone by osteoblasts in areas of previous bone reabsorption. 4. The otosclerotic phase, characterized by spongy bone deposits developing into dense bone that narrows ...
Is otosclerosis a progressive hearing loss?
Otosclerosis is a progressive yet treatable form of hearing loss. Improvements in technology and research have paved the way for additional diagnostic techniques and advancement in treatments. Understanding of this complex disease leads to earlier diagnosis, referral, treatment, and improved patient education for those with otosclerosis.
What is the mechanics of otosclerosis?
Otosclerosis involves an abnormal overgrowth of bone that prevents one of the tiny bones in the middle ear from vibrating like it should. This limits the transmission of sound to the inner ear, causing conductive hearing loss. The middle ear contains a chain of three tiny bones—the auditory ossicles, ...
How to deal with otosclerosis?
Following a healthy lifestyle generally helps people better manage the stress associated with any hearing disorder. This includes stress reduction, regular exercise—to the extent possible and approved by a physician, a healthy diet, adequate sleep, and avoiding nicotine and other unhealthy substances. Generally, addressing any type of hearing loss tends to improve quality of life.
What is mixed hearing loss?
Mixed hearing loss occurs when otosclerosis affects both the auditory ossicles ( conductive hearing loss) and the cochlea or hair cells of the inner ear (sensorineural hearing loss). It’s true that bone tissue in the body renews itself as part of a lifelong process known as bone remodeling. But in otosclerosis, this bone remodeling goes awry.
What is the smallest bone in the auditory ossicles?
Only 3 x 2.5 mm in size, the stapes is the smallest bone of the auditory ossicles, and it’s the one that otosclerosis most often affects. All three bones of the auditory ossicles play an important role in the hearing process. For hearing to occur, sound waves must collect in the outer ear, pass through the ear canal, ...
What causes hearing loss in young adults?
Otosclerosis. Otosclerosis affects the bones of the middle ear that conduct sound. Sometimes called otospongiosis, it’s one of the most common causes of progressive hearing loss in young adults. What triggers otosclerosis is still uncertain. But it often runs in families, and experts consider it an inherited disease.
When does otosclerosis peak?
Otosclerosis also tends to be a younger person’s disease. Symptoms typically crop up between the ages of 10 and 45 and most commonly during a person’s twenties. Often, but not always, the damage caused by the disorder peaks sometime in the person’s thirties.
Does otosclerosis cause hearing loss?
When it continues to progress, the result is hearing loss, which typically worsens over time. Usually, people only realize they have otosclerosis after the abnormal bone growth has reached the stapes or the other auditory ossicles, causing hearing loss.
What is the treatment for otosclerosis?
There is no local treatment (ear drops) to the ear itself or any other medication that will improve the hearing in persons with otosclerosis. In some cases, medication (sodium fluoride) is used to prevent further loss of hearing related to the inner ear.
Can you have a stapes operation with otosclerosis?
The stapes operation is recommended for patients with otosclerosis who have a conductive or mixed hearing loss and are candidates for surgery. This operation is performed under local or general anesthesia in an outpatient setting, requiring only a short period of convalescence. Over 90% of these operations are successful in restoring hearing permanently.
Can hearing be lost after ear surgery?
Whenever an ear is operated upon, there is a chance that the hearing could be made worse or lost altogether. The possibility of this happening differs from one operation to another and may occur even if the surgery goes well and there are no other complications.