Medication
Prophylactic therapy beginning at an early age should be considered the evidence-based treatment of choice for children with severe hemophilia, enabling normal physical, psychologic, and social development. The optimal regimen is still debated.
Therapy
Clotting-factor tests can reveal a clotting-factor deficiency and determine how severe the hemophilia is. For people with a family history of hemophilia, genetic testing might be used to identify carriers to make informed decisions about becoming pregnant.
Self-care
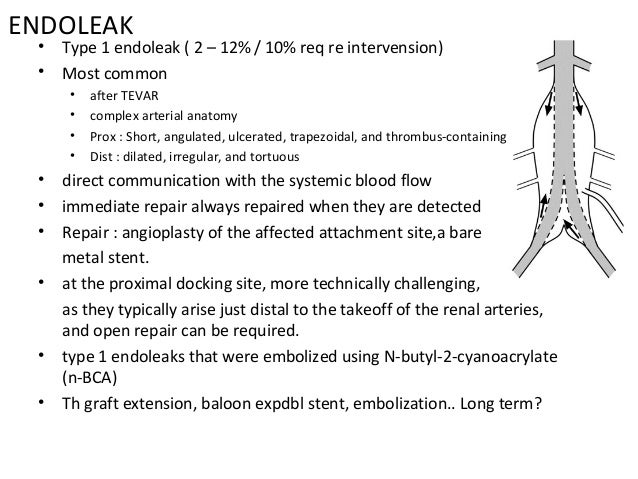
The Targets of Replacement Therapy in Hemophilia The main aim of hemophilia treatment is to prevent life-threatening bleeding and/or treat muscle and joint bleeding.
Nutrition
Antifibrinolytic medicines such as tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid are oral medicines that are sometimes used with replacement therapy in certain situations to help keep blood clots from breaking down. Other health issues associated with hemophilia may need to be addressed. The most common include:
What is the evidence-based treatment of choice for hemophilia A?
What tests are used to diagnose hemophilia?
What are the targets of replacement therapy in hemophilia?
What are antifibrinolytic medicines for hemophilia?

What are some treatment options for hemophilia?
Treatment MedicationsClotting Factor Products. ... Plasma-derived Factor Concentrates. ... Recombinant Factor Concentrates. ... Hemlibra® (also known as ACE 910 or emicizumab) ... DDAVP® or Stimate® (Desmopressin Acetate) ... Amicar® (Epsilon Amino Caproic Acid) ... Cryoprecipitate. ... Blood Roots Documentary.
What is the most common treatment option for hemophilia?
TreatmentDesmopressin. In some forms of mild hemophilia, this hormone can stimulate the body to release more clotting factor. ... Emicizumab (Hemlibra). This is a newer drug that doesn't include clotting factors. ... Clot-preserving medications. ... Fibrin sealants. ... Physical therapy. ... First aid for minor cuts.
What is a new treatment alternative for hemophilia patients?
Emicizumab, a bispecific antibody that acts as a substitutive therapy for HA, has been approved for patients with and without inhibitors.
What is the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia?
Replacement of the congenitally deficient factor VIII or IX through plasma-derived or recombinant concentrates is the mainstay of treatment for hemophilia.
What is non factor therapy?
Therapies not based on replacing the missing factor (nonfactor-replacement approaches) include bispecific antibody technology that mimics the FVIII coagulation function, and inhibition of anticoagulant proteins (tissue factor pathway inhibitor [TFPI] and antithrombin [AT]) using antibodies, aptamers or RNA interference ...
What is prophylactic treatment in hemophilia?
Although initially FVIII/IX was administered on demand once bleeding started, increasingly it is now being used prophylactically. In haemophilia, prophylaxis can be defined as the administration of clotting factor concentrate in anticipation of or to prevent bleeding.
How do you stop haemophilia from bleeding?
Apply pressure to the bleeding area. Use an ice pop or piece of ice on the area. When the bleeding stops, help your child avoid hard or hot foods because they can restart the bleeding. If the bleeding does not stop within 20 minutes, call your care team.
How was hemophilia treated in the past?
Some of the early treatments used for hemophilia included lime, bone marrow, oxygen, thyroid gland, hydrogen peroxide or gelatin. In the 1930s, snake venom was used to help blood clotting. Hospital-based plasma transfusions were common treatments for hemophiliacs in the late 1920s and continued until the 1950s.
How is hemophilia diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis includes screening tests and clotting factor tests. Screening tests are blood tests that show if the blood is clotting properly. Clotting factor tests, also called factor assays, are required to diagnose a bleeding disorder. This blood test shows the type of hemophilia and the severity.
How can hemophilia be prevented?
At this time, there is no way to prevent hemophilia in someone who inherits a defective gene and thus produces too little clotting factor. If hemophilia runs in your family, you can be tested to see whether you carry the defective gene and receive counseling about your chance for having children with hemophilia.
What treatment options are available for a hemophiliac child who is bleeding and has a high factor VIII inhibitor titer?
Treatment options for bleeding BPAs provide hemostasis through pathways that circumvent the need for fVIII or fIX to generate thrombin. The 2 currently available BPAs are recombinant fVIIa (rfVIIa; Novoseven RT, Novo Nordisk) and activated prothrombin complex concentrate (aPCC; FEIBA VH, Baxalta).
Is FFP used to treat hemophilia?
FFP is the first product used to treat patients with hemophilia C.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- The main treatment for severe hemophilia involves replacing the clotting factor you need through a tube in a vein. This replacement therapy can be given to treat a bleeding episode in progress. It can also be given on a regular schedule at home to help prevent bleeding episodes. Some people receive continuous replacement therapy. Replacement clotti...