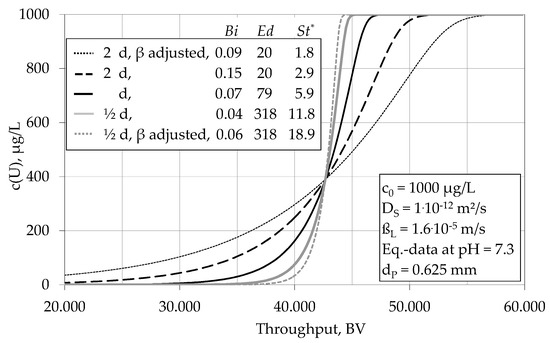
Treatment Technique (TT) - A required process intended to reduce the level of a contaminant in drinking water. Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level (MRDL) - The highest level of a disinfectant allowed in drinking water. There is convincing evidence that addition of a disinfectant is necessary for control of microbial contaminants.
Full Answer
What are the surface water treatment rules?
The Surface Water Treatment Rules were established to protect against these pathogens. To protect public health, drinking water from lakes, rivers streams and some other sources needs to be treated. This treatment includes disinfection and, in most cases, filtration.
What are the regulations for drinking water in the US?
Drinking Water Standards and Regulations The U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets standards and regulations for many different contaminants in public drinking water, including disease-causing germs and chemicals. Read the information below to learn more about EPA’s drinking water regulations. The Safe Drinking Water Act
What are the legal limits for contaminants in drinking water?
EPA sets legal limits on over 90 contaminants in drinking water. The legal limit for a contaminant reflects the level that protects human health and that water systems can achieve using the best available technology.
Does health and safety legislation apply to commercial water treatment?
Health and safety legislation, which covers water treatment practices, aims to minimise risk to building occupants and members of the public. The law, as discussed in the following article, applies to commercial settings.
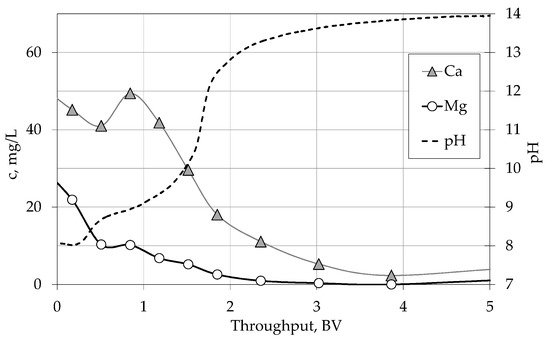
What are the 2 laws that protect water in America?
Other Environmental Laws Support the Protection of Drinking Water Sources. Other environmental laws help to protect drinking water, including the Clean Water Act. The Clean Water Act recommends states to designate surface waters used for drinking water and to establish water quality standards for those waters.
What are the 3 types of water quality standards?
Water quality standards consist of three core components. This includes designated uses of a water body, criteria to protect designated uses, and antidegradation requirements to protect existing uses and high quality/high value waters.
What is the acceptable level of TOC in drinking water?
All Answers (9) According to US EPA < 2 mg/L as TOC in treated / drinking water, and < 4 mg/Lit in source water which is use for treatment.
What is the EPA required level of turbidity for surface water treatment?
Conventional and direct filtration: The turbidity level of representative samples of CFE must be less than or equal to 0.3 NTU in at least 95% of the measurements taken each month. The maximum level of turbidity of the CFE must not exceed 1 NTU at any time.
What is water quality guidelines?
dd) “Water Quality Guidelines (WQG)” refer to the level for a water constituent or numerical values of physical, chemical, biological, and bacteriological or radiological parameters which are used to classify water resources and their use, which do not result in significant health risk.
What are the water quality parameters?
Water quality parameters include chemical, physical, and biological properties and can be tested or monitored based on the desired water parameters of concern. Parameters that are frequently sampled or monitored for water quality include temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, conductivity, ORP, and turbidity.
What is considered high TOC?
High-temperature catalytic oxidation at 680°C in an oxygen-rich environment inside tubes filled with a platinum catalyst followed by NDIR. Thermo-chemical oxidation with heat and a chemical oxidizer, usually a persulphate.
What is TOC in water treatment?
TOC is short for Total Organic Carbon, which within water treatment is referring to the total amount of organic carbon found in water.
What is the maximum contaminant level goal?
Maximum contaminant level goal or MCLG means the maximum level of a contaminant in drinking water at which no known or anticipated adverse effect on the health of persons would occur, and which allows an adequate margin of safety.
Who turbidity standards for drinking water?
The WHO (World Health Organization), establishes that the turbidity of drinking water shouldn't be more than 5 NTU, and should ideally be below 1 NTU.
What is turbidity EPA?
Turbidity is a measure of water clarity how much the material suspended in water decreases the passage of light through the water. Suspended materials include soil particles (clay, silt, and sand), algae, plankton, microbes, and other substances.
How much chlorine is in tap water ppm?
Municipal potable water supplies are usually chlorinated to provide a residual concentration of 0.5 to 2.0 ppm.
What are the primary standards for drinking water?
These standards require that contaminants within drinking water do not surpass regulatory levels in PWS. Common examples of contaminants that are within the primary standard category are arsenic, chlorine, chlorite, copper, fluoride, lead, and mercury.
What is alternative water treatment?
Alternative water sources typically require some form of treatment to remove contaminants from the water, depending on the application that will consume the water. Generally, water treatment includes filtration to physically separate solids and disinfection to kill bacteria and other biological contaminants.
What education do I need to become a scuba diver?
Education: Most states require at least a high school diploma or general education diploma. Experience: Some on-the-job experience, set by the state. Examination: Pass a certification test that covers mandatory capabilities and decision-making skills.
What is a PWS water system?
A PWS is considered a system that serves at least 25 people or 15 service connections. A certified operator is required ...
Why is it important to maintain disinfecting protocols?
Maintain disinfecting protocols to ensure that water is treated properly and that the process does not exceed regulation levels. Water sources that will be used in potable water end uses must be tested regularly for water quality. If it is determined that contaminant levels exceed EPA allowable levels – which will likely be ...
Is water potable or non potable?
Non-Potable. Water at this treatment level has not been treated to standards safe for human consumption, but is useful for specific end uses such as irrigation, dust suppression, toilet and urinal flushing, or make-up water for mechanical equipment.
Is potable water safe for humans?
Potable water is of sufficient quality for human consumption and is classified, permitted, and approved for human consumption. With proper treatment, it is possible to produce potable water from any alternative water source. Potable alternative water systems need to produce reliable potable water that meets SDWA requirements.
What is the purpose of the National Secondary Drinking Water Regulations?
National Secondary Drinking Water Regulations (NSDWR) are guidelines to help public water systems manage their drinking water for issues not related to health, such as taste, color, and smell. Water systems are not required to follow these water quality standards. external icon.
How often does the EPA publish the Contaminant Candidate List?
EPA must publish this list of contaminants—called the “Contaminant Candidate List,” or CCL—every five years and decide whether to regulate at least five or more of the contaminants on the list (called “Regulatory Determinations”).
What is the EPA water test?
EPA rules also set water-testing schedules and methods that water systems must follow. The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) gives individual states the opportunity to set and enforce their own drinking water standards if the standards are at a minimum as stringent as EPA's national standards.
How many contaminants are in the EPA?
Overview. EPA sets legal limits on over 90 contaminants in drinking water. The legal limit for a contaminant reflects the level that protects human health and that water systems can achieve using the best available technology. EPA rules also set water-testing schedules and methods that water systems must follow.
What is the EPA's unregulated contaminants program?
EPA uses the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Program to collect data for contaminants suspected to be present in drinking water, but that do not have health-based standards set under the SDWA. Every five years EPA reviews the list of contaminants, largely based on the Contaminant Candidate List.
What are the laws that protect drinking water?
Other environmental laws help to protect drinking water, including the Clean Water Act . The Clean Water Act recommends states to designate surface waters used for drinking water and to establish water quality standards for those waters. The Act also establishes programs to prevent the release of pollution to these waters.
What is the Safe Drinking Water Act?
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) of 1974 and its amendments establishes the basic framework for protecting the drinking water used by public water systems in the United States. This law contains requirements for ensuring the safety of the nation's public drinking water supplies.
What act regulates pesticides?
Pesticide affects on drinking water are primarily regulated by the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act and Food Quality Protection Act. Shipping of crude oil on the ocean is regulated by the Oil Pollution Act of 1990. Top of Page.
What is the stage 1 rule for disinfectants?
Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfectants By-Products Rule. Bladder Cancer, Reproductive Effects: Sets MCLs to reduce disinfectant and disinfectant by-products that may be found in the treatment plant and distribution system. Consumer Confidence Rule.
How many people are served by the public drinking water system?
Public drinking water supplies include water systems which regularly serve 25 or more people per day or which have at least 15 service connections.
What are the laws that regulate the use, transport, storage, release and generation of hazardous waste?
Laws regulating the use, transport, storage, release and generation of hazardous waste include the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (commonly known as Superfund ), and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
When was the SDWA amended?
In 1996 , the SDWA was amended, requiring EPA to, among other things, develop new regulations for a variety of contaminants. Below is a list of these new regulations and a brief description of the rule. The complete text of each rule may be found at the following web page:
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
Why is surface water more contaminated than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
Why is chlorine added to water?
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.
Why do people use water treatment units?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: Remove specific contaminants. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system. Improve the taste of drinking water.
Potable Water Treatment
While there are many regulations for drinking water, in this article we’ll highlight two key standards that are used to monitor the safety/purity of drinking water treatment chemicals. These are NSF/ANSI/CAN 60 and ABNT NBR 15784:
Swimming Pool Water Treatment
The Model Aquatic Health Code (MAHC) is a voluntary model pool code created and maintained by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the U.S. It is designed to help local, state and regional authorities and the aquatics industry sector reduce the risk of outbreaks, drowning and pool-related injuries.
Cooling and Retort Water Treatment
The U.S. FDA’s Code of Federal Regulations (21 CFR) contains sections that pertain to water treatment products used in food handling and food processing facilities, such as for cooling and retort water. NSF’s nonfood compounds (NFC) registration program, based on 21 CFR, registers water treatment products in the publicly listed White Book ™.
Boiler Water Treatment
An important regulation for boiler water treatment chemical manufacturers is the Chemical Inhibitor Approval Scheme (CIAS) in the UK. It is often used as a benchmark by manufacturers and third-party certifiers worldwide.
The NSF Mark Is Recognized Worldwide
No matter the end-use application you pursue, you can gain greater product acceptance through NSF certification and/or registration. Our programs address key regional and global requirements for water treatment chemicals, helping to ensure product compliance.
Rule Summary
This site provides information about the suite of the Surface Water Treatment Rules (SWTRs).
Rule History
EPA has developed the Surface Water Treatment Rules (SWTRs) to improve your drinking water quality. The regulations provide protection from disease-causing pathogens, such as Giardia lamblia, Legionella, and Cryptosporidium. The regulations also protect against contaminants that can form during drinking water treatment.
Compliance
EPA provides guidance documents to help states and public water systems implement the Surface Water Treatment Rules (SWTRs).