What is the maximum number of ECT treatments?
Feb 28, 2022 · Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a medical treatment that involves electrically stimulating the brain with electrodes to prompt a general seizure. This impacts the neurochemicals of the brain. It has been found to be a safe and effective treatment for treatment-resistant depression and bipolar disorder, as well as other mental health disorders not …
What are the pros and cons of ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT for short, is a treatment that involves sending an electric current through your brain, causing a brief surge of electrical activity within your brain (also known as a seizure). The aim of the treatment is to relieve …
How many ECT treatments does it take to work?
Oct 08, 2020 · Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a non-medication medical treatment that addresses severe psychiatric symptoms, after trials of medications and psychotherapy have been unsuccessful or a mental health disorder is determined to be severe and acute enough to warrant this intervention.
What are the long term effects of ECT treatment?
Oct 12, 2018 · Transcranial magnetic stimulation, Electroconvulsive therapy, Depression, Mood disorder, Mental disorder due to a gener ... Show more areas of focus Research Mayo Clinic's electroconvulsive therapy research group is part of the Consortium for Research in ECT, a federally-funded multisite research initiative.
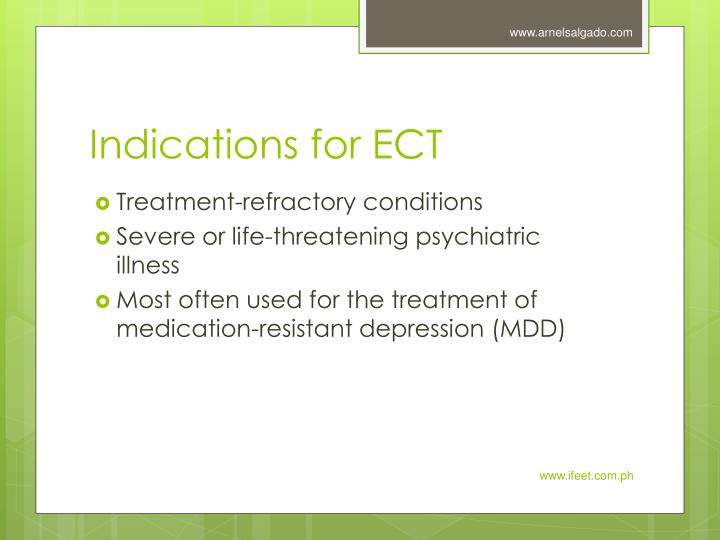
Is ECT a biological treatment?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a biological treatment procedure involving a brief application of electric stimulus to produce a generalized seizure.
Is ECT a cognitive treatment?
ECT treatment has been linked to decrements in anterograde and retrograde memory, attention, and executive function, with impairments persisting up to 6 months following completion of a course of ECT [11, 12]. Of note, there is great variability in the occurrence and severity of ECT-induced cognitive side effects.Oct 8, 2021
Is ECT a first line treatment?
ECT may be considered as a primary treatment (or first-line treatment) for persons exhibiting syndromes such as: severe major depression, acute mania, mood disorders with psychotic features, and catatonia.
Is ECT an alternative therapy?
It is most often used to treat severe depression and depression with psychosis that has not responded to medications. In some cases of treatment resistant bipolar disorder, ECT may be considered as a treatment option.
Does ECT lower IQ?
However, former patients have publicly testified that ECT can result in a very significant (>30 point) permanent decrement in IQ score (Food and Drug Administration, 1982; Andre, 2001; Cott, 2005: p.Jan 2, 2018
Does ECT cause confusion?
Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: Confusion. Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there.Oct 12, 2018
Does ECT damage the brain?
Despite many scientific and governmental authorities having concluded that ECT does not cause brain damage, there is significant evidence that ECT has indeed caused brain damage in some patients, both historically and recently, and evidence that it always causes some form or degree of brain damage.
Does ECT worsen anxiety?
ECT may have a role in people who have comorbid depression and anxiety. The concern of some psychiatrists is that while ECT may help with depressive symptoms, it could worsen anxiety symptoms, including obsessional thoughts or panic attacks.Mar 22, 2020
What part of the brain does ECT target?
In this study, results showed that ECT significantly increased GM voxel of the bilateral amygdale in the whole brain. Considering ECT as a kind of fast and effective treatment, the amygdala could be used as an important target in the treatment of MDD.Nov 26, 2016
What happens when ECT doesn't work?
If nothing else has helped, including ECT, and you are still severely depressed, you may be offered neurosurgery for mental disorder (NMD), deep brain stimulation (DBS) or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS).
When should ECT not be used?
Do not use electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) routinely for people with moderate depression but consider it if their depression has not responded to multiple drug treatments and psychological treatment.
Is electric shock therapy painful?
Freeman and R. E. Kendell of the University of Edinburgh found that 68 percent reported that the experience was no more upsetting than a visit to the dentist. For the others, ECT was more unpleasant than dentistry, but it was not painful. Still, the treatment is not hazard-free.
What is the treatment for ECT?
This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
Is ECT effective for mental health?
ECT’s effectiveness in treating severe mental illnesses is recognized by the American Psychiatric Association, the American Medical Association, the National Institute of Mental Health, and similar organizations in Canada, Great Britain and many other countries. Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, ...
Is ECT good for depression?
Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, ...
What is ECT therapy?
What is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT for short, is a treatment that involves sending an electric current through your brain, causing a brief surge of electrical activity within your brain (also known as a seizure).
Why is ECT used?
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends that ECT is only used to achieve quick, short-term improvements if you have: severe or life-threatening depression and your life is at risk so you need urgent treatment.
What are the benefits of ECT?
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends that ECT is only used to achieve quick, short-term improvements if you have: 1 severe or life-threatening depression and your life is at risk so you need urgent treatment 2 moderate to severe depression and other treatments such as medication and talking therapies haven't helped you 3 catatonia (staying frozen in one position, or making very repetitive or restless movements) 4 a severe or long-lasting episode of mania.
Can ECT cause memory loss?
This has sometimes been shown in films and TV shows, which may not reflect how ECT is carried out today. It can sometimes cause memory loss. This is often short-term, but can be longer-lasting as well. See our page on the side effects of ECT for more information.
Is repeated ECT good for schizophrenia?
a severe or long-lasting episode of mania. Repeated ECT is only recommended if you have previously responded well to it, or if all other options have been considered. ECT is not recommended for ongoing management of schizophrenia, or as a routine treatment for mild to moderate depression.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a non-medication medical treatment that addresses severe psychiatric symptoms, after trials of medications and psychotherapy have been unsuccessful or a mental health disorder is determined to be severe and acute enough to warrant this intervention. During this brain stimulation procedure, ...
Why is ECT important in psychiatry?
ECT is quite useful in psychiatry for the care of certain patients with significant depression, particularly for those who cannot take or are not responding to antidepressants, suffer from severe depression, or are at a high risk for suicide.
How much does an ECT cost?
The cost of each ECT session is about $2,500, for a total of $25,000 for the 10 sessions an average course of treatment entails.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
ECT relieves symptoms of depression within one to two weeks after beginning treatments. After a course of ECT, some patients will continue to have maintenance ECT, while others will return to or continue antidepressant or other psychiatric medications to maintain their mental health on a long-term basis.
How long does it take to get awake after ECT?
A person usually needs six to 12 treatments for this medical therapy to be effective. The patient is awake in five to 10 minutes. The most common side effects of ECT include brief confusion immediately after the procedure, as well as a temporary loss of short-term memory, which usually resolves within about six weeks.
What is the EEG used for?
In addition to having the person's breathing, temperature, heart functioning, and blood pressure monitored during the procedure, the doctor will monitor for the desired presence of seizure activity in the brain using an electroencephalogram ( EEG ), since seizure activity is not always physically visible.
Does ECT cause headaches?
Other side effects may include headache, high or low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, nausea, and sore muscles, although the muscle relaxant given to the ECT recipient decreases the frequency and severity of muscle soreness.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is available for people suffering from particular behavioral and emotional disturbances, including some forms of depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. It is most often used in the treatment of severe depression that has not responded to medications and psychotherapy.
How many sessions are there in ECT?
Conducted by the ECT Program coordinator on the same day as the PrePare clinic appointment. Treatment is a series of 6–15 sessions occurring on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays. ECT treatments occur in the morning and about three hours from the time of arrival until discharge.
Does UCSF cover ECT?
ECT is generally covered by health insurance providers. However, not all providers will cover ECT treatments at UCSF (even if the initial evaluation is covered). This is because many insurance providers have preferred, contracted ECT centers.
What is ECT in medical terms?
ECT is a procedure where controlled electric currents are passed through the brain while the person is under general anesthesia. This results in a brief, controlled seizure that affects neurons and chemicals in the brain. It is most often used to treat severe depression and depression with psychosis that has not responded to medications. In some cases of treatment resistant bipolar disorder, ECT may be considered as a treatment option.
What are the side effects of ECT?
Side effects of ECT may include: Physical effects, such as headaches, muscle pain, nausea. Confusion following treatment, which may last a few minutes or hours. Memory loss, which can range from forgetting conversations or events right before and after a treatment, forgetting things from weeks or months before treatment, and less commonly, ...
What is the most widely used brain stimulation therapy?
Other Brain Stimulation Therapies. ECT and TMS are the most widely used brain stimulation therapies, but there are two other options available. However, they have not been widely studied and their effectiveness remains unclear.
What is the procedure called to stimulate the brain?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) TMS is a procedure that creates magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of depression. With TMS, a large electromagnetic coil is placed on a person’s forehead and short pulses are directed into an area of the brain believed to control moods.
How long does TMS treatment last?
TMS treatments will last about 40 minutes. Unlike ECT, TMS does not require the use of anesthesia and person will remain awake during the treatment. Several sessions generally are required over a period of weeks.
Is ECT a treatment for bipolar disorder?
In some cases of treatment resistant bipolar disorder, ECT may be considered as a treatment option. Once called electroshock therapy, ECT still has many negative associations. When it was first used in the 1940s, it was very primitive. The reality today is different.
What is an ECT?
ECT is a medical procedure that can only be performed by a qualified physician or psychiatrist. Because general anesthesia is administered, electroconvulsive therapy carries with it similar risks that any medical procedure using anesthesia does. Hospital staff and an anesthesiologist monitor your vital signs during the procedure — including heart rate and blood pressure — to watch for any signs that you may be having difficulty with the treatment.
What is the side effect of ECT?
Memory Loss. Memory loss is the primary side effect associated with ECT treatment. Most people experience what’s called retrograde amnesia, which is a loss of memory of events leading up to and including the treatment itself. Some people’s memory loss is longer and greater with ECT. Some have trouble recalling events that occurred during ...
How long does confusion last after electroconvulsive therapy?
Many people who undergo the electroconvulsive therapy find that they experience a period of confusion after the procedure has been completed. You may forget why you’re in the hospital, or even what hospital you’re in. For most people, this confusion fades after a few hours, but can last as long as a few days after ...
How long does it take for memory to improve after ECT?
Memory loss generally improves within a few weeks after ECT treatment. As with psychiatric medications, no professional or doctor can tell you for certain what kind of memory loss you will experience, but virtually all patients experience some memory loss. Sometimes the memory loss in some patients is permanent. 2.
Why should patients with a history of heart problems not undergo ECT treatment?
Patients with a history of heart problems generally should not undergo ECT treatment, because the risk associated with receiving the electrical stimulation is greater. Last medically reviewed on May 17, 2016.
Can ECT cause headaches?
4. Other Side Effects. Similar to some psychiatric medications, some people undergoing ECT may experience physical side effects such as nausea, headaches, muscle aches or spasms, and vomiting.
Is electroconvulsive therapy safe?
Modern electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is generally considered a safe and effective treatment for severe, chronic depression and treatment-resistant depression, although it may occasionally be used to treat other conditions as well. Despite its general safety and efficacy, like psychiatric medications, it carries with it a number of side effects.

Why It's Done
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to e…
Risks
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…
How You Prepare
- Before having your first ECT treatment, you'll need a full evaluation, which usually includes: 1. Medical history 2. Complete physical exam 3. Psychiatric assessment 4. Basic blood tests 5. Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check your heart health 6. Discussion of the risks of anesthesia These exams help make sure that ECT is safe for you.
What You Can Expect
- The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
Results
- Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illness…
Does Ect Work?
- Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, such as bipolar disorder an...
What Are The Steps Involved When Getting ect?
- Before beginning a series of ECT treatments, a patient should receive a thorough psychiatric assessment, including a medical examination and sometimes a basic blood test and an electrocardiogram (ECG) to check heart health. Informed consent is another important part of the process. A patient must provide written informed consent before ECT is administered. In situati…
What Are The Risks and Benefits?
- Like any medical procedure, ECT is has some risks. ECT treatment has been associated with short-term memory loss and difficulty learning. Some people have trouble remembering events that occurred in the weeks before the treatment or earlier. In most cases, memory problems improve within a couple of months. Some patients may experience longer lasting problems, incl…
Other Brain Stimulation Treatments
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies. It involves the use of rapidly alternating magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Unlike ECT, TMS does not cause a seizure and the patient remains awake through the noninvasive process. TMS typically only has mild side effects including headaches, …
Resources
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2012. Therapies for Treatment Resistant Depression: A Review of the Research.
- National Institute of Mental Health: Brain Stimulation Therapies
- Mental Health America: Electroconvulsive Therapy
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): ECT, TMS And Other Brain Stimulation Therapies