convulsive therapy treatment of mental disorders, primarily depression, by induction of convulsions. The type almost universally used now is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), in which the convulsions are induced by electric current. In the past, drugs were sometimes used.
What is the initial treatment for a convulsion?
convulsive therapy treatment of mental disorders, primarily depression, by induction of convulsions. The type almost universally used now is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), in which the convulsions are induced by electric current. In the past, drugs were sometimes used.
What is the medical definition of convulsions?
Convulsive therapy has undergone many refinements since the first chemical inductions with camphor as early as the 16th century. Based on his observation that patients with both epilepsy and psychosis had fewer symptoms of psychosis when their epilepsy was active, Ladislas Joseph von Meduna first hypothesized in 1934 that inducing convulsions in patients with …
What are the different types of convulsions?
Jul 12, 2017 · In some cases, a convulsion may be the sign of an as-of-yet undiagnosed condition or caused by a drug treatment that can be adjusted or stopped. If epilepsy is involved, early diagnosis can ensure you get the appropriate treatment to better prevent future episodes.
What is electroconvulsive therapy used to treat?
Definition of convulsive. 1 a : constituting or producing a convulsion. b : caused by or affected with convulsions. 2 : resembling a convulsion in being violent, sudden, frantic, or spasmodic …

What to expect after ECT treatment?
When you awaken, you may experience a period of disorientation lasting from a few minutes to several hours. Headaches, jaw pain, and muscle soreness may occur. ECT requires a series of treatments, often initiated two to three times a week for a few weeks and then the frequency is tapered down.May 12, 2020
What is ECT treatment used for?
How many ECT treatments do you need?
What does shock treatment do to the brain?
Does ECT damage the brain?
Who qualifies for ECT?
Does ECT reset the brain?
Can ECT stop working?
Who is ECT Not recommended for?
What are the long term effects of electric shock?
| PSYCHOLOGICAL SYMPTOMS | NEUROLOGIC SYMPTOMS | PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS |
|---|---|---|
| Depression | Memory loss | Generalized pain |
| Posttraumatic stress disorder | Numbness | Fatigue, exhaustion |
| Insomnia | Headache | Reduced range of motion |
| Nightmares | Chronic pain | Contracture |
Is electro shock therapy still used today?
What was the consequences of shock therapy?
The shock therapy ruined the economies of Russia and east European countries. Since restructuring was carried out by market driven forces and not by the government implement policies, there was a disappearance of almost all industries in the region.Mar 31, 2018
Is convulsive therapy effective?
Convulsive therapy is still the most effective and rapidly acting antidepressant available, and is useful for the treatment and management of other conditions where less invasive pharmacological treatments have failed.
When was the first medically induced convulsive therapy introduced?
Medically induced convulsive therapies were introduced in 1934. Medically induced seizures involved the intramuscular (IM) administration of camphor and later pentylenetetrazol to elicit a therapeutic seizure (Sackeim and Prudic, 2005). The procedure had some success, which was remarkable during that time when few treatment options were available. In one report, approximately 50% of the patients had some degree of remission of their psychotic symptoms after an intervention. Unfortunately, chemically induced seizures were painful and could be difficult to control. Seizures could last longer than desired. The introduction of ECT by Cerletti and his assistant Bini provided a much improved mechanism to induce a therapeutic seizure.
What is ECT used for?
Not surprisingly, and in the absence of any other reliable and effective intervention, ECT was soon used throughout the world for the treatment of all major mental illnesses. It was effective in severe affective psychosis and offered new hope to those who had previously been considered ‘untreatable’. Patients had a series of electrically induced grand-mal seizures and often recovered from their mental illness but, because of the intensity of the uncontrolled seizure, they were prone to fractures and soft tissue injuries. In 1940, the British anaesthetist A.E. Bennett introduced curare, the first neuromuscular blocking agent, specifically for use in convulsive therapies. This successfully reduced physical movements but was replaced in 1951 by the more reliable agent suxamethonium, now widely used in many anaesthetic settings (Bennett 1994 ). Barbiturate anaesthetics were introduced soon afterwards, heralding modern ‘modified’ ECT.
What is a convulsion?
A convulsion is a general term used to describe uncontrollable muscle contractions. Among some of the common causes of convulsions are epileptic seizures, febrile seizures, non-epileptic seizures, and medication-induced convulsions.
How to diagnose a convulsion?
To diagnose the cause of a convulsion, a doctor will first take a medical history and consider any other symptoms a person has, followed by a physical examination. This likely will be followed by a focus on potential neurological causes or conditions that can trigger abnormal brain activity.
What are the conditions that can cause a convulsion?
A convulsion may be associated with any number of medical conditions, including epilepsy, a head injury, severe fever, an inflammatory brain infection, exposure to toxins, and certain medications. 1 .
How long does a convulsion last?
An episode may involve the whole body or be limited to a certain part, such as an arm or a leg. It may be brief, lasting for only a few seconds, or continue for a long period of time, increasing the risk injury.
What is the difference between a seizure and a convulsion?
The words convulsion and seizure often are used interchangeably, but physiologically they are different events. A seizure occurs due to an electrical disturbance in the brain, while a convulsion describes the involuntary action of jerking and contraction.
Can you have a seizure without a convulsion?
A seizure occurs due to an electrical disturbance in the brain, while a convulsion describes the involuntary action of jerking and contraction. It is possible, for example, to have an epileptic seizure without convulsions. It also is possible to have convulsions in the absence of epilepsy.
Can a convulsion be serious?
As alarming as a convulsion is, it can ultimately be caused by any number of things, some of which may not be serious. As a symptom of a condition (rather than a condition until itself), convulsions often resolve once the underlying cause is identified and treated.
What does "convulsive" mean?
Definition of convulsive. 1 a : constituting or producing a convulsion. b : caused by or affected with convulsions. 2 : resembling a convulsion in being violent, sudden, frantic, or spasmodic convulsive laughter.
What is the synonym for convulsive?
Choose the Right Synonym for convulsive. fitful, spasmodic, convulsive mean lacking steadiness or regularity in movement. fitful implies intermittence, a succession of starts and stops or risings and fallings. fitful sleep spasmodic adds to fitful the implication of rapid or violent activity alternating with inactivity.
What does it mean to be fitful?
fitful, spasmodic, convulsive mean lacking steadiness or regularity in movement. fitful implies intermittence, a succession of starts and stops or risings and fallings. fitful sleep spasmodic adds to fitful the implication of rapid or violent activity alternating with inactivity. spas modic growth convulsive suggests the breaking of regularity or quiet by uncontrolled movement. convulsive shocks
What are some examples of convulsive?
Examples of convulsive in a Sentence. the assassination of Martin Luther King was one of the most convulsive events of the 1960s after a day of convulsive trading, the stock market was down 300 points.
What was the most convulsive event of the 1960s?
the assassination of Martin Luther King was one of the most convulsive events of the 1960s after a day of convulsive trading, the stock market was down 300 points. Recent Examples on the Web On the heels of a humbling year, the Oscars — usually a frothy night of self-congratulation — this year may feel more like a therapeutic rally ...
Who was the first wife of the sailor?
His first wife, Maria Dmitrievna Isaeva, who knew nothing of his previous ailments, suddenly heard his unearthly shriek and witnessed his convulsive movements, fainting, foaming at the mouth, and uncontrolled urination. — Gary Saul Morson, The New York Review of Books, 15 June 2021 On the heels of a humbling year, ...
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, ...
What is it called when you have trouble remembering things that happened before you were treated?
This condition is called retrograde amnesia. You may also have trouble recalling events that occurred during the weeks of your treatment.
What is treatment resistant depression?
Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity that occurs as part of bipolar disorder.
Is ECT a serious procedure?
During ECT, heart rate and blood pressure increase, and in rare cases, that can lead to serious heart problems. If you have heart problems, ECT may be more risky.
What is a convulsion?
A convulsion is a type of seizure. Seizures involve bursts of electrical activity in the brain. There are many different types of seizures, and the symptoms of a seizure depend on where in the brain the seizure is happening. These electrical storms in the brain may be caused by illness, a reaction to a medication, or other medical conditions.
What causes a convulsion?
Convulsions can be a symptom of a number of conditions, including a sudden fever spike, tetanus, or very low blood sugar. Keep reading to learn more about what causes them and what to do if someone is having a convulsion.
What is a tonic clonic seizure?
There are many types of seizures, but a tonic-clonic seizure, otherwise known as grand mal seizure, is the type that usually involves convulsions. Having had febrile convulsions does not increase the risk of developing epilepsy. Some conditions that can lead to convulsions or seizures with convulsions are: brain tumor.
Can you have a convulsion if you don't have epilepsy?
Convulsions can occur during certain kinds of epileptic seizures, but you can have convulsions even though you don’t have epilepsy. Convulsions can be a symptom of a number of conditions, including a sudden fever spike, tetanus, or very low blood sugar. Keep reading to learn more about what causes them and what to do if someone is having ...
How long do convulsions last?
Convulsions are easy to spot, with symptoms such as: These symptoms usually last from a few seconds to several minutes, though they can last longer. Children may be cranky after a febrile convulsion and some may fall into a deep sleep lasting an hour or more.
How do you know if you have a convulsion?
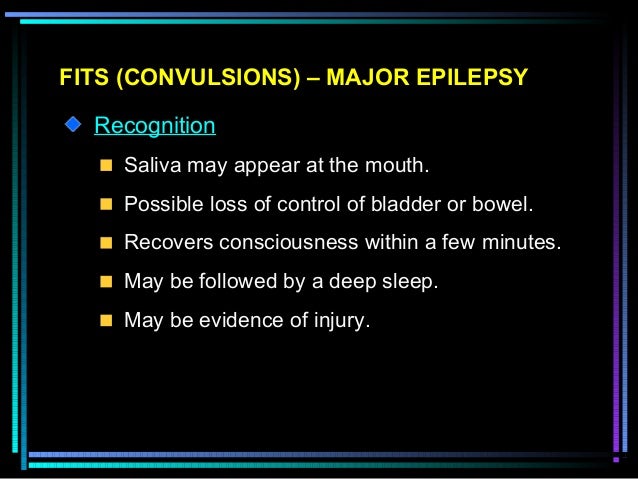
symptoms of convulsions. lack of awareness, loss of consciousness. eyes rolling back in the head. face that appears red or blue. changes to breathing. stiffening of the arms, legs, or whole body. jerky movements of the arms, legs, body, or head. lack of control over movements. inability to respond.
Can a child wake up after a convulsion?
Your child won’t wake up or looks very sick when the convulsion is over. Your child was already very ill before the convulsion. If your child had more than one convulsion. If a febrile convulsion was less than five minutes long, call your doctor and make an appointment as soon as possible.
What is the treatment for ECT?
This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
Is ECT a cure for mental illness?
Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, it is not a cure. To prevent a return of the illness, most people treated with ECT need to continue with some type of maintenance treatment. This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
Is ECT good for depression?
Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, ...
Is ECT effective for mental health?
ECT’s effectiveness in treating severe mental illnesses is recognized by the American Psychiatric Association, the American Medical Association, the National Institute of Mental Health, and similar organizations in Canada, Great Britain and many other countries. Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, ...
How long does a seizure last after a brain surgery?
The patient's brain is stimulated with a brief controlled series of electrical pulses. This causes a seizure within the brain that lasts for approximately a minute. The patient is asleep for the procedure and awakens after 5-10 minutes, much as from minor surgery.
How long does a seizure last after ECT?
This causes a seizure within the brain that lasts for approximately a minute. The patient is asleep for the procedure and awakens after 5-10 minutes, much as from minor surgery. Most insurance plans offering coverage for psychiatric disorders at least partially reimburse the cost of ECT.