Common Causes
Jaundice is not really a condition on its own but is a sign of another problem. so it is managed by treating the disease that is causing the buildup of bilirubin. 8 For a virus that will resolve on its own, jaundice may not require any special treatment, because the body will clear the bilirubin and the virus on its own.
Related Conditions
Besides the yellow color seen in the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, other symptoms of jaundice may include: 1 Itchy skin 1 1 2 Change in urine and stool color (urine may be pale or yellow-orange, stool may be pale) 3 Fatigue 1
How is jaundice treated?
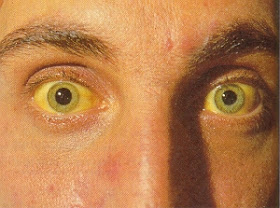
With moderate bilirubin levels, a person’s skin, eyes, and mucous membranes can turn yellow. As it progresses, the color can also change from yellow to green. The green color occurs due to biliverdin, the green pigment present in bile. Jaundice can develop in people of all ages and is normally the result of an underlying condition.
What are the symptoms of jaundice?
Why does jaundice turn my skin yellow?

How is white jaundice treated?
In adults, jaundice itself usually isn't treated. But your doctor will treat the condition that's causing it. If you have acute viral hepatitis, jaundice will go away on its own as the liver begins to heal. If a blocked bile duct is to blame, your doctor may suggest surgery to open it.
Can white jaundice cause death?
Yes, jaundice can be extremely fatal if left untreated for a long time. In certain cases, jaundice can also lead to death. It's important that you seek medical help as soon as you notice the onset of jaundice.
How do you detect white jaundice?
A bilirubin blood test is used to check the health of your liver. The test is also commonly used to help diagnose newborn jaundice. Many healthy babies get jaundice because their livers aren't developed enough to get rid of enough bilirubin. Newborn jaundice is usually not harmful and clears up within a few weeks.
How do you treat jaundice symptoms?
For moderate or severe jaundice, your baby may need to stay longer in the newborn nursery or be readmitted to the hospital....Treatments to lower the level of bilirubin in your baby's blood may include:Enhanced nutrition. ... Light therapy (phototherapy). ... Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg). ... Exchange transfusion.
Which antibiotic is best for jaundice?
Ceftriaxone and Jaundice in Neonates (CEFT) Brief Summary: Ceftriaxone is an antibiotic often used for the management of sepsis. Neonates commonly have jaundice during the first postnatal week. Ceftriaxone will be given as standard of care for sepsis and investigators will observe the effect on jaundice.
Which tablet is best for jaundice?
A healthcare professional may prescribe medications for those experiencing moderate to severe pruritis, such as cholestyramine or colestipol. As jaundice may sometimes indicate damage to the liver, a liver transplant may be necessary in some cases, depending on the severity of the injury.
What are the 3 types of jaundice?
There are three main types of jaundice: pre-hepatic, hepatocellular, and post-hepatic.Pre-Hepatic. In pre-hepatic jaundice, there is excessive red cell breakdown which overwhelms the liver's ability to conjugate bilirubin. ... Hepatocellular. ... Post-Hepatic.
How long can you live with jaundice?
Median overall survival after onset of jaundice was 1.5 months and it was similar between groups, but improved to 9.6 months in patients who were able to receive further chemotherapy.
What is the main cause of jaundice?
Jaundice is often a sign of a problem with the liver, gallbladder, or pancreas. Jaundice can occur when too much bilirubin builds up in the body. This may happen when: There are too many red blood cells dying or breaking down (hemolysis) and going to the liver.
Can jaundice cure itself?
Most types of jaundice go away on their own. Others need treatment to lower bilirubin levels.
How long is jaundice recovery?
Your body needs at least 6 months to recover from Jaundice. This time is needed by the liver to regain its efficacy. Routine tests are done to check the working of the liver and the enzymes that are created by them.
What are the symptoms of jaundice in adults?
In people with jaundice, the following symptoms are cause for concern: Severe abdominal pain and tenderness. Changes in mental function, such as drowsiness, agitation, or confusion. Blood in stool or tarry black stool.
How to treat jaundice?
The following treatments are used: Anemia-induced jaundice may be treated by boosting the amount of iron in the blood by either taking iron supplements or eating more iron-rich foods. Iron supplements are available for purchase online.
Why does jaundice happen?
Jaundice most often happens as a result of an underlying disorder that either causes the production of too much bilirubin or prevents the liver from getting rid of it. Both of these result in bilirubin being deposited in tissues.
What is the bilirubin level?
The level of bilirubin is defined in a blood test called a bilirubin test. This measures unconjugated, or indirect, bilirubin levels. These are responsible for the onset of jaundice. Bilirubin levels are measured in milligrams per decilitre (mg/dL).
What is the name of the disease that prevents conjugated bilirubin from being secreted from the
Dubin-Johnson syndrome: This is an inherited form of chronic jaundice that prevents conjugated bilirubin from being secreted from of the cells of the liver. Pseudojaundice: This is a harmless form of jaundice. The yellowing of the skin results from an excess of beta-carotene, not from an excess of bilirubin.
What is hepatocellular jaundice?
Hepatocellular jaundice occurs as a result of liver disease or injury. Hemolytic jaundice occurs as a result of hemolysis, or an accelerated breakdown of red blood cells, leading to an increase in production of bilirubin. Obstructive jaundice occurs as a result of an obstruction in the bile duct.
What is the yellow substance that is found in the bloodstream?
Bilirubin is a yellow-colored waste material that remains in the bloodstream after iron is removed from the blood. The liver filters waste out from the blood. When bilirubin reaches the liver, other chemicals attach to it. A substance called conjugated bilirubin results. The liver produces bile, a digestive juice.
What causes jaundice in the liver?
Underlying conditions that may cause jaundice include: Acute inflammation of the liver: This may impair the ability of the liver to conjugate and secrete bilirubin, resulting in a buildup. Inflammation of the bile duct: This can prevent the secretion of bile and removal of bilirubin, causing jaundice.
What are the symptoms of jaundice?
Besides the yellow color seen in the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, other symptoms of jaundice may include: Change in urine and stool color (urine may be pale or yellow-orange, stool may be pale)
How to tell if you have jaundice?
Besides the yellow color seen in the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, other symptoms of jaundice may include: 1 Itchy skin 1 1 2 Change in urine and stool color (urine may be pale or yellow-orange, stool may be pale) 3 Fatigue 1
Why does bilirubin build up?
Causes. The buildup of bilirubin can be caused by an abnormally high number of red blood cells breaking down, gallstones, or liver disease (such as hepatitis or cirrhosis ). 2 Jaundice sometimes affects newborns ("newborn jaundice") because their livers are too immature to process the bilirubin in their bodies.
What is the cause of yellowish skin?
on January 27, 2020. Jaundice is when a buildup of bilirubin in the blood causes the skin, mucous membranes, and the white part of the eyes to appear yellowish. Bilirubin is a reddish-yellow substance produced when red blood cells break down. It is excreted through the liver in the bile and then out of the body in the stool.
What causes jaundice in the liver?
Here's how some of the conditions that cause jaundice might be treated: Alcohol-related cirrhosis or hepatitis: If alcoholic beverages are the cause of liver disease, stopping drinking is going to be crucial to resolving jaundice. Anemia: If hemolytic anemia, the lack of red blood cells caused by increased desruction, is the cause of jaundice, ...
What is the treatment for sclerosing cholangitis?
This liver disease is associated with ulcerative colitis. Treatment is largely to manage symptoms, such as antibiotics and cholestyramine or diphenhydramine for itching.
What is the treatment for liver cancer?
Liver cancer: Cancer of the liver will require treatment from a specialist and may include radiation and chemotherapy, as well as other medications for supportive therapy . Newborn jaundice: Newborn jaundice is common, and will often resolve on its own without any treatment.
Why do I have jaundice?
Jaundice is due to a build-up of a chemical called bilirubin in the tissues of the body. Bilirubin is a normal body chemical but can build up to abnormally high levels in various diseases.
How long does jaundice last?
As a rule, the jaundice is not likely to be physiological jaundice if the baby is unwell and/or the jaundice is present in the first 24 hours after birth or lasts for more than 10 days.
Why does bilirubin build up in the bloodstream?
In some conditions the liver cells are unable to take in the bilirubin very well, so bilirubin builds up in the bloodstream. Sometimes there is a problem with the chemicals (enzymes) within the liver cells that process the bilirubin.
What is the name of the water soluble bilirubin that is taken up by the liver?
This water-soluble bilirubin is called conjugated bilirubin. (The bilirubin in the blood before being taken up by liver cells is called unconjugated bilirubin.) The liver cells pass out the conjugated bilirubin into tiny tubes called bile ducts. The bilirubin is therefore now part of bile.
Why is there a backlog of bilirubin in the blood?
Therefore, a backlog of bilirubin builds up in the blood awaiting the liver cells to process it.
What causes bilirubin to be high?
This increased amount of bilirubin then spills into the tissues of the body to cause jaundice. Conditions that cause an increased rate of breakdown of red blood cells include: Some genetic diseases, such as sickle cell anaemia, thalassaemia, spherocytosis, and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Where is bilirubin carried?
Bilirubin is carried around the bloodstream. As the blood flows through the liver, the liver cells take up the bilirubin. Chemicals in the liver cells slightly alter the structure of the bilirubin to make it water-soluble. This water-soluble bilirubin is called conjugated bilirubin. (The bilirubin in the blood before being taken up by liver cells is called unconjugated bilirubin.)
Symptoms
The common symptoms of jaundice usually include a yellowish or brownish-orange tinge of skin, eyes, body fluids like urine and stool. Other signs and symptoms due to the causative factors include:
Diagnosis And Treatment
The doctor usually does a thorough physical check-up of the skin and eyes and acknowledge the patient’s past medical history to understand the type and cause of jaundice. The doctor may also perform a series of tests including:
What does it mean when you have jaundice?
Jaundice clearly means that there’s too much bilirubin in your blood, but the underlying cause can vary widely. See your doctor right away if you notice yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes.
What are the symptoms of hepatic jaundice?
Common symptoms of hepatic jaundice include: loss of appetite. bloody nose. skin itching. weakness. abnormal weight loss. swelling of your abdomen or legs. dark urine or pale stool.
What is the most common type of jaundice in newborns?
Neonatal jaundice is a common type of jaundice that happens to newborn babies. Most babies are born with a lot of red blood cells, and because the liver isn’t fully developed yet, bilirubin can’t be processed quickly. As a result, your child may have jaundice symptoms a few days after they’re born.
Why is bilirubin high in liver?
Hepatic jaundice happens when your liver tissue is scarred (known as cirrhosis ), damaged, or dysfunctional. This makes it less effective at filtering out bilirubin from your blood. Since it can’t be filtered into your digestive system for removal, bilirubin builds up to high levels in your blood.
What organs are affected by post hepatic jaundice?
of post-hepatic jaundice are: gallstones, hard calcium deposits in the gallbladder that can block bile ducts. pancreatic cancer, the development and spread of cancer cells in the pancreas, an organ that helps produce digestive substances. bile duct cancer, the development and spread of cancer cells in your bile ducts.
What tests are used to test for jaundice?
imaging tests, such as an MRI or ultrasound, to examine your liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts to rule out other forms of jaundice.
Why do babies get jaundice when they are breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding. Breast milk jaundice occurs from a baby having trouble breastfeeding or not getting enough breast milk. Incompatible blood type. This results from a baby and mother having different blood types, which can cause the mother to make antibodies that break down her baby’s red blood cells.
How do you know if you have jaundice?
Individuals with jaundice may experience any of the following signs and symptoms. Pale-colored stools. Dark-colored urine.
What is the cause of jaundice?
The causes of jaundice are generally classified as pre-hepatic (the problem arises before secretion to the liver), hepatic (the problem arises within the liver), and post-hepatic (the problem arises after bilirubin is excreted from the liver).
What are the risks of developing jaundice?
People who are at an increased risk of exposure to the different types of viral hepatitis (for example, hepatitis B and hepatitis C) are at risk of developing jaundice at the time of infection or subsequently, if liver disease occurs or if liver cancer develops later. Other risk factors include:
How long does cirrhosis last?
Symptoms include yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue. The prognosis is good for some people with cirrhosis of the liver, and the survival can be up to 12 years; however the life expectancy is about 6 months to 2 years for people with severe cirrhosis with major complications.
What causes post hepatic jaundice?
This leads to increased levels of conjugated bilirubin in the bloodstream. Conditions that can cause post-hepatic jaundice include. Gallstones, Cancer ( pancreatic cancer, gallbladder cancer and bile duct cancer ), Strictures of the bile ducts, Cholangitis, Pancreatitis, and. Parasites (for example, liver flukes).
What is the yellowish discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and of the white of the
Jaundice definition and facts. Jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes and of the white of the eyes caused by elevated levels of the chemical bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia). The term jaundice is derived from the French word jaune, which means yellow. Jaundice is not a disease per se, ...
What is the normal level of bilirubin in the blood?
Jaundice is typically seen when the level of bilirubin in the blood exceeds 2.5-3 mg/dL (milligrams per deci liter). Jaundice in adults can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, some of which are serious and potentially life-threatening. Any adult who develops jaundice needs to undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation in order ...
What does jaundice mean?
The term jaundice is derived from the French word jaune, which means yellow. Jaundice is not a disease per se, but rather a visible sign of an underlying disease process. Jaundice is typically seen when the level of bilirubin in the blood exceeds 2.5-3 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter).
Why do I have jaundice?
Jaundice in adults is caused by various medical conditions that affect the normal metabolism or excretion of bilirubin. Bilirubin is mostly formed from the daily breakdown and destruction of red blood cells in the bloodstream, which release hemoglobin as they rupture.
What is the yellowing of the skin?
Jaundice, also referred to as icterus, is the yellow staining of the skin and sclerae (the whites of the eyes) by abnormally high blood levels of the bile pigment, bilirubin. The yellowing extends to other tissues and body fluids and also may turn the urine dark.
Why do you need antibiotics for jaundice?
Antibiotics may be required for infectious causes of jaundice, or for the complications associated with certain conditions leading to jaundi ce (for example, cholangitis). Blood transfusions may be required in individuals with anemia from hemolysis or as a result of bleeding.
How long does cirrhosis last?
Symptoms include yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue. The prognosis is good for some people with cirrhosis of the liver, and the survival can be up to 12 years; however the life expectancy is about 6 months to 2 years for people with severe cirrhosis with major complications.
Why do I have jaundice during the hepatic phase?
Jaundice caused during the hepatic phase can arise from abnormalities in the metabolism and/or excretion of bilirubin. This can lead to an increase in both unconjugated and/or conjugated bilirubin levels. Conditions with a hepatic cause of jaundice include:
How do you know if you have jaundice?
Individuals with jaundice may experience any of the following signs and symptoms. Pale-colored stools. Dark-colored urine.
