Medication
- advanced age. At age 70, the risk of developing complications increases; this risk increases further after age 80.
- female sex. There's no specific data why, but research shows women develop more complications postcatheterization than men.
- renal failure/insufficiency. ...
- venous sheath. ...
- previous cardiac intervention. ...
- urgency of procedure. ...
Procedures
Ventricular fibrillation ( V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by death in the absence of treatment.
Nutrition
Treatment
- Medications. You may be prescribed medications to control how fast your heart beats and restore it to a normal rate.
- Cardioversion therapy. If A-fib symptoms are bothersome or if this is the first episode of atrial fibrillation, a doctor may attempt to reset the heart rhythm (sinus rhythm) using a ...
- Surgery or catheter procedures. ...
What causes V fib after a cardiac catheterization?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is the most important shockable cardiac arrest rhythm. The ventricles suddenly attempt to contract at rates of up to 500 bpm. This rapid and irregular electrical activity renders the ventricles unable to contract in a synchronised manner, resulting in immediate loss of cardiac output.
Does V fib have a pulse?
How to treat V fib?
Is V fib a shockable rhythm?
See more
What is the most effective treatment for V-fib?
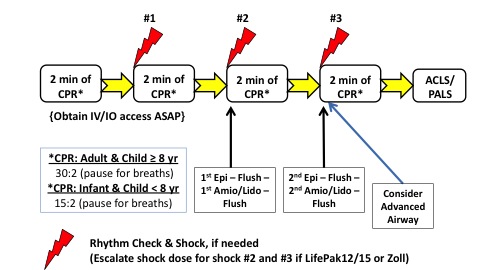
External electrical defibrillation remains the most successful treatment for ventricular fibrillation (VF). A shock is delivered to the heart to uniformly and simultaneously depolarize a critical mass of the excitable myocardium.
How can V-fib be treated?
How is ventricular fibrillation treated?CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation). The first response to V-fib may be CPR. ... Defibrillation. ... Medicines. ... Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). ... Catheter ablation. ... Left cardiac sympathetic denervation.
What is the drug of choice for V-fib?
The guidelines recommend administration of amiodarone for sustained ventricular fibrillation (Vf) and ventricular tachycardia (VT) refractory to CPR, defibrillation, and vasopressor in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Lidocaine is recommended as an alternative to amiodarone.
Is V-fib an emergency?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is an emergency condition that, without immediate treatment, leads to death. In the event of this malignant ventricular arrhythmia chaotic, disorganized electrical activity appears in the ventricular myocardium.
What triggers ventricular fibrillation?
A heart that has been damaged by a heart attack or other heart muscle damage is vulnerable to V-fib. Other causes include electrolyte abnormalities such as low potassium, certain medicines, and certain genetic diseases that affect the heart's ion channels or electrical conduction.
Does a pacemaker help ventricular fibrillation?
A dual chamber pacemaker paces the atrium and ventricle. A biventricular pacemaker paces both ventricles. An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator can work as a pacemaker would. In addition, if it detects ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation, it sends out a shock to reset the heart to a normal rhythm.
Do you give amiodarone for VFib?
In summary, amiodarone may be administered for VF or pulseless VT unresponsive to CPR, shock, and a vasopressor (Class IIb). An initial dose of 300 mg IV/IO can be followed by one dose of 150 mg IV/IO.
Is epinephrine used for V fib?
Clinical studies suggest that epinephrine facilitates ventricular fibrillation (VF) although mechanisms remain unclear. We tested the hypothesis that epinephrine increases the probability of inducing VF and stabilizes VF in association with shortening of fibrillation action potential duration.
When do you give EPI in VFib?
Currently, the ACLS protocol for v fib and pulseless v tach recommends that epinephrine be given after the second defibrillation.
Can V-fib correct itself?
Ventricular fibrillation seldom terminates spontaneously, since several re-entrant wavefronts, independent from each other, coexist, and the simultaneous extinction of all the circuits is unlikely.
How Long Can You Live With V-fib?
Survival: Overall survival to 1 month was only 1.6% for patients with non-shockable rhythms and 9.5% for patients found in VF. With increasing time to defibrillation, the survival rate fell rapidly from approximately 50% with a minimal delay to 5% at 15 min.
Why is V-fib worse than AFIB?
Ventricular fibrillation is more serious than atrial fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation frequently results in loss of consciousness and death, because ventricular arrhythmias are more likely to interrupt the pumping of blood, or undermine the heart's ability to supply the body with oxygen-rich blood.
Diagnosis and Tests
Ventricular fibrillation is usually confirmed by an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), especially after a person has been resuscitated from cardiac arrest. This is also useful to determine the heart’s ability to function going forward.
Management and Treatment
The condition is a life-threatening medical emergency and every minute counts. The following actions can help save the life of someone who has gone into sudden cardiac arrest because of ventricular fibrillation:
Frequently Asked Questions
Atrial fibrillation is similar to ventricular fibrillation, but it’s happening in the upper chambers of the heart, called the atria. When the atria fibrillate, they beat very fast (sometimes several hundred times per minute). This can cause blood to collect in the atria and over time, this can cause the atria to stretch and enlarge.
What is the procedure to eliminate electrical triggers of V-FIB?
Catheter ablation. This procedure uses energy to destroy small areas of your heart affected by the irregular heartbeat. This rarely used procedure for V-fib looks to eliminate electrical triggers of V-fib.
What is a V-fib?
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is a dangerous type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. It affects your heart’s ventricles. Your heart is a muscle system that contains 4 chambers; the 2 bottom chambers are the ventricles. In a healthy heart, your blood pumps evenly in and out of these chambers. This keeps blood flowing throughout your body.
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Key points about ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, that affects your heart’s ventricles. Ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. CPR and defibrillation can restore your heart to its normal rhythm and may be life saving.
What is an implantable cardiac defibrillator?
Implantable cardiac defibrillators are devices that are implanted within the body that can shock the heart back to normal rhythm within seconds if V-fib is present. Although this device does not necessarily prevent V-fib, it can rapidly and automatically diagnose and treat this potentially fatal heart rhythm.
What causes V-FIB in the heart?
Other causes include electrolyte abnormalities such as low potassium, certain medicines, and certain genetic diseases that affect the heart's ion channels or electrical conduction.
Can a defibrillator help with ventricular fibrillation?
Medications and cardiac procedures after an episode of ventricular fibrillation can prevent or reduce the chances of another episode. An implantable cardiac defibrillator can promptly treat V-fib.
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
These warning signs may include: Chest pain. Very fast heartbeat (tachycardia) Dizziness. Nausea.
What to do if you have a fast heartbeat?
If you see someone collapse, seek emergency medical help immediately. Follow these steps: Call 911 or your local emergency number . If the person is unconscious, check for a pulse.
What causes the ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood?
In ventricular fibrillation, rapid, irregular electrical signals cause the ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood. To understand how ventricular fibrillation occurs, it may be helpful to know how the heart normally beats.
How to do CPR with no pulse?
If no pulse, begin CPR to help keep blood flowing through the body until an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available . The American Heart Association recommends hands-only CPR. Push hard and fast on the person's chest — about 100 to 120 times a minute.
What is VF in cardiac arrest?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one . 5 In VF, the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non-ischemic arrhythmia. 8
What is the most important intervention for cardiac arrest?
Irrespective of the cause of cardiac arrest, the most important interventions are early recognition and calling for help—including appropriate management of the deteriorating patient—early defibrillation, high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) with minimal interruption of chest compressions, and treatment of reversible causes. 6
How many joules should a defibrillator be?
If the defibrillator is biphasic, the manufacturer recommended joules should be selected (usually 120 to 200 joules). If the amount is unknown, use the maximum available and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and possibly higher. 1.
What are the causes of VF?
The easiest way to remember the most common causes of VF are to review the reversible “Hs and Ts” in cardiac arrest. The Hs include hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, and hydrogen ions (acidosis). The Ts are tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary).
What to do if you have a V-fib?
Step 2: Defibrillation to fix your heart rhythm. Step 3: Medication to make the rhythm stable again. Defibrillators for V-fib.
What happens if you have a V-FIB?
Shortness of breath. Passing out. Sudden cardiac arrest is the worst thing that can happen with V-fib. The two main signs are not responding to someone touching or speaking to you, and having severe problems breathing (gasping for air or not breathing at all).
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
The main symptom is fainting. You may also have symptoms of ventricular tachycardia (VT). This is when the lower chambers of your heart beat too fast. It can lead to V-fib. Signs and symptoms of VT include: Chest pain. Pounding or fast heartbeat.
What are the complications of V-FIB?
V-fib can lead to serious complications including: Injuries from CPR. Skin burns from defibrillation. Brain injury from a lack of oxygen. Injury to your heart muscle. Death. Ventricular Fibrillation Prevention. You can’t completely prevent an episode of ventricular fibrillation.
Why do doctors not know what causes ventricular fibrillation?
For instance, it happens most often during or right after a heart attack. That may be because the heart’s electrical signals can become unstable when there isn’t enough blood flow.
What tests are used to check for heart damage?
Tests of how well your heart works, such as an EKG. Blood tests to look for heart damage. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI exams, and echocardiograms. Ventricular Fibrillation Treatment. V-fib comes on quickly and needs treatment just as fast.
How to prevent VF?
A healthy lifestyle is vital to keeping your heart healthy and preventing VF. This means: 1 You should eat a healthy diet. 2 You should stay active, such as by walking 30 minutes per day. 3 If you smoke, start thinking about ways to help you quit. Smoking can affect your arteries’ flexibility and overall cell health. Taking steps to quit can make a dramatic difference in your heart health. 4 Maintaining a healthy weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can also help to prevent cardiac issues, such as VF.
What are the symptoms of a ventricular fibrillation?
What Are the Symptoms of Ventricular Fibrillation? When VF occurs, the two chambers in the lower portion of your heart aren’t able to pump hard enough to move blood through your body. These lower chambers are called ventricles. This makes your blood pressure drop quickly and keeps blood from traveling through your body.
What is VF in heart?
VF often begins with ventricular tachycardia, which is a very rapid heartbeat that changes the electrical impulses in your heart. This most often occurs in people who have scar tissue from previous heart attacks or heart muscle damage due to heart conditions.
What is VF in medical terms?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is a condition in which your heart beats in an abnormal rhythm. Your heart should beat in a regular, steady pattern. VF causes your heart to beat quickly and out of rhythm.
What type of surgery is required to bypass a blocked artery?
More invasive surgery types, such as coronary bypass surgery, may also be required. Coronary bypass surgery involves the attachment of a healthy artery to your blocked one. This will allow blood to bypass the blocked artery and flow smoothly through the newly attached artery.
What is the procedure to open a blocked artery?
If any of your heart’s arteries is blocked, you may require cardiac catheterization with angioplasty, which involves the insertion of a thin tube into your heart to open the blocked artery. A cardiac stent, which is a mesh tube, may also be permanently placed in the artery to help it remain open.
How do you know if you have VF?
Fainting or losing consciousness are the most common symptoms of VF, earlier symptoms include: chest pain. dizziness. nausea. rapid, fluttering heartbeat. shortness of breath. These early symptoms can occur one hour or less before fainting or loss of consciousness occurs.
What is the best treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
Reducing your risk. If you’re at risk for ventricular fibrillation and its serious consequences, your doctor may recommend: Arrhythmia medications , which can help control rhythm disturbances. An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), which can correct abnormal heart rhythms.
What to do if you suspect someone is in cardiac arrest?
No normal breathing (the victim is not breathing or is only gasping) If you suspect someone is suffering from cardiac arrest, it’s vital to respond appropriately and quickly. Call 911, give CPR and use an automated external defibrillator (AED) (PDF) if one is available.
What is a Ventricular Arrhythmia (VTACH or VFIB)?
Ventricular arrhythmias are those originating from the ventricles. Since the ventricles are responsible for pumping blood to the lungs and throughout the body, ventricular arrhythmias are often deadly.
What Causes Ventricular Arrhythmias?
Ventricular arrhythmias are usually caused by coronary artery disease (CAD). Any lack of blood flow (i.e. a heart attack) will cause ventricular cells to be deprived of oxygen. When the cardiac myocytes become hypoxic, they become irritable and prone to firing when they shouldn’t, which leads to PVCs, VTACH, and even VFIB.
IDENTIFYING VTACH
VTACH is a tachycardic rhythm originating within the ventricles. This produces very fast heart rates which may or may not be perfusing.
MONOMORPHIC VTACH
Monomorphic VTACH originates from the same ventricular focus. This means that the same ventricular cells or region of cells are functioning as the pacemaker for this rhythm.
POLYMORPHIC VTACH
Polymorphic VTACH originates from multiple different ventricular foci.
QT Prolongation
QT prolongation is the main cause of Torsades and is defined when the QT interval is >440ms in men and >460ms in women.
IDENTIFYING VFIB
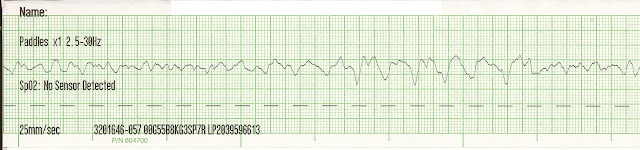
VFIB is similar to polymorphic VTACH, but on a much wider scale. Essentially, all of the ventricular cells are irritable and it produces a disorganized chaotic arrhythmia that does not perfuse the body and is a CODE BLUE.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support