What is monogenic diabetes?
1. Guava...
2. Apples...
3. Cherries...
4. Grapefruit...
5. Gokhru...
6. Avocado...
7. Strawberries...
8. Oranges...
Learn More...How do you know if you have monogenic diabetes?
Monogenic diabetes is a rare condition resulting from mutations (changes) in a single gene. In contrast, the most common types of diabetes— type 1 and type 2 —are caused by multiple genes (and in type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors such as obesity).
What is MODY diabetes and how is it treated?
Most cases of monogenic diabetes are incorrectly diagnosed. For example, when high blood glucose is first detected in adulthood, type 2 diabetes is often diagnosed instead of monogenic diabetes. If your health care provider thinks you might have monogenic diabetes, genetic testing may be needed to diagnose it and to identify which type.
How is genotype testing used to treat monogenic diabetes?
MODY is a monogenic form of diabetes that usually first occurs during adolescence or early adulthood. MODY accounts for up to 2 percent of all cases of diabetes in the United States in people ages 20 and younger. 3 A number of different gene mutations have been shown to cause MODY, all of which limit the ability of the pancreas to produce insulin.
What percentage of diabetes is monogenic?
Genetic testing can be helpful in selecting the most appropriate treatment for individuals with monogenic diabetes. Testing is also important in planning for pregnancy and to understand the risk of having a child with monogenic diabetes if you, your partner, or your family members have monogenic diabetes.
How do doctors diagnose polygenic diabetes?
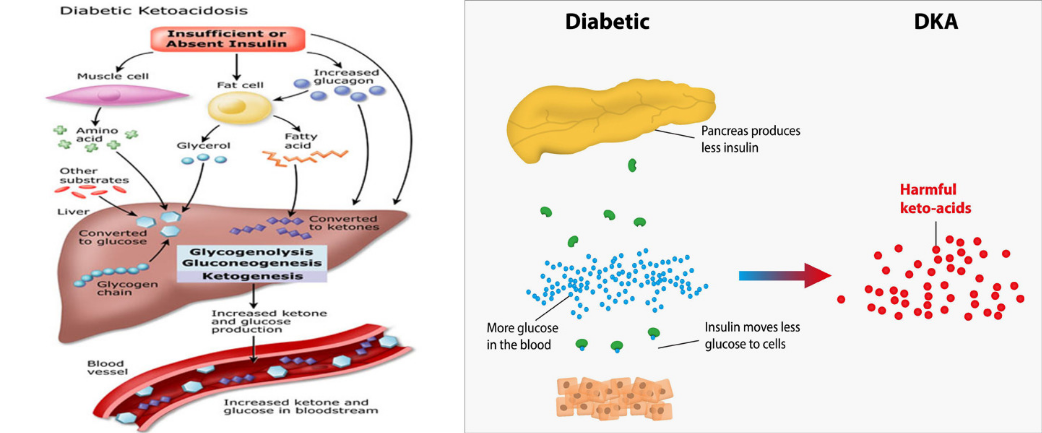
What is the name of the type of diabetes that is characterized by frequent urination, rapid breathing, and
What is the name of the disease that causes the body to produce insulin?
Why is genetic testing important?
How rare is NDM?
What happens if a gene mutation causes diabetes?
See more
About this website

What are the symptoms of monogenic diabetes?
What are the Signs and Symptoms?Frequent urination.Thirst.Dehydration.Blurry vision.Recurrent skin infections.Recurrent yeast infections.
What is monogenic diabetes?
Monogenic diabetes is a rare condition resulting from mutations (changes) in a single gene. In contrast, the most common types of diabetes—type 1 and type 2—are caused by multiple genes (and in type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors such as obesity).
How is monogenic diabetes diagnosed?
Blood sugar tests and genetic testing are used to diagnose monogenic diabetes like MODY and NDM. Genetic testing can be done on blood or saliva samples. The DNA is examined for changes in the genes that cause monogenic diabetes.
What is the treatment for MODY?
MODY 1 and MODY 4. They're usually treated with sulfonylureas, a type of diabetes medication. These drugs cause your pancreas to make more insulin. Some people with MODY 1 and MODY 4 may also need to take insulin.
What is the cause of monogenic diseases?
Monogenic disorders are caused by the inheritance of single gene mutations; alternatively, a monogenic disorder arises as a consequence of a de novo mutation in either the paternal or maternal germ line.
What are monogenic disorders?
Monogenic disorders (monogenic traits) are caused by variation in a single gene and are typically recognized by their striking familial inheritance patterns. Examples include sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, Huntington disease, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Can MODY diabetes be cured?
The most common types of MODY are: Diabetes usually develops in adolescence or early twenties, and people with HNF1-alpha MODY generally don't need to take insulin: they can be treated with small doses of a group of tablets called sulphonylureas (often used in type 2 diabetes).
How many human monogenic diseases are known?
There are 5,000–8,000 monogenic diseases, defined as inherited conditions arising from mutations on a single gene. These often manifest during childhood and lead to morbidity and sometimes premature death.
What is the difference between type 2 diabetes and MODY?
MODY has an early age of onset, whereas type 2 diabetes is more commonly diagnosed in people over age 45. While MODY is not usually associated with overweight or obesity, someone who is obese with MODY may develop symptoms sooner than someone who is not affected by overweight.
What are the different types of MODY diabetes?
There are now at least 14 different known MODY mutations. They include GCK, HNF1A, HNF4A, HNF1B, INS, NEURO1, PDX1, PAX4, ABCC8, KCNJ11, KLF11, CEL, BLK and APPL1. The different genes vary with respect to age of onset, response to treatment, and the presence of extra-pancreatic manifestations.
Is MODY autoimmune?
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a group of inherited disorders of non-autoimmune diabetes mellitus which usually present in adolescence or young adulthood.
Monogenic diabetes: a diagnostic algorithm for clinicians
Monogenic forms of beta cell diabetes account for approximately 1%-2% of all cases of diabetes, yet remain underdiagnosed. Overlapping clinical features with common forms of diabetes, make diagnosis challenging. A genetic diagnosis of monogenic diabetes in many cases alters therapy, affects prognosi …
Diabetes MODY: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
MODY is the name given to a collection of different types of inherited forms of diabetes that usually develop in adolescence or early adulthood. MODY stands for “Maturity-onset diabetes of the young” and was given that name because it acted like an adult type of diabetes but was found in young people.
LADA (Type 1.5) and MODY Diabetes: Symptoms and Treatment
Find out what to expect if you have MODY or LADA, two rare types of diabetes that share some features of type 1 and type 2 diabetes but have their own symptoms and treatments.
Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY): Causes, Symptoms ... - WebMD
Find out the causes, symptoms, and treatment of MODY, a rare kind of diabetes, and learn how it differs from type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
What percentage of diabetes is monogenic?
In the United States, monogenic forms of diabetes account for about 1 to 4 percent of all cases of diabetes. 1,2,3,4 In most cases of monogenic diabetes, the gene mutation is inherited from one or both parents. Sometimes the gene mutation develops spontaneously, meaning that the mutation is not carried by either of the parents.
How do doctors diagnose polygenic diabetes?
Doctors diagnose polygenic forms of diabetes by testing blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, in individuals with risk factors or symptoms of diabetes. Genes provide the instructions for making proteins within the cell. If a gene has a change or mutation, the protein may not function properly.
What is the name of the type of diabetes that is characterized by frequent urination, rapid breathing, and
This type of NDM is called transient neonatal diabetes mell itus (TNDM). Clinical features of NDM depend on the gene mutations a person has. Signs of NDM include frequent urination, rapid breathing, and dehydration. 5 NDM can be diagnosed by finding elevated levels of glucose in blood or urine.
What is the name of the disease that causes the body to produce insulin?
Sometimes the gene mutation develops spontaneously, meaning that the mutation is not carried by either of the parents. Most mutations that cause monogenic diabetes reduce the body’s ability to produce insulin, a protein produced in the pancreas that helps the body use glucose for energy. Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) ...
Why is genetic testing important?
Genetic testing can be helpful in selecting the most appropriate treatment for individuals with monogenic diabetes. Testing is also important in planning for pregnancy and to understand the risk of having a child with monogenic diabetes if you, your partner, or your family members have monogenic diabetes.
How rare is NDM?
NDM is a rare condition accounting for up to 1 in 400,000 infants in the United States. 4 Infants with NDM do not produce enough insulin, leading to an increase in blood glucose.
What happens if a gene mutation causes diabetes?
If a gene has a change or mutation, the protein may not function properly. Genetic mutations that cause diabetes affect proteins that play a role in the ability of the body to produce insulin or in the ability of insulin to lower blood glucose.
A Quick Guide on Monogenic Diabetes
We know about the most common forms of diabetes – Type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Both these kinds are polygenic diabetes. Polygenic diabetes is related to a defect or a change in multiple genes. Monogenic diabetes, on the other hand, is a rare condition that results from change or mutation in just one gene.
What is Monogenic Diabetes?
Monogenic diabetes is a rare kind of diabetes that is caused due to mutation in just a gene. It accounts for nearly 1-2% of all diabetes cases, though the prevalence might be up to 5%. Most importantly, monogenic diabetes showcases both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes symptoms which often gets it misdiagnosed as one of these kinds.
What are the Types of Monogenic Diabetes?
Changes or mutations in a single gene cause a kind of diabetes called monogenic diabetes. It is a rare form of the diabetic condition and accounts for nearly 1-4% of diabetic conditions. In the majority of cases, the diabetic gene mutation is carried forward from either of the parents.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Monogenic Diabetes
Monogenic diabetes is a rare condition. Therefore it might get ignored during diabetes diagnosis. However, some factors can have your professionals suspect that a diabetes type 1 or type 2 diagnosis might not be correct. To diagnose monogenic diabetes a combination of clinical characteristics and tests are run.
Takeaway: Keep an Eye on Early Signs
Monogenic diabetes is a rare condition, and it is not easily diagnosed. People often confuse monogenic diabetes with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes as the symptoms are similar. Monogenic diabetes, if diagnosed at the right time, can be easily treated and managed.
What is Monogenic Diabetes?
Monogenic diabetes is a rare form of diabetes that occurs due to a change to a single gene and is known to be different from type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This type of diabetes often requires genetic testing for diagnosis. Mostly, the cases of monogenic diabetes are inherited.
How is Monogenic Diabetes Different from Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
Monogenic diabetes occurs due to mutation in a single gene while type 1 and type 2 diabetes are polygenic and occur due to mutation in multiple genes.
Causes of Monogenic Diabetes
Monogenic diabetes is caused due to changes in a single gene. It is inherited from just one parent called an autosomal dominant gene. Sometimes the change or mutation are not inherited and happen spontaneously. Monogenic diabetes can be temporary or a lifelong condition.
Symptoms of Monogenic Diabetes
Knowing the symptom of both types of monogenic diabetes help in getting timely proper treatment. ( 1)
How is Monogenic Diabetes Diagnosed?
To diagnose monogenic diabetes, blood sugar and genetic testing are done. Genetic testing involves taking samples from blood or saliva. DNA is examined to look for the changes in the genes.
Treatment for Monogenic Diabetes
The treatment of monogenic diabetes depends on the genetic mutation cause, its type, and severity.
What is monogenic diabetes?
Monogenic diabetes is a rare type of diabetes that’s caused by a single gene mutation. There are currently over 10 different types of MODY and with new genetic testing more are being uncovered. It accounts for about 1-2% of all diabetes cases, though its prevalence may actually be up to 5%. It has characteristics of both Type 1 and Type 2, ...
How many copies of a mutation are needed to develop diabetes?
This means only one copy of the mutation is needed to develop diabetes. There is usually a strong family history of diabetes and in multiple generations, (although it’s possible for someone to have a spontaneous mutation).
How long does it take for diabetes to develop in a newborn?
There are two main forms of Monogenic diabetes (with subtypes in each): Neonatal diabetes is usually diagnosed in infants from birth to 6 months, though diagnosis may occur later in some cases. Often these infants are started on insulin, but this type of diabetes can be treated with pills known as sulfonylurea agents.
What age is a diabetic diagnosed?
A diagnosis of diabetes before 6 months of age (which is neonatal diabetes). A family history of MODY. A strong family history of diabetes, either “type 1” or “type 2” diagnosed at a younger age (teens, 20’s or 30’s.)
Why is it important to know if you have MODY?
The reason it is important to know whether or not you have MODY is because treatment is often different than it would be if you had “classical” type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Patients are sometimes unnecessarily put on insulin. Some types of MODY are easily managed without medication, through diet and exercise.
What does "type 2" mean in diabetes?
Diabetes that doesn’t seem to fit a “type 1” category (meaning negative antibodies, no DKA) or “type 2” (meaning not overweight, with central fat or an older onset).
Does MODY cause diabetes?
Glucokinase gene—very mild and usually requires no treatment. This type of MODY does not seem to cause the complications of diabetes. (MODY 2) Because this is a genetic type of diabetes, the abnormalities are present from birth, but other than with neonatal diabetes there are often no signs or symptoms of diabetes.
What percentage of diabetes is monogenic?
In the United States, monogenic forms of diabetes account for about 1 to 4 percent of all cases of diabetes. 1,2,3,4 In most cases of monogenic diabetes, the gene mutation is inherited from one or both parents. Sometimes the gene mutation develops spontaneously, meaning that the mutation is not carried by either of the parents.
How do doctors diagnose polygenic diabetes?
Doctors diagnose polygenic forms of diabetes by testing blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, in individuals with risk factors or symptoms of diabetes. Genes provide the instructions for making proteins within the cell. If a gene has a change or mutation, the protein may not function properly.
What is the name of the type of diabetes that is characterized by frequent urination, rapid breathing, and
This type of NDM is called transient neonatal diabetes mell itus (TNDM). Clinical features of NDM depend on the gene mutations a person has. Signs of NDM include frequent urination, rapid breathing, and dehydration. 5 NDM can be diagnosed by finding elevated levels of glucose in blood or urine.
What is the name of the disease that causes the body to produce insulin?
Sometimes the gene mutation develops spontaneously, meaning that the mutation is not carried by either of the parents. Most mutations that cause monogenic diabetes reduce the body’s ability to produce insulin, a protein produced in the pancreas that helps the body use glucose for energy. Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) ...
Why is genetic testing important?
Genetic testing can be helpful in selecting the most appropriate treatment for individuals with monogenic diabetes. Testing is also important in planning for pregnancy and to understand the risk of having a child with monogenic diabetes if you, your partner, or your family members have monogenic diabetes.
How rare is NDM?
NDM is a rare condition accounting for up to 1 in 400,000 infants in the United States. 4 Infants with NDM do not produce enough insulin, leading to an increase in blood glucose.
What happens if a gene mutation causes diabetes?
If a gene has a change or mutation, the protein may not function properly. Genetic mutations that cause diabetes affect proteins that play a role in the ability of the body to produce insulin or in the ability of insulin to lower blood glucose.
