
Procedures
Likewise, people ask, what is the life expectancy of someone with aortic stenosis? Without treatment, the average life expectancy after the onset of heart failure due to aortic stenosis is between 6 to 24 months.
Self-care
Stages
- None
- Severe calcification or congenital stenosis with severely reduced opening
- Vmax ≥ 4 m/s or mean ΔP ≥ 40 mmHg
- AVA ≤ 1.0 cm²
- LVEF < 50%
Nutrition
- This is an option that is sometimes considered. This also does not require open heart surgery.
- A catheter is inserted into the main blood vessel in the top of the leg. It is passed up to the heart. ...
- However, for adult patients, balloon valvuloplasty tends to be used only in those who are unsuitable for valvotomy or valve replacement surgery. ...
What is the life expectancy of someone with aortic stenosis?
According to research, patients with severe aortic valve stenosis who do not undergo any treatment can undergo sudden death in a span of two to three years. Surgery and medical treatment is seen to improve the life expectancy, increasing it up to 10 to 15 years of time after surgery.
What are the end stages of aortic stenosis?
How to fix aortic stenosis?
How long does someone with aortic stenosis live?

How serious is moderate aortic valve stenosis?
People with moderate aortic stenosis may not notice physical problems. But it's a life-threatening condition that can progress rapidly and cause heart failure.
What does moderate aortic stenosis mean?
Aortic valve stenosis — or aortic stenosis — occurs when the heart's aortic valve narrows. The valve doesn't open fully, which reduces or blocks blood flow from your heart into the main artery to your body (aorta) and to the rest of your body.
What is the life expectancy of someone with moderate aortic stenosis?
Without treatment, a person's life expectancy with aortic stenosis after symptoms develop is 1–3 years. Around 50–68% of symptomatic people die within 2 years.
Can moderate aortic stenosis be reversed?
However, there are no medications that can reverse aortic stenosis. The only cure is replacing the diseased valve. Usually, heart valve replacement requires open-heart surgery. During this procedure, patients are connected to a heart-lung bypass machine, which does the work of the heart while their heart is stopped.
How fast does moderate aortic stenosis progress?
According to The Cleveland Clinic, catheterization and echocardiographic studies suggest that, on average, the valve area declines 0.1-0.3 square centimeters per year. The Cleveland Clinic also states that the systolic pressure gradient across the aortic valve can increase by as much as 10-15 mm Hg per year.
Does moderate aortic stenosis require surgery?
Mild to moderate aortic stenosis typically does not require surgery. But, surgery is necessary for severe cases of aortic stenosis. If left untreated, severe aortic stenosis can result in heart failure.
Can you live a normal life with aortic stenosis?
Patients with aortic stenosis can live full and rewarding lives. However, they may need to be monitored by a heart specialist with office visits and periodic testing. In many cases, aortic stenosis is discovered in patients before they develop any symptoms.
How do you slow down aortic stenosis?
Statins and ACE-Inhibitors have been identified as the two most promising candidates. Both statins and ACE-Inhibitors have been shown to reduce the progression of atherosclerotic disease and to significantly improve the clinical outcome among patients with coronary artery disease.
Does aortic valve stenosis get worse with age?
Aortic stenosis is a progressive disease, which means it gets worse over time. Because of this, doctors will typically measure it as mild, moderate, or severe aortic stenosis. The stage of aortic stenosis depends on how damaged your aortic valve is.
What medications should be avoided with aortic stenosis?
Antihypertensive treatment with β-blockers has generally been avoided in patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS) due to the concerns for inducing left ventricular dysfunction and hemodynamic compromise in the presence of severe outflow tract obstruction.
What percentage of aortic stenosis requires surgery?
Among patients <70 years of age, the overall surgical mortality associated with isolated aortic valve replacement is ≈1% to 3% (increasing to ≈5%–7% when associated coronary artery disease requires additional intervention), and it is 5% to 15% among older adults, including octogenarians and some nonagenarians.
Do statins help aortic stenosis?
Statins and ACE inhibitors are two potential and promising treatments that may have beneficial effects in patients with aortic stenosis. Statins are likely to reduce cardiovascular events rather than disease progression per se but may potentially be a valuable preventative treatment in these patients.
How to diagnose aortic valve stenosis?
To diagnose aortic valve stenosis, your doctor will review your signs and symptoms, discuss your medical history, and do a physical examination. He or she will listen to your heart with a stethoscope to determine if you have a heart murmur that may signal an aortic valve condition.
What test is used to determine if you have aortic valve stenosis?
Tests also can help determine a cause and the condition's severity. Tests for aortic valve stenosis may include: Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to create images of your heart in motion.
What is the purpose of a aortic valve test?
Exercise tests help your doctor determine whether signs and symptoms of aortic valve disease occur during physical activity. These tests can help determine the severity of your condition. If you are unable to exercise, medications that have similar effects as exercise on your heart may be given to complete the test.
How is a replacement valve inserted?
A replacement valve is inserted through the catheter and guided to your heart. A balloon is expanded to press the valve into place. Some TAVR valves are self-expanding. You may eventually need surgery to repair or replace the diseased aortic valve, even if you don't have symptoms.
How does a TAVR valve work?
In TAVR, doctors insert a catheter in your leg or chest and guide it to your heart. A replacement valve is then inserted through the catheter and guided to your heart. A balloon may expand the valve, or some valves can self-expand. When the valve is implanted, doctors remove the catheter from your blood vessel.
What are some ways to improve heart health?
Your doctor may suggest that you incorporate several heart-healthy lifestyle changes into your life, including: Eating a heart-healthy diet. Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables, low-fat or fat-free dairy products, poultry, fish, and whole grains. Avoid saturated and trans fat, and excess salt and sugar.
Can aortic valve surgery be done at the same time as heart surgery?
Aortic valve surgery may be done at the same time as other heart surgery. Surgery options for aortic valve stenosis include: Aortic valve repair. To repair an aortic valve, surgeons separate valve flaps (cusps) that have fused. However, surgeons rarely repair an aortic valve to treat aortic valve stenosis.
What is the most common left sided valve lesion?
Aortic stenosis is the most common left-sided valve lesion requiring intervention and carries a substantial morbidity and mortality burden. Clear guidelines exist for the management of patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis.
Does aortic stenosis affect the valve?
It is recognised that aortic stenosis not only affects the valve but also has a complex myocardial response. This review discusses the natural history of moderate aortic stenosis along with the role of multimodality imaging in risk stratification in these patients.
Can a patient with aortic stenosis have left ventricular dysfunction?
There are no recommendations for patients with moderate aortic stenosis and left ventricular dysfunction, despite the high associated morbidity and mortality. There is also some evidence that these patients may benefit from early aortic valve intervention.
Is aortic stenosis a disease?
It is well recognised that aortic stenosis is not only a disease of the valve, but also of the myocardium, and that a significant proportion of patients with moderate aortic stenosis will also have left ventricular dysfunction.
How do you know if you have aortic stenosis?
This is usually when the aortic stenosis has advanced from mild or moderate to severe. If you have severe aortic stenosis, you may feel: More tired and exhausted. Be short of breath with activities. Develop chest discomfort with activities.
What is a tavr valve?
TAVR (also known as TAVI): Transcatheter aortic valve replacement, or implantation, has emerged as an alternative approach to treat certain patients with aortic stenosis. TAVR does not require sternotomy or a heart-lung bypass machine.
What is the procedure called when you have no symptoms?
Develop chest discomfort with activities. Lightheaded or even pass out. "Watchful observation" is recommended while patients have no symptoms. Once symptoms are present, replacing the valve may be considered. The less invasive procedure is also referred to as transcatheter aortic valve implantation, or TAVI.
How long does it take to recover from a sternotomy?
The aortic stenosis valve is cut out, and replaced by the new valve. Recovery in the hospital usually takes about five days.
Can a savr unclog an aortic valve?
At present, no medical therapy can "unclog" an obstructed aortic valve. During a surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR), you would be put under general anesthesia, and you would be placed on a ventilator while on a heart-lung bypass machine.
Can a TAVR valve be pushed to the side?
Most important, the durability of TAVR valves compared with surgical valves is unclear. The TAVR valves may not last as long.
Is a TAVR valve a major concern?
Overall, TAVR has been an exciting development in treating patients with aortic stenosis, but there are limitations: There is almost always a leak between the old and the new TAVR valve; however, this is usually not a major concern.
What happens if you leave aortic stenosis untreated?
If left untreated, severe aortic stenosis can result in heart failure. The aortic valve is located between the bottom left chamber of your heart, the left ventricle, and the main artery that leads away from your heart, the aorta. The valve is made of three flaps of tissue, called leaflets, that swing open when blood pushes against them.
Why does my heart have to work harder to squeeze blood through the narrow valve?
Your heart has to work harder to squeeze blood through the narrow valve than it does when the valve opening is normal. Aortic stenosis can be caused when a person is born with an aortic valve that has only two leaflets, rather than three. More commonly, though, the condition develops as a result of aging.
What is the valve that swings open when blood pushes against it?
Aortic stenosis happens when the opening in the aortic valve is narrowed. Valves affected by stenosis limit blood flow.
Can you have surgery to replace aortic valve?
Mild to moderate aortic stenosis typically does not require surgery. But, surgery is necessary for severe cases of aortic stenosis . If left untreated, severe aortic stenosis can result in heart failure.
Can you use balloons for aortic stenosis?
In some cases, a self-expanding valve may be inserted into the aortic valve, and a balloon isn’t used. If you have severe aortic stenosis, but you don’t have any symptoms or any evidence of heart failure, it is possible that surgery to replace the valve could be delayed.
Can aortic stenosis cause shortness of breath?
When it first develops, mild aortic stenosis typically doesn’t have any symptoms. But, as the condition progresses, the extra work required of the heart to pump blood through the narrow valve may cause symptoms, such as fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, lightheadedness or fainting.
How severe is aortic valve stenosis?
Aortic valve stenosis ranges from mild to severe. Signs and symptoms generally occur when narrowing of the valve is severe. Some people with aortic valve stenosis may not have symptoms for many years.
What are the risk factors for aortic valve stenosis?
Risk factors of aortic valve stenosis include: Older age. Certain heart conditions present at birth (congenital heart disease) such as a bicuspid aortic valve. History of infections that can affect the heart. Having cardiovascular risk factors, such as diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure.
How many cusps does the aortic valve have?
However, some people are born with an aortic valve that has two cusps (bicuspid aortic valve). Your heart has four valves that keep blood flowing in the correct direction.
What is the name of the condition where the aortic valve is narrowed?
Aortic valve stenosis. In aortic valve stenosis, the aortic valve opening is narrowed (top row). The narrowing requires increased pressure within the heart to pump blood across a smaller opening. Eventually this reduces the heart's ability to pump blood to the body.
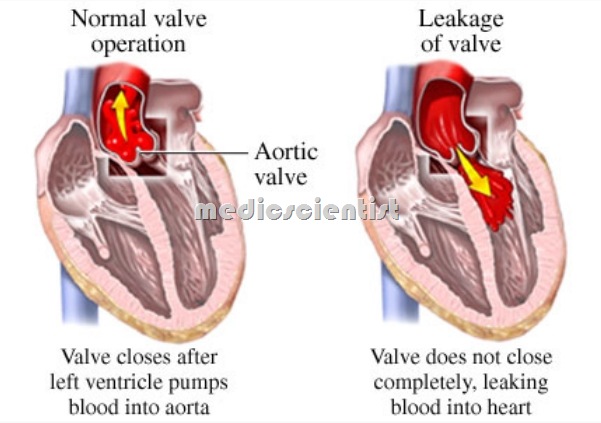
What happens if a valve doesn't close?
Sometimes, the valves don't open or close properly. If a valve doesn't fully open or close, blood flow is reduced or blocked. In aortic valve stenosis, the aortic valve between the lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) and the aorta does not open completely.
Can aortic valve stenosis cause heart failure?
Not eating enough (mainly in children with aortic valve stenosis) Not gaining enough weight (mainly in children with aortic valve stenosis) Aortic valve stenosis may lead to heart failure. Heart failure signs and symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, and swollen ankles and feet.
Can strep throat be treated with antibiotics?
Untreated strep throat can develop into rheumatic fever. Fortunately, strep throat can usually be easily treated with antibiotics. Rheumatic fever is more common in children and young adults.
What happens if your aortic valve is stenosis?
Over time, your aortic valve opening may end up going from the size of a nickel to about the size of the head of a golf tee. This continues to cause more wear and tear on your heart. If your aortic stenosis is severe, you may have the same symptoms as some people with moderate cases -- such as chest pain, tightness, ...
What is aortic stenosis?
In this Article. Aortic stenosis is a type of heart valve disease. Your doctor may classify it as mild, moderate, or severe. Which stage you have depends on how damaged your aortic valve is and the amount of blood that’s still able to pass through it.
How do you know if you have a small aortic valve?
If your condition is moderate, you may notice: Feeling out of breath, especially when you’re active. Chest pain. Tightness or pressure in your chest.
How long does it take for the aortic valve to shrink?
As your aortic valve’s opening slowly starts to shrink with this condition, your heart muscle picks up the slack. It can take many years for this extra work to cause severe damage to your heart muscle. The most common early warning signs are: Needing to make more effort than usual during a physical activity.
What is asymptomatic aortic stenosis?
Because signs of this condition vary so widely, your doctor will want to do tests to see how well your heart is working. Your treatment will be based on your symptoms as well as what these tests show. In severe cases, procedure may be possibly needed to repair or replace your aortic ...
Can you get blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta?
Even so, not everyone will have the same symptoms or need the same treatments. Your aortic valve transfers blood from the left ventricle of your heart to your aorta, the largest artery you have. If something causes this valve to narrow, you can’t get as much blood flow to your heart and the rest of your body.
Can aortic stenosis cause shortness of breath?
These signs can also mean that the disease is starting to worsen more quickly. If left untreated, severe aortic stenosis can lead to heart failure. Intense fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling of your ankles and feet are all signs of this. It can also lead to heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) and even sudden cardiac death.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment