
Medication
The following may be needed to make a diagnosis:
- an assessment of symptoms – for example, whether there are typical symptoms of dementia with Lewy bodies
- an assessment of mental abilities – this will usually involve a number of tasks and questions
- blood tests to rule out conditions with similar symptoms
Therapy
Lewy body dementia (LBD) can be difficult to diagnose. Talking to both patients and caregivers helps doctors make a diagnosis. It is important to ask the patient and their care partners about any symptoms involving thinking, movement, sleep, behavior, or mood.
Self-care
Lewy body dementia can occur alone or along with other brain disorders. It is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms start slowly and worsen over time. The disease lasts an average of five to eight years from the time of diagnosis to death, but can range from two to 20 years for some people.
Nutrition
The average lifespan of a person newly diagnosed with Lewy body dementia is between five and eight years. However, there are those who have lived up to 20 years after diagnosis. Summary
How to diagnose dementia with Lewy bodies?
How to diagnose Lewy body?
How long does end stage of Lewy body dementia last?
What is the lifespan of someone with Lewy body dementia?
See more
Can you survive Lewy body dementia?
The life expectancy of individuals with dementia with Lewy bodies varies; people typically survive about 5 to 7 years after they are diagnosed. REM sleep behavior disorder may be the first sign of dementia with Lewy bodies. It can occur years before other symptoms appear.
How do you slow down Lewy body dementia?
Physical exercise has been repeatedly recommended as a way to prevent, slow down, and treat dementia. This includes Lewy body dementia. Exercise has also been shown to decrease stress and provide both physical and emotional benefits.
Are there any treatments for Lewy body dementia?
There's no cure for Lewy body dementia but many of the symptoms can improve with targeted treatments.
What medication is given for Lewy body dementia?
Cholinesterase inhibitors are important drugs for managing patients in all stages of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), since they improve global cognitive function and reduce visual hallucinations and other behavioral symptoms.
What triggers Lewy dementia?
Lewy body dementia is characterized by the abnormal buildup of proteins into masses known as Lewy bodies. This protein is also associated with Parkinson's disease. People who have Lewy bodies in their brains also have the plaques and tangles associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Do you sleep a lot with Lewy body dementia?
People who have dementia caused by Lewy body disease, such as Parkinsons' disease (PD) or dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) are often sleepy by day but have very restless and disturbed nights. They can suffer from confusion, nightmares and hallucinations.
What drugs should be avoided with Lewy body dementia?
If possible, avoid medications with anticholinergic properties, which can worsen cognition, or dopamine agonists, which can cause hallucinations. First-generation antipsychotic medications, such as haloperidol (Haldol), should not be used to treat Lewy body dementia.
What are the 7 stages of Lewy body dementia?
WHAT ARE THE 7 STAGES OF DEMENTIA?Stage One: No Cognitive Decline. ... Stage Two: Very Mild Cognitive Decline. ... Stage Three: Mild Cognitive Decline. ... Stage Four: Moderate Cognitive Decline. ... Stage Five: Moderately Severe Cognitive Decline. ... Stage Six: Severe Cognitive Decline. ... Stage Seven: Very Severe Cognitive Decline.
At what age does Lewy body dementia start?
It usually happens to people who are 50 or over. There are two types: Dementia with Lewy bodies often starts when you have a hard time moving your body. Within a year, you start to have thinking and memory problems that are similar to Alzheimer's disease, along with changes in behavior.
Do Lewy bodies show up on MRI?
HealthDay News — Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain may aid diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies versus Alzheimer's disease, according to a study published online Nov. 2 in Neurology.
What are the causes of Lewy body dementia?
The precise cause of LBD is unknown, but scientists are learning more about its biology and genetics. For example, we know that an accumulation of Lewy bodies is associated with a loss of certain neurons in the brain that produce two important chemicals that act as messengers between brain cells (called neurotransmitters).
What are Lewy body dementia signs and symptoms?
People with LBD may not have every symptom associated with the disease. Any sudden or major change in functional ability or behavior should be reported to a doctor.
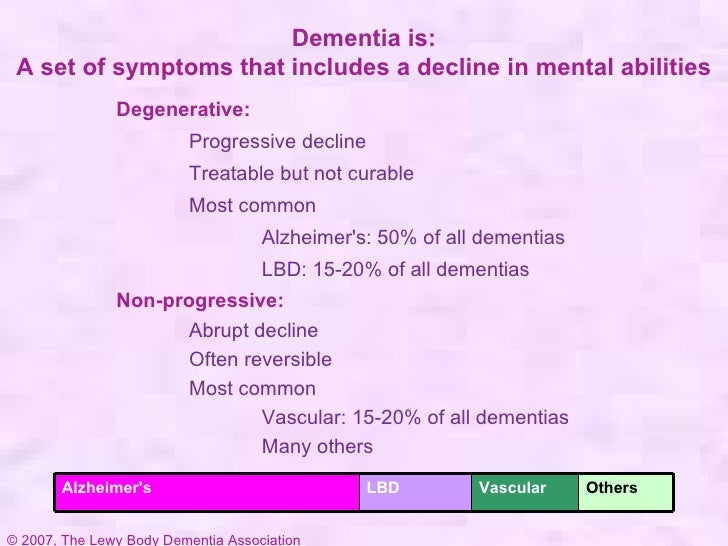
Types of Lewy body dementia and diagnosis
LBD refers to either of two related diagnoses — dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson's disease dementia. Both diagnoses have the same underlying changes in the brain and, over time, people with either diagnosis develop similar symptoms. The difference lies largely in the timing of cognitive (thinking) and movement symptoms.
Treatment and care for Lewy body dementia
While LBD currently cannot be prevented or cured, some symptoms may respond to treatment for a period of time. An LBD treatment plan may involve medications, physical and other types of therapy, and counseling. A plan to make any home safety updates and identify any equipment can make everyday tasks easier.
Other treatment considerations
LBD affects the part of the nervous system that regulates automatic actions like blood pressure and digestion. One common symptom is orthostatic hypotension, a drop in blood pressure when standing up that can cause dizziness and fainting.
Lewy body dementia research
Many avenues of research are being explored to improve our understanding of LBD. Some researchers are working to identify the specific differences in the brain between the two types of LBD. Others are looking at the disease's underlying biology, genetics, and environmental risk factors.
For more information about Lewy body dementia
NIA Alzheimer’s and related Dementias Education and Referral (ADEAR) Center 800-438-4380 (toll-free) [email protected] (link sends email) www.nia.nih.gov/alzheimers The NIA ADEAR Center offers information and free print publications about Alzheimer’s and related dementias for families, caregivers, and health professionals.
What is the treatment for cognitive impairment?
Cognitive Impairment and Fluctuations. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs): AChEIs are the current standard of care for treating cognitive and psychiatric symptoms of LBD. Three have been approved by the FDA for treatment of AD; donepezil (Aricept), rivastigmine (Exelon), and galantamine (Razadyne). Rivastigmine is the only one of the three ...
Is dopamine agonist more effective than levodopa?
Dopamine agonists are less effective than levodo pa for treating motor symptoms and are more likely to cause non-motor side effects, especially drug-induced psychosis even at low doses. Dopamine agonists may also cause excessive daytime sleepiness and swelling of the legs.
Is DLB better for AD or LBD?
The importance of early treatment is supported by recent data suggesting that patients with LBD, might respond better to cholinesterase inhibitors than patients with AD. In addition, an early diagnosis of DLB will help treating physicians know which medications to avoid or use cautiously, especially the antipsychotics (aka neuroleptics).
Is Memantine approved for LBD?
Memantine (Namenda) is another drug (with a different pharmacological mechanism of action) approved for AD but not LBD and is also used off label as an add-on therapy to AChEIs, typically in patients with more severe dementia. Only a few studies of memantine have been done in LBD, with mixed results. 3,4.
Can you treat hallucinations with a drug?
If hallucinations (usually visual) are not frightening to the patient, even if they are considered bothersome by the family, treatment with a drug may not be needed, especially if the patient understands that the hallucinations are not real.
Is levodopa safe for PD?
Levodopa is an effective and relatively safe drug for treating motor symptoms in PD; most patients with LBD respond with improvement in motor function, without side effects, as long as the dosing is kept at the lowest, most effective level. 5 However, all patients with LBD are vulnerable to the development of medication-induced behavioral or psychotic symptoms. Not everyone with LBD requires anti-parkinsonian treatment, particularly those with DLB. In fact, some patients with DLB may go years before showing signs of parkinsonism. Given the potential for adverse effects, healthcare providers should use levodopa in this setting only when symptoms are truly bothersome and should start with a low dose and titrate up slowly.
How to help someone with Lewy Body dementia?
Plus exercise and eat a healthy diet to keep mind and body as strong as possible. Use music and aromatherapy to reduce anxiety and improve mood. Other things you can do involve seeking the help and assistance of others. Therapists can improve the quality of life of someone living with Lewy body dementia.
What are the medications that can be used for Lewy Body Dementia?
These are known as the typical or traditional antipsychotics and include such drugs as thoridazine, haloperidol, chlorpromazine and perphenazine.
How long do people with LBD live?
After diagnosis, most people with LBD live between five and seven years. Some people with LBD live up to 20 years after their diagnosis. However, there’s always hope. Research on LBD, dementia with lewy bodies, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease with dementia are ongoing.
What is a LBD?
Lewy Body Dementia. Lewy body dementia (LBD) is a broad term covering two neurological disorders: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia. The disease affects areas of the brain that control behavior, movement, and mental ability. Medications and nonmedical therapies, like physical, occupational and speech therapies, ...
What causes LBD?
A buildup of Lewy bodies (proteins called alpha-synucleins) causes LBD. Lewy bodies build up in neurons located in certain areas of the brain that are responsible for behavior, movement, and cognitive ability. Doctors do not know why you or your loved one develop LBD while others do not.
What is a lewy body?
Lewy bodies are clumps of a specific protein (alpha synuclein) that build up in the brain. The lewy bodies form in areas in the brain involved in memory, thinking and movement. Technically, the lewy bodies overwhelm brain cells’ (neurons) normal biologic functions, causing cells to die.
What is the best test for dementia?
Imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are done to rule out other causes of dementia such as brain tumors, brain bleeds, stroke, hydrocephalus or other structural causes. Imaging studies for Lewy body dementia (LBD) are usually normal. The only way to make an absolute diagnosis ...
What are the symptoms of LBD?
Certain features distinguish LBD from Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia: 1 Fluctuations in mental functioning 2 Recurrent visual hallucinations 3 Parkinson’s-like movement challenges 4 Lack of spontaneous movement 5 Many other symptoms associated with LBD
What is LBD in medical terms?
Lewy body dementia (LBD) is a syndrome of severe cognitive impairment that results from diseases such as dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Together, these conditions affect an estimated 1.4 million Americans.
How does Lewy body dementia affect people?
Lewy body dementia affects a person’s ability to think and process information — and it can negatively impact memory and alter personality. Though it shares aspects of other forms of dementia, there are distinct hallmarks of LBD. Lewy body dementia symptoms include: 1 Fluctuating attention/alertness: These shifts can last hours or go on for days. The person may stare into space, appear lethargic or drowsy, and have hard-to-understand speech, appearing a lot like delirium. At other times, the person may have much more clarity of thought. 2 Visual hallucinations: Often, these are very detailed hallucinations and visions of people or animals, and they can recur. 3 Movement disorders: Parkinson’s-like movement issues, such as muscle rigidity, tremors, falls, or a shuffling gait or way of walking, may occur.
What neurotransmitter is associated with Lewy body dementia?
As with Parkinson’s, Lewy body dementia is associated with a depletion of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. These are: Dopamine: This neurotransmitter helps transmit signals that control muscle movement.
What is the term for clumps of abnormal protein particles that accumulate in the brain?
Lewy bodies are clumps of abnormal protein particles that, for reasons that are not fully understood, accumulate in the brain. These deposits cause a form of dementia called Lewy body dementia, or LBD — which is what the late actor and comedian Robin Williams suffered from.
What are the symptoms of LBD?
LBD has three features that distinguish it from other forms of dementia: Fluctuating effects on mental functioning, particularly alertness and attention, which may resemble delirium. Recurrent visual hallucinations. Parkinson-like movement symptoms, such as rigidity and lack of spontaneous movement.
What neurotransmitter is involved in Parkinson's disease?
When the accumulation of Lewy bodies blocks dopamine’s production and transmission, the result is the hallmark movement issues of Parkinson’s disease. Acetylcholine: This neurotransmitter does its work in the parts of the brain responsible for memory, thinking and processing.
Is LBD the same as Parkinson's?
LBD is not the same as Parkinson’s, but the two are closely related: LBD causes some or all of the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s. More than 1 million people in the U.S. are affected by Lewy body dementia, according to the Lewy Body Dementia Association.
Can you see Lewy bodies in an autopsy?
It’s not until an autopsy that they can be seen, says Liana Rosenthal, M.D., assistant professor of neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “If we see Lewy bodies in someone’s brain during an autopsy, that’s considered a ‘pathologic certainty’ of Parkinson’s disease,” she says. As with Parkinson’s, Lewy body dementia is ...
What is a lewy body dementia?
What Can You Do? More Resources on Lewy Body Dementia. Lewy body dementia (LBD) is a brain disorder that can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. Visual hallucinations, or seeing things that are not there, are a common symptom, and tend to happen early on.
What is the difference between dementia and lewy bodies?
The main difference is the timing of when thinking and movement symptoms begin. In dementia with Lewy bodies, problems with thinking, unpredictable changes in attention and alertness, and visual hallucinations develop early in relation to movement symptoms, such as slow movement, difficulty walking, and muscle stiffness.
What are the two types of dementia?
The two types of Lewy body dementia — dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease dementia — are caused by the same underlying changes in the brain. Over time, these conditions may result in similar symptoms. The main difference is the timing of when thinking and movement symptoms begin. In dementia with Lewy bodies, problems ...
How long do people with LBD live?
People with LBD live on average five to eight years — but may live as few as two years or as long as 20 years — from the time of diagnosis to death.
What are the symptoms of LBD?
The most common symptoms of LBD include changes in thinking abilities, movement, sleep, and behavior. The degree of symptoms can vary widely and people with LBD may not have every symptom. Common symptoms include: Trouble with attention, planning, multitasking, problem-solving, and reasoning. Memory problems are also common ...
Why is it important to plan ahead for LBD?
It’s important to plan ahead because symptoms can worsen quickly. Researchers are working to better understand LBD and related disorders to treat and prevent these diseases. Consider joining the effort: Researchers need volunteers with and without LBD for clinical trials and studies.
What causes lewy bodies?
What Causes Lewy Body Dementia? In people with LBD, abnormal clumps of a protein called alpha-synuclein accumulate in areas of the brain involved in thinking, memory, and movement. The clumps are called "Lewy bodies" after the doctor who discovered them.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of Lewy body dementia requires a progressive decline in your ability to think, as well as at least two of the following: 1. Fluctuating alertness and thinking function 2. Repeated visual hallucinations 3. Parkinsonian symptoms 4. REMsleep behavior disorder, in which people act ou…
Preparing For Your Appointment