Medication
Feb 10, 2017 · Hansen’s disease is treated with multidrug therapy (MDT) using a combination of antibiotics depending on the form of the disease: Paucibacillary form – 2 antibiotics are used at the same time, daily dapsone and rifampicin once per month Multibacillary form – daily clofazimine is added to rifampicin ...
Procedures
The treatment is a combination of three antibiotics known as Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT). No other treatments will cure leprosy. If you have noticed symptoms of leprosy, tell a health worker. They will assess you, and if they confirm that you do have leprosy, they will be able to get you access to Multi-Drug Therapy for free.
Nutrition
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae or Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damage may result in a lack of ability to feel pain, which can lead to the loss of parts of a person's extremities from repeated injuries or …
What is the life expectancy for someone with leprosy?
Antibiotic treatment is a key component of leprosy treatment, as it is vital to prevent the progression of the infection. Treatment with rifampin and other antibiotics is highly effective and cures 98% of patients with the leprosy infection. Furthermore, the relapse rate is very low, at about 1% over 5–10 years.
What are the chances for recovery from leprosy?
Jun 19, 2004 · Treatment of leprosy Antimicrobial chemotherapy. The WHO recommended multidrug regimen of rifampicin, clofazimine, and dapsone has been used... Nerve damage. Detecting and treating nerve damage early is the key to preventing deformity. Nerve damage may occur... Notes. Competing interests: DNJL was a ...
How do you cure leprosy?
Leprosy (also called Hanses's disease) is usually treated with oral antibiotics for six months to two years, although the duration of treatment depends on the clinical circumstances and the choice of regimen.
How did they cure leprosy?
A common pre-modern treatment of leprosy was chaulmoogra oil. The oil has long been used in India as an Ayurvedic medicine for the treatment of leprosy and various skin conditions. It has also been used in China and Burma. It was introduced to the West by Frederic John Mouat, a professor at Bengal Medical College.

What happens if you don't treat leprosy?
If it isn’t treated, it can cause severe disfigurement and significant disability. Leprosy is one of the oldest diseases in recorded history. The first known written reference to leprosy is from around 600 B.C. Leprosy is common in many countries, especially those with tropical or subtropical climates.
What is the cause of leprosy?
What is leprosy? Leprosy is a chronic, progressive bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the nerves of the extremities, the skin, the lining of the nose, and the upper respiratory tract. Leprosy is also known as Hansen’s disease.
When was leprosy first discovered?
Leprosy is one of the oldest diseases in recorded history. The first known written reference to leprosy is from around 600 B.C. Leprosy is common in many countries, especially those with tropical or subtropical climates. It’s not very common in the United States.
How do you know if you have leprosy?
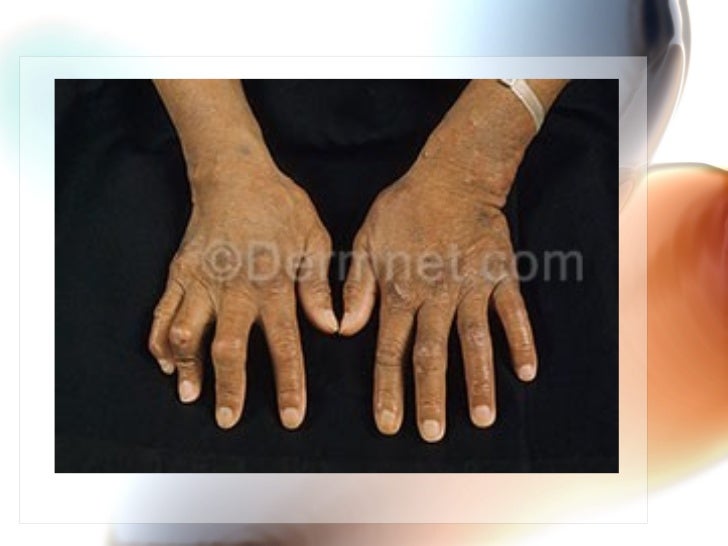
The main symptoms of leprosy include: muscle weakness. numbness in the hands, arms, feet, and legs. skin lesions. The skin lesions result in decreased sensation to touch, temperature, or pain. They don’t heal, even after several weeks.
Is leprosy contagious?
The disease isn’t highly contagious. However, close, repeated contact with an untreated person for a longer period of time can lead to contracting leprosy. The bacterium responsible for leprosy multiplies very slowly. The disease has an average incubation period (the time between infection and the appearance of the first symptoms) of five years.
What are the three types of leprosy?
There are three systems for classifying leprosy. 1. Tuberculoid leprosy vs. lepromatous leprosy vs. borderline leprosy. The first system recognizes three types of leprosy: tuberculoid, lepromatous, and borderline . A person’s immune response to the disease determines which of these types of leprosy they have:
Is lepromatous leprosy contagious?
The disease is mild and only mildly contagious. In lepromatous leprosy, the immune response is poor. This type also affects the skin, nerves, and other organs. There are widespread lesions, including nodules (large lumps and bumps). This form of disease is more contagious.
How long does clofazimine last?
Multibacillary form – daily clofazimine is added to rifampicin and dapsone. Treatment usually lasts between one to two years. The illness can be cured if treatment is completed as prescribed. In the U.S., people with the disease may be treated at special clinics run by the National Hansen’s Disease Program. External.
How long does Hansen's disease last?
Treatment usually lasts between one to two years. The illness can be cured if treatment is completed as prescribed. In the U.S., people with the disease may be treated at special clinics run by the National Hansen’s Disease Program. External.
What is Hansen's disease?
Hansen’s disease is treated with multidrug therapy (MDT) using a combination of antibiotics depending on the form of the disease: 1 Paucibacillary form – 2 antibiotics are used at the same time, daily dapsone and rifampicin once per month 2 Multibacillary form – daily clofazimine is added to rifampicin and dapsone.
What is the best treatment for leprosy?
Multidrug therapy (MDT) is a common treatment for leprosy that combines antibiotics. That means you’ll take two or more medications, often antibiotics: Paucibacillary leprosy: You’ll take two antibiotics, such as dapsone each day and rifampicin once a month.
Can leprosy be cured?
If you do have a reaction, you may have tuberculoid or borderline tuberculoid leprosy. People who don’t have leprosy or who have lepromatous leprosy won’t have a reaction to this test. Leprosy can be cured. In the last 2 decades, 16 million people with leprosy have been cured.
Is leprosy contagious?
Leprosy has been around since ancient times. Outbreaks have affected people on every continent. But leprosy, also known as Hanson’s disease, isn’t that contagious.
Can you catch leprosy from nose droplets?
But leprosy, also known as Hanson’s disease, isn’t that contagious. You can catch it only if you come into close and repeated contact with nose and mouth droplets from someone with untreated leprosy. Children are more likely to get leprosy than adults.
How many people are infected with leprosy?
Today, about 208,000 people worldwide are infected with leprosy, according to the World Health Organization, most of them in Africa and Asia. About 100 people are diagnosed with leprosy in the U.S. every year, mostly in the South, California, Hawaii, and some U.S. territories.
How long does it take for leprosy to show?
It usually takes about 3 to 5 years for symptoms to appear after coming into contact with the bacteria that causes leprosy. Some people do not develop symptoms until 20 years later. The time between contact with the bacteria and the appearance of symptoms is called the incubation period.
What is the diagnosis of leprosy?
Leprosy Diagnosis. If you have a skin sore that might be leprosy, the doctor will remove a small sample of it and send it to a lab to be examined. This is called a skin biopsy. Your doctor may also do a skin smear test. If you have paucibacillary leprosy, there won’t be any bacteria in the test results.
What are the symptoms of leprosy?
Common symptoms present in the different types of leprosy include a runny nose; dry scalp; eye problems; skin lesions; muscle weakness; reddish skin; smooth, shiny, diffuse thickening of facial skin, ear, and hand; loss of sensation in fingers and toes; thickening of peripheral nerves; a flat nose due to destruction of nasal cartilage; and changes in phonation and other aspects of speech production. In addition, atrophy of the testes and impotence may occur.
What causes leprosy?
Most leprosy complications are the result of nerve damage. The nerve damage occurs due to direct invasion by the M. leprae bacteria and a person's immune response resulting in inflammation. The molecular mechanism underlying how M. leprae produces the symptoms of leprosy is not clear, but M. leprae has been shown to bind to Schwann cells, which may lead to nerve injury including demyelination and a loss of nerve function (specifically a loss of axonal conductance). Numerous molecular mechanisms have been associated with this nerve damage including the presence of a laminin -binding protein and the glycoconjugate (PGL-1) on the surface of M. leprae that can bind to laminin on peripheral nerves.
How long does it take for leprosy to show up?
Leprosy symptoms may begin within one year, but, for some people, symptoms may take 20 years or more to occur. Leprosy is spread between people, although extensive contact is necessary. Leprosy has a low pathogenicity, and 95% of people who contract M. leprae do not develop the disease.
How is leprosy spread?
leprae do not develop the disease. Spread is thought to occur through a cough or contact with fluid from the nose of a person infected by leprosy.
How long does paucibacillary leprosy last?
Treatment for multibacillary leprosy uses the same medications for 12 months. A number of other antibiotics may also be used.
How many leprosy cases were there in 2016?
The number of new cases in 2016 was 216,000 . Most new cases occur in 14 countries, with India accounting for more than half. In the 20 years from 1994 to 2014, 16 million people worldwide were cured of leprosy. About 200 cases per year are reported in the United States.
How does leprosy occur?
Transmission of leprosy occurs during close contact with those who are infected. Transmission of leprosy is through the upper respiratory tract. Older research suggested the skin as the main route of transmission, but recent research has increasingly favored the respiratory route.
What is the best treatment for leprosy?
This chapter discusses the antibacterial treatment of leprosy infections. Antibiotic treatment is a key component of leprosy treatment, as it is vital to prevent the progression of the infection. Treatment with rifampin and other antibiotics is highly effective and cures 98% of patients with the leprosy infection.
Is dapsone good for leprosy?
Oral absorption is good and it has a long half-life, averaging 28 h. Dapsone, in the doses recommended for leprosy, causes mild hemolysis and, rarely, anemia or psychosis. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency seldom causes a problem and enzyme levels are not routinely tested before starting MDT.
How long does MB treatment last?
The current recommended length of treatment for MB patients, originally 24 months, is 12 months. No controlled trial data guided this decision, but the classification of MB patients had been widened, so some patients who would previously have received PB treatment for six months now receive MB treatment for 12 months. New evidence supports this decision on the duration of treatment. A study from Bangladesh has followed 1612 patients in two separate cohorts, treated with either six or 12 months of WHO-recommended MDT (monthly doses [supervised] of rifampin 600 mg and clofazimine 300 mg, daily dapsone, and daily clofazimine), for over seven years [30]. No patients have yet presented with a leprosy relapse. The rate of decline of the BI was similar in the two groups, and the loss to follow-up was 16.8% in both groups. The study continues to follow the patients. This study’s findings were supported by data from a randomized and controlled clinical trial (RCT) on U- MDT in Brazil.
How to prevent leprosy?
The most effective way to prevent leprosy is to treat infected patients and thus render them noncontagious. The bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine has had variable efficacy in clinical trials and is not in widespread use to prevent leprosy.
How long does it take to cure leprosy?
Leprosy (also called Hanses's disease) is usually treated with oral antibiotics for six months to two years, although the duration of treatment depends on the clinical circumstances and the choice of regimen.
How long does leprosy last?
Leprosy (also called Hanses's disease) is usually treated with oral antibiotics for six months to two years, although the duration of treatment depends on the clinical circumstances and the choice of regimen. In the United States, the National Hansen's disease Program operates clinics that specialize in leprosy, ...
What is the best treatment for leprosy?
A common pre-modern treatment of leprosy was chaulmoogra oil. The oil has long been used in India as an Ayurvedic medicine for the treatment of leprosy and various skin conditions. It has also been used in China and Burma. It was introduced to the West by Frederic John Mouat, a professor at Bengal Medical College.
What is leprosy caused by?
In a document written in 833, leprosy was described as "caused by a parasite that eats five organs of the body. The eyebrows and eyelashes come off, and the nose is deformed. The disease brings hoarseness, and necessitates amputations of the fingers and toes. Do not sleep with the patients, as the disease is transmittable to those nearby." This was the first document concerning believed infectious aspect of the disease. Japan passed leprosy prevention laws in 1907, 1931, and 1953 that were based on segregation of persons with the disease; this approach intensified leprosy stigma. Lepers were seen as being incurable and infectious. Males admitted to leprosaria in Japan were sterilized, and females found to be pregnant were forced to have abortions. These extreme actions were done to prevent children of diseased parents from being born, lest they carry the disease. (Doctors during this time still mistakenly believed that leprosy was a hereditary disease.) The 1953 law was abrogated in 1996. More than a decade later, in 2008 there were 2,717 ex-patients in 13 national sanatoria and two private hospitals.
Where did leprosy originate?
leprae in 1873. The history of leprosy was traced to its origins by an international team of 22 geneticists using comparative genomics of the worldwide distribution of Mycobacterium leprae. Monot et al. (2005) determined that leprosy originated in East Africa or the Near East and traveled with humans along their ...
Where does the word "leprosy" come from?
The word leprosy comes from ancient Greek Λέπρα [léprā], "a disease that makes the skin scaly", in turn, a nominal derivation of the verb Λέπω [lépō], "to peel, scale off". Λέπος (Lepos) in ancient Greek means peel, or scale; so from Λέπος derives Λεπερός ( Λεπερός, "who has peels—scales") and then Λεπρός ("leprous").
When was leprosy first discovered?
According to the report, two ancestors of Gotama the Budun, Princess Priya and King Rawma, contracted the disease and lived in the wilderness until they were cured with the help of herbal medicine. Historians have made persistent claims that symptoms of leprosy are described among skin afflictions in ancient Greek, Middle Eastern and Indian documentary sources. Scholars acknowledge that it is difficult to make retrospective diagnoses of leprosy from symptoms described in ancient writings, but believe that Hippocrates discussed leprosy in 460 BCE. Documentary evidence also indicates that it was recognized in the civilizations of ancient China, Egypt, Israel, and India. Leprosy was also described in Ancient Rome by the authors Aulus Cornelius Celsus (25 BCE – 37 CE) and Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE).
Which countries in Europe have leprosy?
Discovery of bacterium. After the end of the 17th century, Norway, Iceland, and England were the countries in Western Europe where leprosy was a significant problem. Norway appointed a medical superintendent for leprosy in 1854 and established a national register for people with leprosy in 1856.
What is MDT therapy?
Later, Indian scientist Shantaram Yawalkar and his colleagues formulated a combined therapy using rifampicin and dapsone, intended to mitigate bacterial resistance. Multi-drug therapy (MDT) combining all three drugs was first recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) of the United Nations in 1981.
