The authors concluded that patients with elevated bilirubin levels should initially be treated with a weekly gemcitabine dose of 800 mg/m 2, and subsequently escalated doses if the therapy is tolerated. Irinotecan (Camptosar) is mainly eliminated by the liver and, to a lesser extent, by the kidneys.
Full Answer
What foods lower bilirubin?
What to eat
- Water. Staying hydrated is one of the best ways to help the liver recover from jaundice. ...
- Fresh fruits and vegetables. Fresh fruits and vegetables contain powerful antioxidants and fiber that can help limit liver damage during metabolism and ease digestion.
- Coffee and herbal tea. ...
- Whole grains. ...
- Nuts and legumes. ...
- Lean proteins. ...
How to decrease bilirubin naturally?
Natural Treatments to Reduce Bilirubin Levels:
- Take a hot, high herb enema twice a day. ...
- If fever is present drink a glass of water with lemon juice every hour.
- Take a cup goldenseal and Echinacea juice one hour before meals, three times a day.
- Take pure turmeric powder, add 10gms of this powder to 50gms of pure yoghurt and mix well and divide into equal parts. ...
How do you lower bilirubin levels?
You can help lower your bilirubin levels by:
- Taking deep breaths
- Doing yoga
- Meditating
- Getting a massage
- Listening to music
What is the medication for high bilirubin?
To this end, your doctor will classify the cause as follows: 1
- Pre-hepatic: The underlying process is due to a problem occurring before the liver processes bilirubin, as the result of the rapid breakdown of red blood cells.
- Hepatic: The problem involves the liver.
- Post-hepatic: The problem is the result of something occurring after the liver processes bilirubin, as the result of bile duct obstruction.

What happens if bilirubin is high in cancer patients?
Bilirubin is part of the bile fluid produced by the liver. A normal liver metabolizes bilirubin to keep blood levels low. When liver cells are damaged or when cancer has spread to the liver or bile ducts, the function of the liver is reduced. The bilirubin level in the blood then increases, which causes jaundice.
Does bilirubin increase with chemotherapy?
Certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs, can cause increased bilirubin levels and liver dysfunction. Certain genetic conditions, such as Gilbert's syndrome, may cause slightly increased bilirubin levels.
What is the treatment for elevated bilirubin?
Treatments for elevated bilirubin in adults involves treating the cause and complications, such as: antibiotics to treat infection. corticosteroids to reduce liver inflammation. changing medications if they caused the elevated levels.
How do you lower bilirubin levels in adults with cancer?
However, following these four tips can help you boost overall liver health in addition to medical guidance.Stay hydrated. Staying hydrated helps lower bilirubin levels by facilitating the removal of waste from the body. ... Consume fresh fruits and vegetables. ... Increase your intake of fiber. ... Avoid alcohol.
Can chemo damage liver be reversed?
Chemotherapy-induced liver damage in patients with cancer may occur during chemotherapy or after the total course. Although liver function impairment may be reversed in some patients after treatment, abnormal liver function may lead to an interruption of anti-tumor therapy and jeopardize the prognosis of patients [20].
How long does it take for liver enzymes to return to normal after chemo?
All patients who admitted using alternative agents had started taking them one or two months before the LFT abnormality was detected. After discontinuing the agents, however, the liver function abnormality was normalized within a median 1.9 months (range, 1-8 months).
Is there any medicine to reduce bilirubin?
Phenobarbital therapy has been shown to be effective in reducing plasma bilirubin levels in patients with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 2. Administration of 60-180 mg/day of the drug (in divided doses) can reduce serum bilirubin levels by at least 25%. A response should be expected within 2-3 weeks.
What medications reduce bilirubin?
Drugs that can decrease bilirubin measurements include barbiturates, caffeine, penicillin, and high-dose salicylates.
How long does it take for bilirubin levels to return to normal?
Bilirubin levels slowly improve over 3–12 weeks.
How can I protect my liver from chemo?
If you are at risk of liver damage following cancer treatment, you can help lower the risk by keeping your liver healthy.Get immunized against hepatitis A and B.Avoid alcohol or limit the amount you drink.Drink plenty of water.Eat a well-balanced diet and less fatty, salty, smoked and cured foods.More items...
What foods to avoid if you have high bilirubin?
Foods and drinks to avoid or limit during jaundice recovery include:Alcohol. Alcohol is toxic to most internal bodily tissues, including the liver. ... Refined carbohydrates. ... Packaged, canned, and smoked foods. ... Saturated and trans fats. ... Raw or undercooked fish or shellfish. ... Beef and pork.
How do I detox my liver after chemo?
Consuming water greatly aids in the detoxification process after treatment. Ensure that your water is filtered to eliminate possible toxins that your water may contain. Herbal teas are also wonderful to help the cleansing process. Examples include Dandelion Root tea that aids in liver detoxification and Green Tea.
What causes elevated bilirubin?
Elevated direct bilirubin (conjugated hyperbilirubinemia) can be caused by several factors: Elevated indirect biliru bin (unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia) can be caused by several factors: 3. Bilirubin processing based classification based on location.
What tests are done to determine if a person has unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia?
Adults should undergo urinalysis and laboratory testing to determine if the etiology is conjugated or unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. History, physical examination, and further laboratory testing and imaging should be performed as needed. Management should focus on the underlying etiology (see separate topic reviews).
What causes unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia?
Unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia can be caused by overproduction, impaired uptake by the liver or abnormalities of conjugation , including: The intrahepatic causes of conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia include: The extrahepatic causes of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia include:
What is the differential diagnosis for hyperbilirubinemia?
The differential diagnosis for hyperbilirubinemia is quite broad, and includes hepatic causes, hematologic causes, and inborn errors of metabolism. It is important to note if the hyperbilirubinemia is an isolated lab abnormality, or if it is associated with other liver enzyme or hematologic lab abnormalities.
Can hyperbilirubinemia be seen on urinalysis?
Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is seen with elevated direct bilirubin; bile can be seen on urinalysis. Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia is seen with elevated indirect bilirubin; bile should not be seen on urinanalysis. Elevated direct bilirubin (conjugated hyperbilirubinemia) can be caused by several factors:
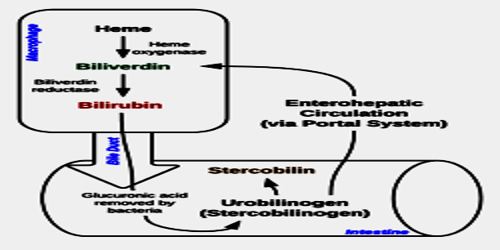
Is bilirubin a byproduct of hemoglobin?
Bilirubin is a normal by-product of hemoglobin metabolism. Plasma unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin is bound to albumin and taken up by hepatocytes, where it is conjugated with glucuronic acid. Conjugated (direct) bilirubin is secreted into bile and excreted.
Is urinalysis negative for bilirubin?
Unconjugated bilirubinemia is seen with elevated indirect bilirubin; urinalysis will be negative for bilirubin. In predominately unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, hemolysis should be excluded with a peripheral blood smear, haptoglobin and lactate dehydrogenase.
What are the symptoms of high bilirubin levels?
Jaundice is the main sign of high bilirubin levels. Other general signs of many of the illnesses that cause high bilirubin can include: abdominal pain or swelling. chills. fever. chest pain. weakness. lightheadedness. fatigue.
What is the bilirubin level?
Typically, bilirubin levels fall somewhere between 0.3 and 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
What causes bilirubin to build up in the liver?
Liver dysfunction. Any condition that affects the function of your liver can cause bilirubin to build up in your blood. This is a result of your liver losing its ability to remove and process bilirubin from your bloodstream. Several things can affect the function of your liver, including: cirrhosis. liver cancer.
Can you have high bilirubin?
If you have high bilirubin, your symptoms will depend on the underlying cause. You can have mildly high bilirubin and have no symptoms at all. Or, with moderately high bilirubin, you may only have jaundice, a yellow cast to your eyes and skin.
Can jaundice cause high bilirubin levels?
If your doctor isn’t immediately sure what’s causing your high bilirubin levels, you may need to return for additional blood, liver function, or other tests. Last medically reviewed on September 17, 2018.
What does it mean when your skin turns yellow after chemo?
When your body can't excrete that excess bilirubin, your skin and the whites of your eyes may appear yellowish in color, called jaundice, according to the Mayo Clinic. Depending on the extent of the jaundi ce and how you're responding to chemo, your doctor may test your bilirubin levels and tweak your treatment accordingly, Dr. Kruse says.
What does a blood test for liver enzymes show?
Your health care provider will routinely test your blood to detect any abnormalities in liver enzymes or other damage to the organ , especially if you have hepatitis or any other underlying liver condition.
Does chemotherapy damage the liver?
Chemotherapy may damage the liver itself and limit its ability to function properly. Such chemical- or drug-induced damage is known as hepatotoxicity, according to a June 2014 review article published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
Can chemotherapy cause high bilirubin levels?
High Bilirubin Levels. Another concern during chemotherapy is that the drugs can cause damage to liver cells that leads to a rise in bilirubin, a red blood cell byproduct found in bile, according to an August 2016 article published in JAMA Oncology.
What is the treatment for hyperbilirubinemia?
The treatment for drug-induced hyperbilirubinemia is cessation of the medication . When bilirubin levels are elevated above 2.5 to 3 milligrams per deciliters, patients may experience yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and the whites of the eyes, also called jaundice, explains MedicineNet.com.
Why is bilirubin elevated?
Patients whose bilirubin levels are elevated because of an increase in the breakdown of blood may require a blood transfusion .
What drugs can cause bilirubin to rise?
Sulfonamides and the medication nitrofurantoin can elevate bilirubin levels by increasing the breakdown of blood. Chloramphenicol, probenecid and rifampin are drugs that decrease the uptake of bilirubin in the liver and also increase bilirubin levels.
What are the symptoms of bilirubin deposition?
Other symptoms include pale-colored stools, dark-colored urine, skin itching, nausea, vomiting, rectal bleeding, diarrhea, fever and chills, weakness, loss of appetite, confusion, abdominal pain, headaches and leg or abdominal swelling. Skin itching from bilirubin deposition on the skin can be treated with cholestyramine.
I. Problem/Condition.
A. What Is The Differential Diagnosis For This Problem?
B. Describe A Diagnostic approach/method to The Patient with This Problem
Historical Information Important in The Diagnosis of This problem.
A. Management of hyperbilirubinemia.
- Newborns should be screened for jaundice, and severe hyperbilirubinemia should promptly be treated with phototherapy in order to prevent kernicterus. Adults should undergo urinalysis and laboratory testing to determine if the etiology is conjugated or unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. History, physical examination, and further laboratory testing and...
What's The Evidence?