Medication
… The ketogenic diet (KD) is a high-fat, adequate-protein, and very-low-carbohydrate diet regimen that mimics the metabolism of the fasting state to induce the production of ketone bodies.
Therapy
One of the ketone bodies formed (acetone) leaves the body via the lungs, giving the breath of the person with DKA a characteristic, fruity smell. This is how DKA can be detected. DKA can induce coma or even death if not treated immediately. Signs & symptoms of DKA:
Self-care
The simple answer is no. Ketosis is not dangerous, it’s ketoacidosis that is dangerous but you’ve nothing to worry about. The confusion between the two is usually the reason people make false statements about the dangers of keto.
Nutrition
nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and. dehydration. Risk factors for diabetic ketoacidosis are type 1 diabetes, and missing insulin doses frequently, or being exposed to a stressor requiring higher insulin doses (infection, etc).
How to treat ketoacidosis naturally?
What happens If DKA is not treated?
How dangerous is ketoacidosis?
What are the signs and dangers of diabetic ketoacidosis?
See more

What is the first treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis?
The initial priority in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis is the restoration of extra-cellular fluid volume through the intravenous administration of a normal saline (0.9 percent sodium chloride) solution.
How long does it take to resolve diabetic ketoacidosis?
A blood glucose concentration of less than 200 mg per dL, a bicarbonate level of 18 mEq per L or greater, and a venous pH level of greater than 7.3 indicate that the DKA has resolved. Typical duration of therapy is about 48 hours.
Is diabetes ketoacidosis curable?
Diabetes-related ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and life-threatening, but treatable, complication that affects people with diabetes and those who have undiagnosed diabetes.
What triggers diabetic ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis usually happens because your body doesn't have enough insulin. Your cells can't use the sugar in your blood for energy, so they use fat for fuel instead. Burning fat makes acids called ketones. If the process goes on for a while, they could build up in your blood.
What are the warning signs of diabetic ketoacidosis?
DKA Signs and SymptomsFast, deep breathing.Dry skin and mouth.Flushed face.Fruity-smelling breath.Headache.Muscle stiffness or aches.Being very tired.Nausea and vomiting.More items...•
How long can you live with ketoacidosis?
Mortality after intensive care unit admission was 8% at 30 days, 18% at one year, and 35% at five years. A total of 349 patients survived their first intensive care unit diabetic ketoacidosis admission [mean (SD) age 42.5 (18.1) years; 50.4% women; 46.1% required ≥1 organ support].
How do you reverse diabetic ketoacidosis?
Insulin therapy. Insulin reverses the processes that cause diabetic ketoacidosis. In addition to fluids and electrolytes, you'll receive insulin therapy — usually through a vein.
What happens when you go into diabetic ketoacidosis?
You have many signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis — excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, stomach pain, weakness or fatigue, shortness of breath, fruity-scented breath, and confusion.
Is diabetic ketoacidosis fatal?
Know the warning signs of DKA and check urine for ketones, especially when you're sick. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is life-threatening—learn the warning signs to be prepared for any situation. DKA is no joke, it's a serious condition that can lead to diabetic coma or even death.
How do I bring my ketones down?
Also try these steps to bring down your ketone levels:Drink extra water to flush them out of your body.Test your blood sugar every 3 to 4 hours.Don't exercise if you have high blood sugar and high ketones.
What organs are affected by ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at a rate that is much too fast. The liver processes the fat into a fuel called ketones, which causes the blood to become acidic.
What happens if diabetic ketoacidosis goes untreated?
Left untreated, diabetic ketoacidosis can cause potentially fatal complications, such as severe dehydration, coma and swelling of the brain.
How to prevent DKA?
Prevent DKA. DKA is a serious condition, but you can take steps to help prevent it: Check your blood sugar often, especially if you’re sick. Keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible. Take medicines as prescribed, even if you feel fine.
What is DKA in diabetes?
DKA is most common among people with type 1 diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA. DKA develops when your body doesn’t have enough insulin to allow blood sugar into your cells for use as energy. Instead, your liver breaks down fat for fuel, a process that produces acids called ketones. When too many ketones are produced too ...
What does DKA mean in Spanish?
Español (Spanish) minus. Related Pages. Elevated ketones are a sign of DKA, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated right away. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening. DKA is most common among people with type 1 diabetes.
What causes DKA in diabetics?
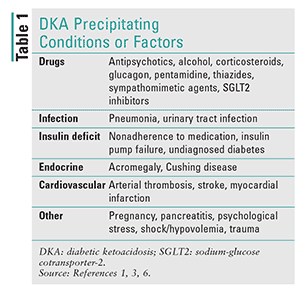
Missing insulin shots, a clogged insulin pump, or the wrong insulin dose. Other causes of DKA include: Heart attack or stroke. Physical injury, such as from a car accident. Alcohol or drug use. Certain medicines, such as some diuretics (water pills) and corticosteroids (used to treat inflammation in the body).
What happens when you have too many ketones?
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up to dangerous levels in your body. Read on to learn more about DKA, how you can prevent DKA, and how to treat it if needed.
Can you test for ketones if you have DKA?
You should also test for ketones if you have any of the symptoms of DKA. Call your doctor if your ketones are moderate or high. Elevated ketones are a sign of DKA, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
How to prevent ketoacidosis?
Good blood sugar control will help you avoid ketoacidosis in the future. Make sure you manage your diabetes through your diet, exercise, medications, and self-care. Follow these steps to help prevent DKA: Drink lots of water or sugar -free, nonalcoholic beverages. Take your medicines as directed.
Why does diabetic ketoacidosis happen?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Causes and Risk Factors. Diabetic ketoacidosis usually happens because your body doesn't have enough insulin. Your cells can't use the sugar in your blood for energy, so they use fat for fuel instead. Burning fat makes acids called ketones.
What is the risk of having type 2 diabetes?
If you have type 2, especially when you're older, you're more likely to have a condition with some similar symptoms called HHNS (hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome). It can lead to severe dehydration. Risk factors for DKA include: Having type 1 diabetes, even if it’s undiagnosed.
How to manage blood sugar?
Manage your insulin dose with help from your doctor or diabetes coach. Make adjustments based on your blood sugar levels, what you eat, activity levels, or during any illness. Create a DKA emergency plan.
What is a DKA?
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis? Diabetic ketoacidosis, also known as DKA, is a buildup of acids in your blood. It can happen when your blood sugar is too high for too long. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes and could be life-threatening, but it usually takes many hours to become that serious.
How to know if ketones are high?
Shortness of breath. Call your doctor or go to the emergency room right away if you have any of the symptoms below and your ketones are moderate to high when you test them using a home kit, or if you have more than one symptom: You've been throwing up for more than 2 hours.
What happens if you don't treat ketoacidosis?
If you don't treat ketoacidosis, you could pass out, go into a coma, and possibly die. You should go to the hospital to treat DKA. There, you will receive emergency treatments like: Insulin through an IV to bring your ketones down. Fluids to get you hydrated and bring your blood chemistry back into balance.
How to treat ketoacidosis?
Increase your fluid intake. One of the first things that will be done to treat your diabetic ketoacidosis is to replace fluids. This can be in the hospital, a doctor’s office, or home. If you are receiving medical care, they will give you an IV. At home, you can drink fluids by mouth.
How to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis?
Follow your diabetic management plan. One good way to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis is to follow your management plan. This includes making sure you eat a healthy diet and avoid foods that can affect your blood sugar level. [15]
How does insulin help with ketoacidosis?
Undergo insulin therapy. Insulin helps reverse diabetic ketoacidosis. Insulin helps reduce the acid in your blood and balance your blood sugar level. This therapy is usually given intravenously by a medical professional.
How to lower blood sugar in diabetics?
With diabetic ketoacidosis, your blood sugar becomes too high due to the lack of insulin. You may consider taking an increased dosage of insulin to help try to lower your blood sugar.
What to do if your ketoacidosis is not working?
If you believe you have diabetic ketoacidosis and the at-home treatments have not worked, you should immediately go to the emergency room or call emergency services. If your blood sugar doesn't lower, your at-home treatments are not working, or your symptoms worsen, you should seek immediate medical attention.
What are the causes of ketoacidosis?
Some illnesses or infections can produce hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which can block the effects of insulin. Missing treatments of insulin can also trigger diabetic ketoacidosis. Some medications or alcohol and drug abuse may also trigger the condition.
What electrolytes are needed for ketoacidosis?
Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, are important to keep your body functioning properly. During diabetic ketoacidosis, your body doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the amount of insulin that your body needs has changed and you aren't giving it enough.
What is the treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is treated with fluids, electrolytes — such as sodium, potassium and chloride — and insulin. Perhaps surprisingly, the most common complications of diabetic ketoacidosis are related to this lifesaving treatment.
What causes ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is usually triggered by: An illness. An infection or other illness can cause your body to produce higher levels of certain hormones, such as adrenaline or cortisol. Unfortunately, these hormones counter the effect of insulin — sometimes triggering an episode of diabetic ketoacidosis.
How long does it take for ketoacidosis to develop?
Diabetic ketoacidosis signs and symptoms often develop quickly, sometimes within 24 hours. For some, these signs and symptoms may be the first indication of having diabetes. You may notice: Excessive thirst. Frequent urination. Nausea and vomiting. Stomach pain. Weakness or fatigue.
How to check blood sugar levels?
Monitor your blood sugar level. You might need to check and record your blood sugar level at least three to four times a day, or more often if you're ill or stressed.
Can ketones cause shortness of breath?
You have ketones in your urine and can't reach your doctor for advice. You have many signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis — excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, stomach pain, weakness or fatigue, shortness of breath, fruity-scented breath, and confusion.
Is ketoacidosis a risk factor?
Risk factors. The risk of diabetic ketoacidosis is highest if you: Have type 1 diabetes. Frequently miss insulin doses. Uncommonly, diabetic ketoacidosis can occur if you have type 2 diabetes. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis may be the first sign that you have diabetes.
How many hospitalizations for diabetic ketoacidosis in 2009?
In 2009, there were 140,000 hospitalizations for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) with an average length of stay of 3.4 days.1The direct and indirect annual cost of DKA hospitalizations is 2.4 billion US dollars.
What are the therapeutic goals of DKA?
The therapeutic goals of DKA management include optimization of 1) volume status; 2) hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis; 3) electrolyte abnormalities; and 4) potential precipitating factors. The majority of patients with DKA present to the emergency room. Therefore, emergency physicians should initiate the management of hyperglycemic crisis while a physical examination is performed, basic metabolic parameters are obtained, and final diagnosis is made. Several important steps should be followed in the early stages of DKA management: 1 collect blood for metabolic profile before initiation of intravenous fluids; 2 infuse 1 L of 0.9% sodium chloride over 1 hour after drawing initial blood samples; 3 ensure potassium level of >3.3 mEq/L before initiation of insulin therapy (supplement potassium intravenously if needed); 4 initiate insulin therapy only when steps 1–3 are executed.
Why is bicarbonate not indicated in mild and moderate forms of DKA?
Bicarbonate therapy is not indicated in mild and moderate forms of DKA because metabolic acidosis will correct with insulin therapy.3, 8The use of bicarbonate in severe DKA is controversial due to a lack of prospective randomized studies.
What is the name of the regimen that contains both long-acting and short-acting insulin?
The regimen containing both long-acting and short-acting insulin is called a basal-bolus insulin regimen; it provides physiological replacement of insulin. If a patient used insulin prior to admission, the same dose can be restarted in the hospital.
Is ketoacidosis a type 1 or 2 diabetes?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a rare yet potentially fatal hyperglycemic crisis that can occur in patients with both type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to its increasing incidence and economic impact related to the treatment and associated morbidity, effective management and prevention is key. Elements of management include making ...
Can DKA cause hypokalemia?
A “normal” plasma potassium concentration still indicates that total body potassium stores are severely diminished, and the institution of insulin therapy and correction of hyperglycemia will result in hypokalemia.
What is the treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis?
The main aims in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis are replacing the lost fluids and electrolytes while suppressing the high blood sugars and ketone production with insulin. Admission to an intensive care unit (ICU) or similar high-dependency area or ward for close observation may be necessary.
How is diabetic ketoacidosis diagnosed?
Diabetic ketoacidosis may be diagnosed when the combination of hyperglycemia (high blood sugars), ketones in the blood or on urinalysis and acidosis are demonstrated. In about 10% of cases the blood sugar is not significantly elevated ("euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis").
Why does ketoacidosis occur?
Diabetic ketoacidosis arises because of a lack of insulin in the body. The lack of insulin and corresponding elevation of glucagon leads to increased release of glucose by the liver (a process that is normally suppressed by insulin) from glycogen via glycogenolysis and also through gluconeogenesis.
What causes DKA in the body?
Triggers may include infection, not taking insulin correctly, stroke and certain medications such as steroids. DKA results from a shortage of insulin; in response, the body switches to burning fatty acids, which produces acidic ketone bodies.
What causes DKA in diabetics?
There is often a particular underlying problem that has led to the DKA episode; this may be intercurrent illness ( pneumonia, influenza, gastroenteritis, a urinary tract infection ), pregnancy, inadequate insulin administration (e.g. defective insulin pen device), myocardial infarction (heart attack), stroke or the use of cocaine. Young people with recurrent episodes of DKA may have an underlying eating disorder, or may be using insufficient insulin for fear that it will cause weight gain.
How long does it take for ketoacidosis to show symptoms?
Signs and symptoms. The symptoms of an episode of diabetic ketoacidosis usually evolve over a period of about 24 hours. Predominant symptoms are nausea and vomiting, pronounced thirst, excessive urine production and abdominal pain that may be severe. In severe DKA, breathing becomes rapid and of a deep, gasping character, ...
What is gliflozin used for?
Drugs in the gliflozin class ( SGLT2 inhibitors), which are generally used for type 2 diabetes, have been associated with cases of diabetic ketoacidosis where the blood sugars may not be significantly elevated ("euglycemic DKA").
Drugs used to treat Diabetic Ketoacidosis
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
