
What is the recovery time for carotid surgery?
From our data, we concluded that the stroke-free interval is improved, whereas survival is unaffected in the surgically treated patient. Endarterectomy of a contralateral stenotic carotid artery is particularly successful in achieving this reduction in morbidity.
How to improve carotid endarterectomy recovery?
· Treatment for carotid artery occlusion generally includes management of high blood pressure, treatment of high cholesterol with statin medications, and anticoagulant therapy such as aspirin or warfarin.
Is there any natural treatment for carotid artery dissection?
· A high revascularisation rate has been reported with angioplasty and stenting (endovascular treatment) for acute carotid occlusions. Sugg et al 34 reported a 64% immediate recanalisation rate with endovascular treatment in patients with ICA occlusion treated within 3 h of onset of stroke.
When to operate in carotid artery disease?
· • Thirty-four patients, each with a totally occluded common or internal carotid artery, were treated over a 15-year period. Seventeen patients were treated nonsurgically, 17 underwent surgery. There were four patients in the nonsurgical group and six patients in the surgical group who were followed up until death.
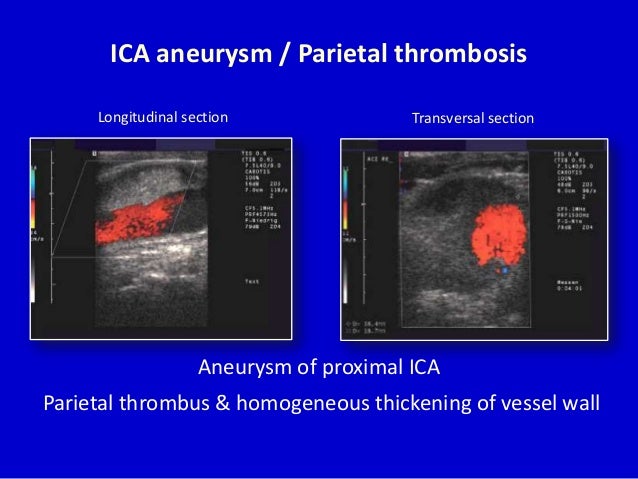
Can a 100% blocked carotid artery be unblocked?
If you have had a stroke or TIA, or if you have a severely blocked carotid artery, you may benefit from surgery to remove the plaque. This surgery is called a carotid endarterectomy. This procedure is time-sensitive and should be done soon after the stroke or TIA, with the goal of preventing another stroke.
What happens if carotid artery is completely blocked?
Carotid artery disease occurs when fatty deposits (plaques) clog the blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain and head (carotid arteries). The blockage increases your risk of stroke, a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or seriously reduced.
Can you live with an occluded carotid artery?
Carotid artery stenosis can lead to a stroke. People who have carotid artery stenosis are at increased risk for a stroke, which can lead to disability or death. Sometimes, strokes can be mild and recoverable. In other cases, strokes are very large and devastating. Carotid stenosis can cause a stroke in two ways.
What happens when your carotid artery is 90% blocked?
If the artery is 80 to 99 percent blocked This includes slurred speech, visual deficit in one eye, weakness on one side of the body, or any facial asymmetry such as a droopy mouth. If you have no symptoms, we won't recommend intervention until the artery is at least 80 percent blocked off.
How long can you live with a blocked carotid artery?
In this long-term follow-up, the median survival after carotid endarterectomy for patients with an asymptomatic stenosis was 10.2 years.
What is the survival rate for carotid artery surgery?
Results— A total of 6169 CEAs in 5808 patients were registered, with a median time at risk of 5.1 (range, 0.1 to 11.8) years. The indication for CEA was asymptomatic stenosis in 10.8% of the patients. Survival after CEA for asymptomatic stenosis was 78.2% after 5 and 45.5% after 10 years.
When does a blocked carotid artery need surgery?
Surgery to remove the buildup in your carotid artery may be done if the artery is narrowed by more than 70%. If you have had a stroke or temporary brain injury, your provider will consider whether treating your blocked artery with surgery is safe for you.
Can blocked arteries be treated with medication?
In serious cases, medical procedures or surgery can help to remove blockages from within the arteries. A doctor may also prescribe medication, such as aspirin, or cholesterol-reducing drugs, such as statins.
What causes carotid artery occlusion?
Carotid artery disease is also called carotid artery stenosis. The term refers to the narrowing of the carotid arteries. This narrowing is usually caused by the buildup of fatty substances and cholesterol deposits, called plaque. Carotid artery occlusion refers to complete blockage of the artery.
Which artery is the most common to have blockage?
Although blockages can occur in other arteries leading to the heart, the LAD artery is where most blockages occur.
Does a CT scan show blocked carotid artery?
Computed Tomography (CT) Angiography A CT scan can give your physician extensive information about where you may have narrowing in the carotid arteries. For the test, you may also be administered contrast dye, a substance that makes it easier to see the blood vessels.
Does your neck hurt when your carotid artery is blocked?
It is linked with physical changes that can happen in a carotid artery in your neck. Your neck may feel tender in the area of the artery. The pain often goes up the neck to the jaw, ear, or forehead.
What is required to treat carotid artery blockage?
Surgical intervention may be required to treat carotid artery blockage if other forms of treatment fail.
What is the best treatment for carotid blockage?
Angioplasty may be used to treat carotid artery blockage.
Which artery supplies the brain with oxygenated blood?
The carotid artery, which is located in the neck, supplies the brain with oxygenated blood.
How to tell if a neck artery is blocked?
In addition, the physician can usually suspect the presence of a blocked neck artery when he detects a swooshing sound called a carotid bruit while listening to the carotid artery with a stethoscope. Although a bruit does not confirm nor rule out the presence of a carotid artery occlusion, it can be cause for a referral for a carotid ultrasound. This test, known as a carotid duplex ultrasound uses sound waves to generate pictures of the carotid arteries, enabling the physician to further diagnose the condition. One of the most accurate tests for diagnosing this condition is the carotid angiogram where a catheter and x-rays are used to determine patency of the neck arteries.
What is the best treatment for distal ICA occlusion?
Thrombolytic treatment using a combination of intravenous and intra‐arterial routes or using the intra‐arterial only route has been reported to be effective in distal ICA occlusion, particularly when given soon after the onset of stroke.32
What is ICA occlusion?
A complete occlusion of the internal carotid artery (ICA) is an important cause of cerebrovascular disease. A never‐symptomatic ICA occlusion has a relatively benign course, whereas symptomatic occlusion increases future risk of strokes. Ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging and contrast angiography are useful diagnostic tests, and functional imaging of the brain (eg, with positron emission tomography) helps to understand haemodynamic factors involved in the pathophysiology of brain ischaemia. Recently, there has been a resurgence of interest in the role of extracranial–intracranial bypass surgery for the treatment of completely occluded ICA. With advances in the measurement of cerebral haemodynamics, it may be possible to identify high‐risk patients who could benefit from the bypass surgery.
How to prevent ischaemia in ICA occlusion?
Compensatory mechanisms can prevent ischaemia in ICA occlusion. Development of collateral circulation is one of them. The most important source of collateral flow is provided by the contralateral ICA via the circle of Willis. The blood flows in an anterograde manner up the contralateral ICA and then across the circle of Willis to the anterior communicating artery. From here, it goes in an anterograde manner along the cortical branches of the anterior cerebral artery and in a retrograde manner along the anterior cerebral artery to the middle cerebral artery (MCA), and then distally into the MCA territory in the usual anterograde manner. The other important source of collateral flow is from the orbital branches of the ipsilateral ECA. Anterograde flow up in the ECA to the orbit (mainly via its maxillary branches, but also via facial, frontal branches or leptomeningeal branches) allows links with the ophthalmic branch (OA) of the ICA. Blood flows in a retrograde manner in the ophthalmic branch to join the supraophthalmic part of the ICA, where it flows in the usual anterograde fashion. Less commonly, collateral circulation may come from the vertebrobasilar systems or the cortical surface branches.
Can ICA occlusion cause brain ischaemia?
ICA occlusion can produce brain or retinal ischaemia by the following mechanisms:
Can ICA occlusion manifest as syncopal episodes?
ICA occlusion can also manifest as syncopal episodes.12
Is ICA occlusion asymptomatic?
The clinical spectrum of ICA occlusion ranges from being a completely asymptomatic occlusion (often noted on the “wrong” side during investigation of a TIA or stroke) to a devastating stroke or death. It is possible that in patients with adequate collateral flow, ICA occlusion may remain asymptomatic. TIA or stroke caused by ICA occlusion can present with clinical features similar to those due to any other aetiology. An episode of transient monocular blindness (amaurosis fugax) is highly suggestive of ICA disease proximal to the ophthalmic branch. ICA occlusion is an independent predictor of neurological worsening in stroke.4
How accurate is ICA occlusion?
In a retrospective, population‐based study on patients with symptomatic ICA occlusion, an incidence rate of 6/100 000 was reported.1The authors of the study consider it to be an underestimation as many patients with transient ischaemic attack (TIA) do not seek medical attention and some patients with stroke or TIA do not undergo carotid imaging. The same study suggests that about 15% of large‐vessel infarctions may be caused by ICA occlusion. In a study in Manchester, UK, Mead et al2reported ICA occlusion in 50 of 380 patients with ischaemic stroke consecutively over a 1‐year period. In a study on the correlation of arteriographic findings and symptoms in patients with cerebrovascular disease, 25% of patients with ischaemic stroke had ICA occlusion.3The prevalence of asymptomatic ICA occlusion is unknown.
What is it called when the carotid artery is blocked?
The area where the main carotid artery branches is a common location for a blockage. If an artery becomes completely blocked (which is called carotid occlusion) or if piece of the blockage breaks off and travels to a smaller vessel where it completely blocks blood flow, a part of the brain may be completely deprived of oxygen, ...
What is the condition where one or both of the carotid arteries becomes narrowed or blocked?
Carotid occlusive disease, also called caro tid stenosis, is a condition in which one or both of the carotid arteries becomes narrowed or blocked. It is a serious condition that increases the risk of stroke if left untreated.
What happens when arteries become narrowed?
When those arteries become narrowed or blocked by plaque, not enough oxygen gets to the brain. The plaque may also break off into small pieces (emboli) that can travel into smaller vessels in the brain and lead to stroke. The area where the main carotid artery branches is a common location for a blockage. If an artery becomes completely blocked ...
What is the name of the two vessels that connect the heart and the brain?
Just above the pulse point, the carotid artery branches into two smaller vessels, called the internal and external carotid arteries. Healthy, unobstructed carotid arteries are the critical pathways that supply freshly oxygenated blood from the heart to the brain.
What is a TIA stroke?
A TIA, sometimes called a “mini-stroke,” can cause temporary neurological deficits and is an indicator of an increased risk of a future stroke. A mini-stroke is often small enough to be overlooked or dismissed, but it’s a warning sign that should not be ignored. (See Symptoms of Carotid Occlusive Disease .)
What is the name of the disease that causes the carotid artery to narrow?
Carotid Occlusive Disease. The buildup of plaque in the carotid artery can reduce the flow of oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the brain. A healthy carotid artery is shown at left; an artery narrowed by plaque is at right. Carotid occlusive disease, also called carotid stenosis, is a condition in which one or both of ...
Can a partial blockage of the carotid artery cause a stroke?
The carotid arteries are large enough to allow good short-term blood supply even when they start to narrow, and other arteries sometimes expand to compensate for the reduced flow, but carotid stenosis can still cause a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA). The larger danger of carotid stenosis is that a piece of the atherosclerotic plaque will break off and completely block an artery in the brain, which can also result in a stroke or TIA. A TIA, sometimes called a “mini-stroke,” can cause temporary neurological deficits and is an indicator of an increased risk of a future stroke. A mini-stroke is often small enough to be overlooked or dismissed, but it’s a warning sign that should not be ignored. (See Symptoms of Carotid Occlusive Disease .)
What is the narrowing of the carotid artery?
The narrowing of the carotid artery is known as carotid stenosis. The plaque in the artery is common in people who smoke, have diabetes, a family history of this problem, uncontrolled high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Carotid artery narrowing may cause a temporary loss of sight in one eye that lasts only several minutes.
What is it called when you have plaque in your carotid arteries?
This condition is known as amaurosis fugax. Patients with plaque and narrowing in their carotid arteries will also frequently have plaque in the arteries to their heart and may be at increased risk for a heart attack.
What is the balloon used for in angiogram?
Sometimes a balloon is used to open up the narrowed artery. The stent holds the walls of the artery open so more blood can flow through. In the angiogram at the near right, the narrowing of the carotid artery (shown in the circle) can be seen.
Can a stent be placed in the neck?
It can also happen is the narrow portion of the artery is too high up the neck to reach with surgery. In these cases, a stent can be placed in the carotid artery. In this procedure, the patient has an angiogram. A small tube is placed in an artery in the groin.
What is the procedure called when the artery is cleaned out of the plaque?
This procedure is called carotid endarterectomy. During the surgery, the artery is cleaned out of the plaque. For women the statistics are slightly different. A woman usually must have a narrowing greater than 70% to benefit from carotid endarterectomy surgery.
Can a 50% narrowing of the carotid artery cause stroke?
Studies of patients with carotid stenosis but no symptoms have shown that as little as a 50% narrowing of the artery may increase the patient's risk for stroke. For otherwise healthy men with a 50% or greater narrowing of the carotid artery, recent studies have shown that they may benefit from surgery.
What causes carotid stenosis?
Other more rare conditions that can cause carotid stenosis include fibromuscular dysplasia and Takayasu's arteritis. In these diseases, there may be many areas of one artery (or many arteries) involved with narrowing
How to treat carotid stenosis?
Treatment for severe carotid stenosis involves eliminating the artery blockage. The most common way to do that is with a surgery called “ carotid endarterectomy .”. It’s performed by making an incision along the front of the neck, opening the carotid artery and removing the plaque.
What is a TCAR procedure?
There is a new treatment, however, called transcarotid arterial revascularization, or TCAR, that uses a different approach to opening a blocked carotid artery. The risk of a stroke during that procedure may be lower than it would be with other methods.
What is a TCAR stent?
With TCAR, a stent can be placed to open the artery and relieve the blockage, while the brain is protected from any debris that could lead to a stroke.
Where is the stent placed in the neck?
It involves making a tiny incision at the base of the neck and, from there, inserting a stent into the carotid artery. While the stent is being placed, blood flow through the carotid artery is reversed temporarily.
What is the coil called that is inserted to keep the artery open?
The balloon is inflated to widen the artery, pushing the plaque to the side, and a small wire mesh coil, called a stent, is inserted to keep the artery open. During both procedures, there is a risk that a stroke could occur if, as the surgeon is working, plaque is dislodged and travels to the brain. During angioplasty, there’s also ...
What is the procedure called when a balloon is inflated to widen the artery?
If the blockage is too difficult to reach using surgery, or if a patient has other health conditions that make surgery too risky, another option is carotid angioplasty and stenting. For this procedure, a catheter with a tiny balloon at the tip is threaded through an artery in the groin up to the area of the clog. The balloon is inflated to widen the artery, pushing the plaque to the side, and a small wire mesh coil, called a stent, is inserted to keep the artery open.
Is carotid stenosis dangerous?
Carotid stenosis is particularly dangerous because as plaque builds up inside a carotid artery, the plaque becomes increasingly unstable, and the plaque blockage bursts, releasing pieces of plaque into the bloodstream. Those pieces are carried up into the brain, where they can become lodged in a blood vessel and lead to a stroke.
