Treatment Options. Catheter: A long, thin tube is threaded through blood vessels until it reaches the affected area. Physical, occupational and speech therapy: These brain bleed treatments can help individuals regain brain functions (such as the ability to speak) that may have been affected by brain bleed.
How long does it take to recover from brain bleeding?
The recovery period is long for many people, lasting for months or even years. However, most people with small strokes and no additional complications during the hospital stay are able to function well enough to live at home within weeks. There are certain risk factors for a hemorrhagic stroke.
What is it like to recover from a brain bleed?
Some people recover from injuries within a week, and others ta. Continue Reading. Actually, only hemorrhagic strokes are caused by bleeding, there are also strokes caused by clots and other kinds of obstructions, and each of these will have varying effects depending on the severity and area of the brain affected.
What is the recovery time for a brain bleed?
Understanding TBI: Part 3 - The Recovery Process
- Possible stages of recovery. ...
- Length of recovery. ...
- Long-term impacts. ...
- Recovery two years after brain injury. ...
- More in the Understanding TBI Series. ...
- More TBI Factsheets from the Model Systems Knowledge Translation Center (MSKTC) Several of the issues mentioned in this factsheet are presented in more detail in other MSKTC factsheets on TBI.
- References. ...
What are the chances of surviving a brain bleed?
What are the chances of surviving from brain hemorrhage? Dr. Julie Abbott answered Preventive Medicine 45 years experience Around 50%: Bleeding within the brain, an intracerebral hemorrhage, either from trauma or a type of stroke, results in survival of about 50% often with disability... Read More 3.5k views Answered >2 years ago Thank 1 thank

How is a bleed on the brain treated?
If a burst cerebral aneurysm causes a hemorrhage, a surgeon may remove part of the skull and clip the artery. This procedure is called a craniotomy. Other treatment options include anti-anxiety drugs, anti-epileptic drugs, and other medications to control symptoms, such as seizures and severe headaches.
How serious is a brain bleed?
A brain bleed causes brain damage and yes, they can be life-threatening. The seriousness and outcome of a brain bleed depends on its cause, location inside the skull, size of the bleed, the amount of time that passes between the bleed and treatment, your age and overall health.
What is the survival rate of bleeding in the brain?
Intracerebral hemorrhage has a 30-day mortality rate of 44%. Pontine or other brainstem intracerebral hemorrhage has a mortality rate of 75% at 24 hours.
Can a brain bleed be treated without surgery?
Diagnosis & treatment Many hemorrhages do not need treatment and go away on their own. If a patient is exhibiting symptoms or has just had a brain injury, a medical professional may order a computerized tomography (CT) scan or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to check for brain hemorrhages.
Can you fully recover from a brain bleed?
Some patients recover completely. Possible complications include stroke, loss of brain function, seizures, or side effects from medications or treatments. Death is possible, and may quickly occur despite prompt medical treatment.
How long does a brain bleed take to heal?
Adults will have the majority of their recovery during the first six months. Then you might have smaller, more-gradual improvements for up to two years after the hematoma. To aid your recovery: Get enough sleep at night, and rest in the daytime when you feel tired.
How long can you live after brain bleed?
In a recent review, 34% of patients died from their intracerebral bleed 3 months after the event. Another study documented death rates after an intercerebral bleed of 31% at 7 days, 59% at one year, 82% at 10 years and more than 90% at 16 years. Clearly this is a serious and frequently fatal condition.
Is a brain bleed worse than a stroke?
While brain aneurysms are less frequent than ischemic strokes, they are more deadly. Most aneurysms happen between the brain itself and the tissues separating it from your skull; this is called the subarachnoid space. Therefore, this kind of aneurysm is termed subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Can an elderly person survive a brain bleed?
Even patients over the age of 75 may recover from severe traumatic brain injury, suggests new research. This is the first study to describe the results of surgically treated elderly patients with acute subdural hematomas.
What are the 4 types of brain bleed?
Intracranial hemorrhage encompasses four broad types of hemorrhage: epidural hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and intraparenchymal hemorrhage.
What is the difference between a brain bleed and a stroke?
Ischemic stroke: An artery is blocked, and blood supply no longer reaches all the parts of the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke: A blood vessel bursts or leaks, and blood enters parts of the brain where it would not normally be. The two types of hemorrhagic stroke are: Intracerebral: Bleeding occurs within the brain.
Overview
Brain bleeds are a breaking point in which a ruptured blood vessel causes bleeding inside the brain. This is known as brain bleeds in the standard term. The causes for brain bleeds can be high blood pressure, trauma, and, more specifically, consuming blood-thinning drugs. The high pace of brain bleeds needs immediate care.
Causes of brain bleeds
Brain bleeds can be caused by various actions like increased intake of alcohol, overemphasize on exercise, chain-smoking, high cholesterol consumption, heavy nose-blowing, stress, anger, sudden shock, constant sex, and masturbation, drinking coffee constantly, stroke, excessive use of soda, and cola, constipation, traumatic brain injury after a fall, head injury, using cocaine, and a rare genetic disorder..
Types of brain bleeds
There are two types of major bleeding or hemorrhages in the brain: intracerebral hemorrhage and intra-ventricular hemorrhage.
Types of head bleeds
Let me help you with a little background to understand the brain bleeds with the types of head bleeds. There are 3 types of head bleeds. They are epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Types of head bleeds may not include intraparenchymal hematoma because, it is an intraventricular hemorrhage happening in the brain.
Symptoms of brain bleeds
There are manifold symptoms to understand the brain bleeds. People going unconscious, can be a single symptom. Brain bleeds symptoms can vary from individual to individual as per the location of the brain’s damaged tissues.
Diagnosis for brain bleeds
The doctor will be able to understand the symptoms by seeing the patients with brain bleeds. However, he or she will be suggesting various diagnostic procedures to see the exact nature of the brain bleeds. The diagnostic techniques include imaging tests like MRI.
Treatment for brain bleeds -the new way
The reader needs to understand that brain bleeds are regular, resulting from a minor injury affecting the head. The question is, how to treat them in the new way available to the broader public.
Where does bleeding occur in the brain?
Bleeding can occur inside the brain, between the brain and the membranes that cover it, between the layers of the brain's covering or between the skull and the covering of the brain. What Causes Bleeding in the Brain? There are several risk factors and causes of brain hemorrhages. The most common include:
How to control cerebral hemorrhage?
The single most important thing you can do is control yours through diet, exercise, and medication. Don’t smoke. Don’t use drugs. Cocaine, for example, can increase the risk of bleeding in the brain.
What causes a brain hemorrhage?
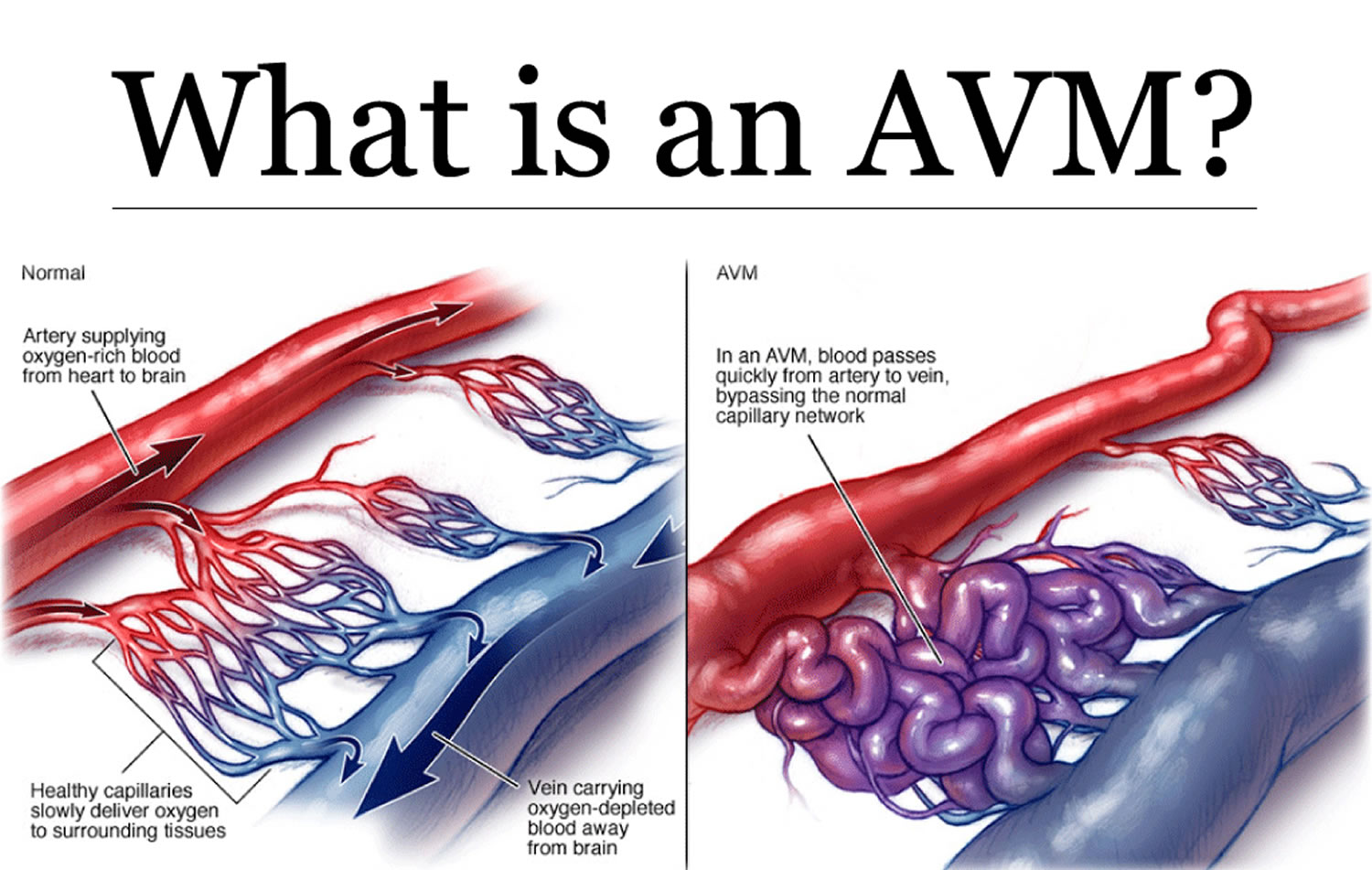
There are several risk factors and causes of brain hemorrhages. The most common include: 1 Head trauma. Injury is the most common cause of bleeding in the brain for those younger than age 50. 2 High blood pressure. This chronic condition can, over a long period of time, weaken blood vessel walls. Untreated high blood pressure is a major preventable cause of brain hemorrhages. 3 Aneurysm. This is a weakening in a blood vessel wall that swells. It can burst and bleed into the brain, leading to a stroke. 4 Blood vessel abnormalities. (Arteriovenous malformations) Weaknesses in the blood vessels in and around the brain may be present at birth and diagnosed only if symptoms develop. 5 Amyloid angiopathy. This is an abnormality of the blood vessel walls that sometimes occurs with aging and high blood pressure. It may cause many small, unnoticed bleeds before causing a large one. 6 Blood or bleeding disorders. Hemophilia and sickle cell anemia can both contribute to decreased levels of blood platelets and clotting. Blood thinners are also a risk factor. 7 Liver disease. This condition is associated with increased bleeding in general. 8 Brain tumors.
What is the term for the mass of blood that collects in the brain?
This is known as cerebral edema. The pooled blood collects into a mass called a hematoma. These conditions increase pressure on nearby brain tissue, and that reduces vital blood flow and kills brain cells. Bleeding can occur inside the brain, between the brain and the membranes that cover it, between the layers of the brain's covering ...
What is the meaning of "hemorrhage" in Greek?
This bleeding kills braincells. The Greek root for bloodis hemo. Hemorrhage literally means "bloodbursting forth.".
How to prevent bleeding from aneurysms?
Investigate corrective surgery. If you suffer from abnormalities, such as aneurysms, surgery may help to prevent future bleeding. Be careful with Coumadin. If you take this blood-thinning drug, also called warfarin, follow up regularly with your doctor to make sure your blood levels are in the correct range.
What test can reveal internal bleeding?
Once you see a doctor, they can determine which part of the brain is affected based on your symptoms. Doctors may run a variety of imaging tests, such as a CT scan , which can reveal internal bleedingor blood accumulation, or an MRI.
What is the term for a bleed in the brain?
Brain Bleed, Hemorrhage (Intracranial Hemorrhage ) Brain bleeds – bleeding between the brain tissue and skull or within the brain tissue itself – can cause brain damage and be life-threatening. Some symptoms include headache; nausea and vomiting; or sudden tingling, weakness, numbness or paralysis of face, arm or leg.
What does it mean when your brain bleeds?
To most people, a “brain bleed” simply means any bleed inside your head. However, a doctor – and specifically doctors who treats brain bleeds (neurologists and neurosurgeons) – would say that a “brain bleed” (also known by the medical term intracranial hemorrhage) is too broad of a term. These doctors further describe brain bleeds by their exact ...
What is the name of the bleed that occurs inside the brain?
Bleeding inside the brain tissue. Two types of brain bleeds can occur inside the brain tissue itself – intracerebral hemorrhage (also called cerebral hemorrhage and hemorrhagic stroke) and intraventicular hemorrhage.
How does a hemorrhage affect the brain?
When a hemorrhage interrupts blood flow around or inside the brain, depriving it of oxygen for more than three or four minutes, the brain cells die.
Why can't the brain store oxygen?
Since the brain cannot store oxygen, it relies upon a series of blood vessels to supply oxygen and nutrients. When a brain hemorrhage occurs, oxygen may no longer be able to reach the brain tissue supplied by these leaky or burst vessels.
What causes a tumor to bleed?
Brain tumor that presses on brain tissue causing bleeding. Smoking, heavy alcohol use, or use of illegal drugs such as cocaine. Conditions related to pregnancy or childbirth, including eclampsia, postpartum vasculopathy, or neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage.
Why does my brain bleed?
Bleeding in the brain has a number of causes, including: Head trauma, caused by a fall, car accident, sports accident or other type of blow to the head. High blood pressure ( hypertension ), which can damage the blood vessel walls and cause the blood vessel to leak or burst.
What is a bleed on the brain called?
A bleed on the brain is known as a hemorrhage, which is a type of stroke. The kind of bleed depends on where it occurs in the brain. For example, if a person hits their head, they may experience a subdural hematoma. .
Why does my brain bleed?
Physical activity or strain can cause an aneurysm to rupture. This is why a brain bleed might happen if someone lifts something heavy, or feels a strong emotion, such as anger, which causes their blood pressure to rise. The symptoms can vary, depending on where the bleed occurs.
What are the two types of bleeds on the brain?
Types of bleed on the brain. There are two types. Trusted Source. of bleed on the brain: intracerebral hemorrhage , where the bleed occurs within the brain tissue, and subarachnoid hemorrhage, where the bleed happens on the brain surface.
Why do people have brain bleeds?
It may be obvious that a person has a brain bleed because of their symptoms. Clear causes and risk factors, such as a head injury, or previous stroke, can also help diagnose a brain bleed. A person will usually need tests in the hospital to diagnose a brain bleed.
What are the symptoms of a brain bleed?
Prevention. Summary. Symptoms of a brain bleed include severe headaches, blurred vision, weakness on one side of the body, and a stiff neck. A brain bleed is a medical emergency that needs hospital treatment. A bleed on the brain is known as a hemorrhage, which is a type of stroke. The kind of bleed depends on where it occurs in the brain.
How do you know if you have a bleed on your brain?
A person with a bleed on the brain may experience: sudden severe headache. stiff neck. feeling or being sick.
What happens to the brain after a stroke?
Symptoms include drowsiness, and signs similar to a stroke. Fluid can build up on the brain after a brain bleed.
How to prevent brain hemorrhage?
They can also be overweight, have high cholesterol and high blood pressure, all of which can lead to stroke. Changing diets and doing exercise are some of the best changes that can help minimize the risk of brain hemorrhages.
What are the complications of a brain hemorrhage?
Long-term complications can occur, depending on the damage and location of the brain hemorrhage. These include: 1 Inability to speak/understand words 2 Paralysis 3 Vision loss 4 Personality change/Emotional problems 5 Numbness/Weakness in the body 6 Confusion/Memory loss 7 Difficulty swallowing
How long do you stay in hospital after a brain hemorrhage?
Subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by an aneurysm will need the patient to stay in hospital for a minimum of two weeks to be monitored in case of a cerebral vasospasm. Recovery is easier and faster for patients who didn't suffer any rupturing of the aneurysm. These patients can leave after a few days and continue with their lives. Patients that had a craniotomy surgery will have to stay for a few days after their release from the ICU.
Why is brain hemorrhage so bad?
Brain hemorrhage can be caused by blood leaking from weak blood vessels, trauma, drug abuse and high blood pressure. Brain hemorrhage should be treated immediately to avoid serious complications.
How long does it take to recover from a craniotomy?
These patients can leave after a few days and continue with their lives. Patients that had a craniotomy surgery will have to stay for a few days after their release from the ICU.
Why is it important to protect your brain?
For this reason, it is important that people take care to protect their brains. This can be done by protecting the head by wearing helmets when cycling and motorcycling and wearing seat belts when driving.
Can a craniotomy be done on a hematoma?
Open surgery or craniotomy can be done to help the patient. The surgeon will carefully and partially remove a part of the skull to perform the open surgery to drain the hematoma. The ruptured blood vessels will also be drained, but this surgery will only be done in case the hematoma is too large.
What causes brain bleeds?
Brain bleeding primarily results from the irritation of brain tissues, which leads to swelling or cerebral palsy. The swelling increases pressure on arteries causing them to burst and create hematomas that prevent blood flow to the affected brain parts, thus damaging or killing the brain cells. Causes may include, but or not limited to: 1 chronic high blood pressure over a long period of time 2 trauma, such as a blow to the head 3 aneurysms that weaken the walls of blood vessels may also make the arteries swell and burst into the brain 4 malformations in brain arteries and blood vessels 5 amyloid angiopathy which is an abnormality of the walls of blood arteries often related to high blood pressure and aging 6 bleeding disorders such as sickle cell anemia and hemophilia 7 brain tumors and liver disease may also lead to brain bleeding
What is the treatment for a hemorrhage?
Some diagnoses will require surgery to stop bleeding and to alleviate swelling. Others will require medications such as anticonvulsants that control seizures, diuretics that reduce swelling, and corticosteroids and painkillers.
What is the difference between a subdural and an epidural hematoma?
A subdural hematoma results from blood collecting between the outermost layer of the brain, also known as the dura, and the next layer called the arachnoid. An epidural hematoma refers to the bleeding between the dura matter and the skull. Hematomas can result in excess pressure and/or swelling of the brain, and in the worst cases can lead to death.
Why does my brain swell?
The swelling increases pressure on arteries causing them to burst and create hematomas that prevent blood flow to the affected brain parts, thus damaging or killing the brain cells. Causes may include, but or not limited to: chronic high blood pressure over a long period of time. trauma, such as a blow to the head.
Does a minor bleed affect the lifespan?
Minor bleeding may not cause any significant or visible health challenges, and may not affect the lifespan of the individual. Where the bleed is located within the brain, as well as when it is detected and subsequently treated, may be determining factors of survival.
Can you recover from a bleed?
Some patients recover fully after the bleeding if proper treatment is provided, but others survive with various complications. Possible complications that the patients could endure include loss of brain function, stroke, and adverse reactions to medications.
Can a brain bleed cause death?
Not all brain bleeds result in death. In fact, death is generally caused by the most extreme cases. Most patients can survive if treatment is sought in due time. How well an affected person responds to brain bleeds is determined by the size of the severity of the bleeding, its location, and the amount of swelling that result from the bleeding.
How to stop a brain injury?
Check with your doctor before you begin driving, playing sports, riding a bicycle or operating heavy machinery. Your reaction times likely will have slowed as a result of your brain injury. Check with your doctor before taking medication. Don't drink alcohol until you've recovered fully.
How to treat a hematoma?
Hematoma treatment often involves surgery. The type of surgery depends on the type of hematoma you have. Options include: 1 Surgical drainage. If the blood is localized and has transitioned from a solid clot to a liquid consistency, your doctor might create a small hole in your skull and use suction to remove the liquid. 2 Craniotomy. Large hematomas might require that a section of your skull be opened (craniotomy) to remove the blood.
How long does it take to recover from intracranial hematoma?
Recovery after an intracranial hematoma can take a long time, and you might not recover completely. The greatest period of recovery is up to three months after the injury, usually with lesser improvement after that. If you continue to have neurological problems after treatment, you might need occupational and physical therapy.
What is the most common imaging scan for intracranial hematoma?
CT is the most commonly used imaging scan to diagnose intracranial hematomas. MRI scan. This is done using magnetic field and radio waves to make computerized images. During an MRI scan, you lie on a movable table that's guided into a tube. Angiogram.
What type of surgery is used for hematoma?
The type of surgery depends on the type of hematoma you have. Options include: Surgical drainage. If the blood is localized and has transitioned from a solid clot to a liquid consistency, your doctor might create a small hole in your skull and use suction to remove the liquid. Craniotomy.
How long does it take to recover from a brain injury?
Patience is important for coping with brain injuries. Adults will have the majority of their recovery during the first six months. Then you might have smaller, more-gradual improvements for up to two years after the hematoma.
Can intracranial hematoma cause loss of consciousness?
However, doctors generally assume that bleeding inside the skull is the cause of progressive loss of consciousness after a head injury until proved otherwise.
What is the term for the blood that forms between the brain and the outer covering of the brain?
Over time, especially after multiple bumps, the blood forms a pool between the brain and its outer covering (the dura) called a chronic (as opposed to acute) subdural hematoma. The hematoma puts pressure on the brain, leading to symptoms that include headache, nausea, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, even seizures.
Can a broken hip cause a brain bleed?
These falls can be devastating – the dangers of a broken hip are well known, but the effects of even a minor brain bleed can be insidious. A major fall resulting in an acute bleed may be diagnosed and treated quickly, but tiny bleeds may not even be apparent when they begin.
Can a 90 year old have open brain surgery?
Even the heartiest 90-year-old may not be a great candidate for open brain surgery. But thanks to new technology, advanced training, and pioneering surgeons, we can offer older patients a minimally invasive treatment that doesn’t involve major brain surgery.
Can a subdural hematoma cause death?
Left untreated, some chronic subdural hematomas can lead to death. Until recently, unless a subdural hematoma was life-threatening, the surgical risk of repairing it often outweighed the potential benefit. Even the heartiest 90-year-old may not be a great candidate for open brain surgery.

Brain Bleed Symptoms
Causes
- All blood vessels can bleed, but bleeding of a blood vessel in the brain is not common. If it occurs, there is usually a precipitating factor. Some blood vessels in the brain are more likely to bleed than others. Causes and types of bleeding in the brain include: 1. Head trauma: Head trauma can be caused by a fall, car accident, sports injury, or assault. When bleeding occurs, it's usually bet…
Diagnosis
- Brain bleeds are typically diagnosed with a computerized tomography (CT) scan of the brain. This imaging test is generally more sensitive to acute bleeds in emergency situations than magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). With that said, MRIs are better able to detect smaller intracranial hemorrhages than CT.12 Imaging tests are able to discover the location and size of a bleed and …
Summary
- Bleeding in the brain is a serious medical emergency that can lead to disability or death. If you suspect a brain bleed, call for emergency help. Symptoms can be non-specific but include head pain, neck pain, visual changes, weakness, slurred speech, lethargy, confusion, seizures, vomiting, and collapsing. Brain bleeding can be caused by head trauma from a fall or accident. It can also …
A Word from Verywell
- There are several types of brain bleeds, and while they are dangerous, recovery is possible. If you experience or encounter someone who is experiencing signs of a brain bleed, seek help immediately. Getting emergency treatment is the best way to optimize the outcome.