Medication
How to Treat Parkinson’s Disease with Natural Remedies?
- Consuming Fresh Raw Vegetables and Fruits. It is widely held that fresh organic vegetable and fruits consumed raw can provide all the nutrients necessary for the cleansing of the body.
- Consume More Fermented Foods. ...
- Avoid Unnecessary Iron Consumption. ...
- Choose Green Tea. ...
Procedures
There is no definite timeline when it comes to the final stage of Parkinson's disease. Hospice care is available when a patient has a life expectancy of six months or less. What are the first steps toward getting hospice care? First, discuss hospice care with the person with PD and include their family members/caregivers.
Therapy
The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) in its updated treatment guidelines for early Parkinson’s disease recommends initiating patients with the lowest effective dose of immediate-release ...
Self-care
Amantadine (Symmetrel) may help people with mild Parkinson's disease by raising the amount of dopamine that your brain cells can use, which leads to fewer symptoms. It may help ease the involuntary movements that can happen when you take levodopa. But it may cause side effects, such as confusion and memory problems.
Nutrition
See more
How to cure Parkinson's disease naturally?
How long can a person live with Stage 5 Parkinson?
How to cure Parkinson?
How does amantadine help Parkinson's?
See more
What are the treatments for Parkinson's disease?
Treatment for Parkinson's disease may include the following: Medications. Surgery. Complementary and supportive therapies, such as diet, exercise, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. [ 6 Medication-Free Ways to Feel Better with Parkinson’s Disease]
How does surgery help Parkinson's?
Most of the treatments are aimed at helping the tremor or rigidity that comes with the disease . In some patients, surgery may decrease the amount of medication that is needed to control the symptoms . There are three types of surgeries that may be performed for Parkinson's disease, including the following:
How does a Parkinson's stimulator work?
The stimulator is then turned on and interrupts the normal flow of information in the brain and can help to decrease symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Neural grafting or tissue transplants.
What is the procedure called when the brain is burned?
Lesion surgery (burning of tissue). In this procedure, deep parts of the brain are targeted and small lesions are made in critical parts of the brain that help control movement. The surgery may be done while the patient is awake to help determine the exact placement of the lesion.
What is the next decision for a Parkinson's patient?
Once the doctor diagnoses Parkinson’s disease, the next decision is whether a patient should receive medication, which depends on the following: No two patients react the same way to a given drug, therefore, it takes time and patience to find an appropriate medication and dosage to alleviate symptoms.
Is there a cure for Parkinson's disease?
With today's medicine, we have yet to find a cure for Parkinson's disease. However, based on the severity of the symptoms and medical profile, ...
Can Parkinson's disease be cured?
With today's medicine, we have yet to find a cure for Parkinson's disease. However, based on the severity of the symptoms and medical profile, the doctor will establish an appropriate treatment protocol. Treatment for Parkinson's disease may include the following: Medications. Surgery.
What is the best treatment for Parkinson's disease?
The main therapy for Parkinson's is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain's dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa.
What does Parkinson's disease do to the body?
People with Parkinson's also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure.
How many symptoms are there of Parkinson's disease?
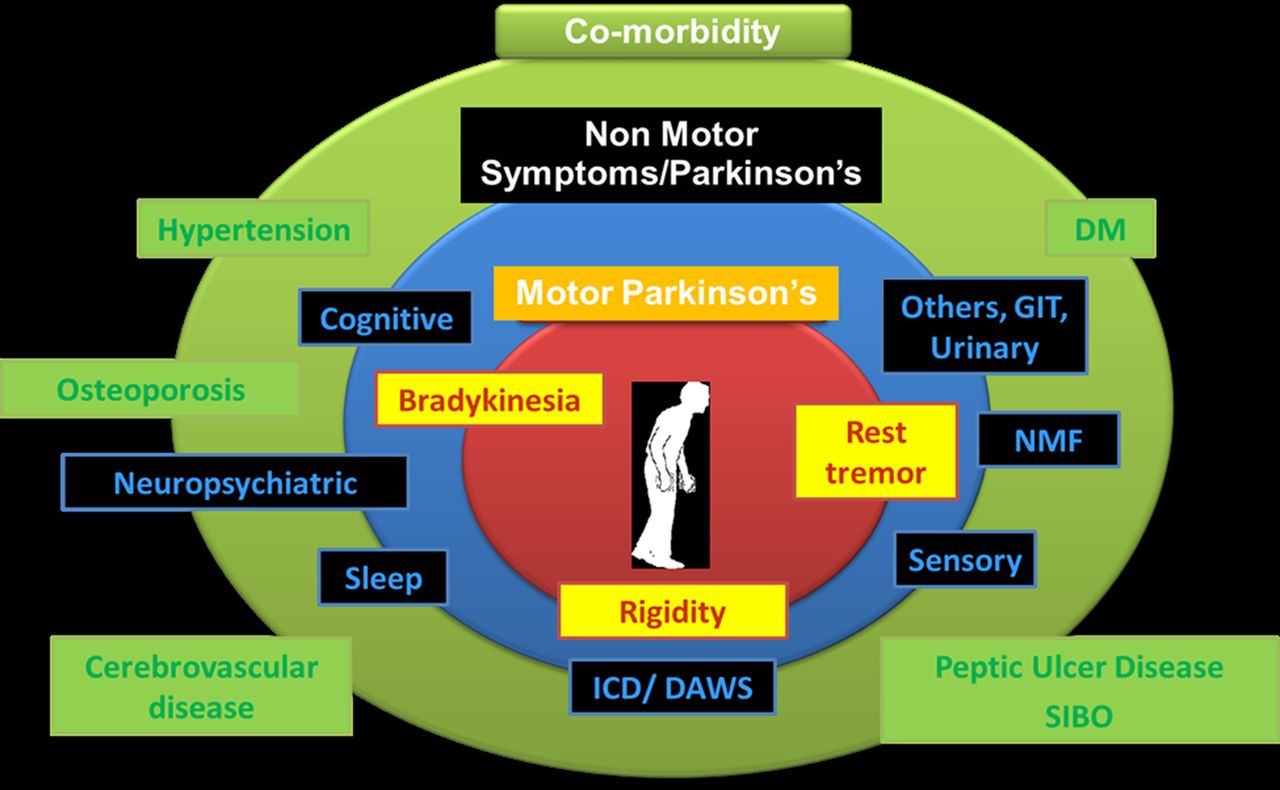
Parkinson's disease has four main symptoms: Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes; difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking; urinary problems or constipation; skin problems; and sleep disruptions. Symptoms of Parkinson’s and the rate of progression differ among individuals.
What age do you get Parkinson's?
Although most people with Parkinson’s first develop the disease at about age 60, about 5 to 10 percent of people with Parkinson's have "early-onset" disease, which begins before the age of 50. Early-onset forms of Parkinson's are often, but not always, inherited, and some forms have been linked ...
Does Parkinson's disease have lewy bodies?
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson's contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia. Although some cases of Parkinson's appear ...
Can you get a blood test for Parkinson's?
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose nongenetic cases of Parkinson's disease. Diagnosis is based on a person's medical history and a neurological examination. Improvement after initiating medication is another important hallmark of Parkinson's disease.
Can Parkinson's cause parkinsonism?
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinson's disease. People with Parkinson's-like symptoms that result from other causes are sometimes said to have parkinsonism.
What is the treatment for Parkinson's disease?
Treatments may include medicine, therapy, and even surgery. Each case of Parkinson’s disease is unique, and your treatment plan should be, too.
How to slow the onset of Parkinson's disease?
You can also make improvements in your daily life to slow the onset of symptoms. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting plenty of sleep . Tai chi and yoga have both proven to encourage better balance and coordination for people with Parkinson’s disease. Alternative therapies include massage, acupuncture, ...
How old do you have to be to get Parkinson's?
While anyone can develop Parkinson’s disease, age is the greatest factor in receiving a diagnosis. The average age of developing this disease is 60, and men are more likely to receive a diagnosis than women. Having a close relative, like a parent or sibling, who has Parkinson’s disease doubles your risk factor.
What type of imaging is needed for Parkinson's disease?
This may include brain imaging, an MRI, or a PET scan to see activity in the area of the brain typically affected by Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor may also refer you to a movement disorder specialist. Seeing subspecialists is very important to avoid being misdiagnosed.
How many cases of Parkinson's come from genetics?
Scientists who have studied this disorder estimate that 10-15% of cases come from genetics after seeing a series of genetic mutations that were common in Parkinson’s patients. Doctors suspect that environmental factors and lifestyle choices may have effects on the severity of Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
What are the side effects of Parkinson's?
Talk to your doctor about risk factors and assess the possibility of additional complications. Some side effects of Parkinson’s medication include: Nausea. Involuntary motions.
Is there a cure for Parkinson's disease?
While there is not currently a cure for Parkinson’s disease, many treatment options are available that can help ease your symptoms. Treatments may include medicine, therapy, and even surgery. Parkinson’s disease is the deterioration of brain nerves that control movement.
Is there a cure for Parkinson's disease?
There is no cure for Parkinson's disease, but it can be managed -- and the symptoms of the disease can be relieved or reduced. Treating Parkinson's disease is often a "team effort" involving not only your neurologist but also a wide variety of specialists. Your health care team should include:
Can Vitamin E be used for Parkinson's?
Alternative Treatments for Parkinson's Disease. Alternative therapy may also be used to treat Parkinson's disease. The most touted in recent years has been the effect of Vitamin E on reversing the progression of the disease; although, this effect is still being debated by the scientific community.
What is the best treatment for Parkinson's disease?
Physical, occupational and speech therapy. Physical, occupational and speech therapists can be important partners in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Physical therapy can improve your gait and direct you to the right exercise regimen. Occupational therapy can be helpful to maximize your fine motor skills.
How to improve your health with Parkinson's?
Lifestyle changes. A healthy diet can increase energy, maximize the potential of medications, and promote overall well-being. Click here to review a Webinar entitled Living Well Everyday which reviews the principles of good nutrition for Parkinson’s disease.
What is DBS in Parkinson's?
Some patients with Parkinson’s disease may benefit from deep brain stimulation (DBS), a surgical therapy that has been FDA approved for over a decade. DBS involves implanting an electrode into a targeted area of the brain, usually the subthalamic nucleus (STN) or the globus pallidus interna (GPI).
How have clinical trials helped Parkinson's patients?
They have helped make available many new treatments in addition to improving the delivery methods of medications and new deep brain stimulation techniques.
What is the American Parkinson's Association?
The American Parkinson Disease Association nationwide network provides information and referral, education and support programs, health and wellness activities, and events to facilitate a better quality of life for the Parkinson's community.
How does a healthy diet help with Parkinson's?
A healthy diet can increase energy, maximize the potential of medications, and promote overall well-being. Click here to review a Webinar entitled Living Well Everyday which reviews the principles of good nutrition for Parkinson’s disease.
Is there a cure for Parkinson's disease?
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s at this time, there are a number of treatments that can ease symptoms. Parkinson’s medications are the mainstay of treatment, but modalities are often used in combination. Physical, occupational and speech therapy can be critical to the treatment plan. Surgical options also have an important role ...
Medications already available
The older medications that were used, and continue to be used to treat Parkinson’s, include carbidopa/levodopa formulations, dopamine agonists (available in immediate-release, long-acting, patch form, and injectable form), catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors, monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitors, anticholinergics, and amantadine.
Important points about the new medications
With multiple new medications available for the treatment of PD, there is more hope than ever that Parkinson’s symptoms can be successfully managed for many years. A few things to consider:
New Medications for OFF time
A number of new medications approved recently are designed to reduce OFF time. These medications fall into two major categories:
Medications for dyskinesias
Amantadine formulations (Gocovri® and Osmolex ER™) Originally used to prevent or treat influenza, amantadine was observed to ease the tremor of Parkinson’s as well as muscle It has therefore been used as an adjunct medication to other therapies for PD. In addition, it was also observed to be effective at decreasing dyskinesias caused by levodopa.
Aiming for timely diagnosis
As with many chronic conditions, earlier recognition of Parkinson’s disease can help people experience an enhanced quality of life.
Genes and biomarkers
Currently, many Parkinson’s treatments are intended to limit the effects of the disease’s symptoms. Researchers are aiming to develop disease-modifying drugs that can stall or limit its progression overall.
Promising therapies
Some of the key recent research on Parkinson’s disease highlighted by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke includes:
Medications
Doctors use different medications to treat Parkinson’s disease, including:
Deep brain stimulation
In 1997, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved deep brain stimulation (DBS) as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease tremors. If the medication levodopa stops working for treating a person’s Parkinson’s, a doctor may recommend DBS.
Diet and lifestyle changes
Additional therapies for Parkinson’s disease treatment include eating a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise.
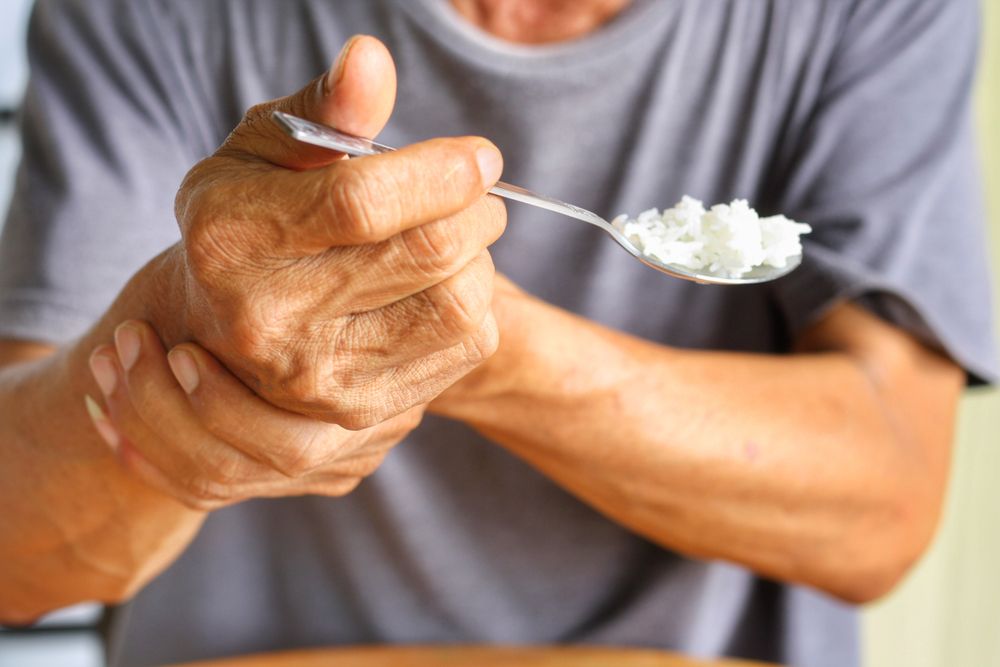

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
- No specific test exists to diagnose Parkinson's disease. Your doctor trained in nervous system conditions (neurologist) will diagnose Parkinson's disease based on your medical history, a review of your signs and symptoms, and a neurological and physical examination. Your doctor may sug…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.