
Explore
Treatment of First-Degree AV Block
- Medications. If the patient is symptomatic and does not have any immediately reversible causes and is demonstrating signs or symptoms of poor perfusion as a result of a bradyarrhythmia, the ...
- Pacing. ...
- Next Steps and Considerations. ...
What is the treatment for first degree AV block?
Drugs that most commonly cause first-degree AV block include the following: Class Ia antiarrhythmics (eg, quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide) Class Ic antiarrhythmics (eg, flecainide, encainide, propafenone)
What medications cause AV block?
Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is a common treatment.
Is AV block considered heart disease?
What Are ECG Characteristics of First-Degree AV Block?
- P wave for every QRS complex
- Prolonged PR interval that is greater than 0.20 seconds
- If the PR interval is greater than 0.30 seconds, a P wave may appear to be buried in the previous T wave
- If the PR interval is extended for more than 0.30 seconds, it is considered “marked”
- No beats are dropped in this rhythm
What are the symptoms of a 1st degree AV block?
What is the treatment for a first-degree AV block?
In general, no treatment is required for first-degree AV block unless prolongation of the PR interval is extreme (>400 ms) or rapidly evolving, in which case pacing is indicated. Prophylactic antiarrhythmic drug therapy is best avoided in patients with marked first-degree AV block.
Which medication is used for AV block treatment?
Medications that may be used in the management of third-degree AV block (complete heart block) include sympathomimetic or vagolytic agents, catecholamines, and antidotes.
Can AV block be cured?
Heart block caused by a heart attack or heart surgery may go away as you recover. If medicine is causing heart block, changing medicines can fix the problem.
What is the main cause of AV blocks?
The most common causes of AV block include: Fibrosis or sclerosis. Extra tissue can thicken, scar, and damage the pathways that send signals from the upper part to the lower part of your heart. Coronary artery disease.
Which is the best treatment for heart block?
With first-degree heart block, you might not need treatment. With second-degree heart block, you may need a pacemaker if symptoms are present or if Mobitz II heart block is seen. With third-degree heart block, you will most likely need a pacemaker.
How serious is a first-degree AV block?
Traditionally, first-degree AV block has been considered a benign condition. However, epidemiologic data from the Framingham Study have shown that first-degree AV block is associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality in the general population.
Can we remove heart blockage without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
Can medicine cure heart block?
There is no heart-block-specific treatment. Most people with bundle branch block have no symptoms, and they do not require treatment. However, any underlying causes, such as hypertension, will need treatment. Share on Pinterest Patients with second- or third-degree heart block may need a pacemaker.
How long can you live with heart block?
A follow-up study of the survival rate of 164 patients with complete heart block treated with permanent pacemaker showed 87% survival after one year, 76 after two, and 50% after five years.
Is AV block heart failure?
First-degree atrioventricular block is associated with heart failure and death in persons with stable coronary artery disease: data from the Heart and Soul Study.
Is AV block normal?
Some AV blocks are benign, or normal, in certain people, such as in athletes or children. Other blocks are pathologic, or abnormal, and have several causes, including ischemia, infarction, fibrosis, and drugs.
What does AV block feel like?
Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can't pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath.
How does an AV block work?
They team up to pump blood through your body. An electrical signal starts out in a spot called the sinoatrial (SA) node. It's known as your heart's natural pacemaker. The current heads down to a group of cells called the atrioventricular (AV) node.
What happens when you have a heart block?
When you have heart block, the electrical signal from your heart's upper chamber slows down or gets interrupted on its way to the lower chambers. You can get mild AV block as your heart adapts to an intensive exercise routine. It's sometimes called "athlete's heart.".
What is the condition where the heart is blocked?
But sometimes this current gets delayed or stopped. The result: a condition called atrioventricular (AV) block or heart block. Certain health conditions, heart defects, and medicines can cause it.
Why does my heart block after a heart attack?
Extra tissue can thicken, scar, and damage the pathways that send signals from the upper part to the lower part of your heart. Coronary artery disease. This damages your heart's blood vessels. It may cause AV block before or after a heart attack. Some other causes are: Medication.
Can AV block be life threatening?
You might not have symptoms or need treatment. But if you do, a doctor can help you manage your condition. Without the right care, serious AV block can be life threatening.
Can blood pressure medications slow your heartbeat?
Certain drugs can slow your heartbeat. This includes blood pressure medicine like beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers. I ncreased vagal tone. This happens when you have more activity in a nerve called the vagus nerve. It's a problem that sometimes shows up if you're very physically fit.
What is AV block?
AV block, or atrioventricular block, is a major cause of significant bradyarrhythmias. To diagnose and manage AV block, it is important to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the conduction system of the heart.
What causes AV block?
Acquired AV block is most commonly caused by idiopathic fibrosis, acute myocardial infarction, or drug effects. AV block can also be congenital. If AV block is symptomatic, and determined to be permanent, pacing is the only effective long-term therapy. Conduction Terminology.
What is the P–R interval of AV block?
First-degree AV block, with a P–R interval greater than 200 ms , is rarely found in young, healthy adults during activity. However, a longer P–R interval, and even Mobitz I (Wenckebach) block can be seen in young, well-conditioned individuals at rest and during sleep. The P–R interval decreases and the Wenckebach block disappears with increased activity, and is considered normal vagal influence on the AV node.
How long can you keep anticoagulant for atrial fibrillation?
Patients on anticoagulants who need temporary or permanent pacemaker placement are at increased risk of bleeding complications. If the procedure is not emergent, and the patient is on warfarin for atrial fibrillation, the drug can be withheld for 3 to 5 days, and restarted postprocedure when the risk of bleeding is acceptable.
Why is my heart block reversible?
Reversible causes of complete heart block can be due to metabolic abnormalities, drug effects, Lyme disease, or vasovagal episodes. In these cases, the complete heart block resolves once the abnormality has been treated. In true complete heart block, the sinus rate is faster than the ventricular rate.
Where does blood come from in the AV node?
The blood supply to the AV node is from the AV nodal artery, a branch of the right coronary artery in 90% of hearts, with the remaining 10% arising from the left circumflex coronary artery. The His-bundle has a dual blood supply from branches of the anterior and posterior descending coronary arteries.
Is a complete heart block asymptomatic?
Patients with acquired complete heart block or high-grade AV block with two or more nonconducted P waves in a row, are usually symptomatic. Children with congenital complete heart block are generally asymptomatic, but tend to develop symptoms as adults.
What is the mildest heart block?
First-degree heart block: The electrical impulse still reaches the ventricles, but moves more slowly than normal through the AV node. The impulses are delayed. This is the mildest type of heart block. Second-degree heart block is classified into two categories: Type I and Type II.
What medications slow the heart's electrical impulses?
You take medications that slow the conduction of the heart’s electrical impulses including some heart medications (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin), high blood pressure drugs, antiarrhythmics; muscle relaxants and sedatives; antidepressants and antipsychotics; diuretics; lithium.
What is the name of the block that makes your heart beat?
Heart Block. Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is ...
How long do you need to wear a Holter monitor?
You may need to wear a portable ambulatory monitor device, such as a Holter monitor or an event recorder, for 24 to 48 hours or longer to collect more information about your heart’s electrical activity. If you need to use a monitor, you’ll get detailed information about how to use it.
Can heart block cause lightheadedness?
Type of heart block, its location and severity, and symptoms vary from person to person. If left untreated, severe heart block can cause sudden cardiac arrest (your heart suddenly stops beating), but most commonly can cause either lightheadedness or fainting spells.
Is a heart block a first degree or second degree?
First-degree heart block: May not have any symptoms. May be found during a routine electrocardiogram (ECG) although heart rate and rhythm are usually normal. First-degree block is common in athletes, teenagers, young adults and those with a highly active vagus nerve. Second-degree heart block symptoms:
Can you get heart block if your mother has autoimmune disease?
You may be at increased risk of a heart block if: Your mother has an autoimmune disease, such as lupus. You are of older age. Risk of heart block increases with age. You have other heart conditions including coronary artery disease, heart valve disease. You have birth defects of the heart.
What is the goal of AV block therapy?
The goals of therapy are to treat symptoms and to prevent syncope and sudden cardiac death due to very slow or absent ventricular rates. Patients with advanced AV block (usually type II second-degree, third-degree, or infranodal AV block) of irreversible cause should undergo permanent pacemaker placement.
What is an AV block?
Atrioventricular (AV) block is a cardiac electrical disorder defined as impaired (delayed or absent) conduction from the atria to the ventricles. The severity of the conduction abnormality is described in degrees: first-degree; second-degree, type I (Wenckebach or Mobitz I) or type II (Mobitz II); and third-degree (complete) AV block. This classification scheme should be applied only during sinus rhythm and not during rapid atrial arrhythmias or to premature atrial beats. [1]#N#Josephson ME. Clinical cardiac electrophysiology: techniques and interpretations. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008.
What is an AV block?
AV block is a term to describe abnormal impulse conduction through the AV node. This can be manifest as slower than usual propagation through the AV nodal structure to the ventricles, or complete disconnection of the atrial electrical signals to the ventricles. Figure 1. Animation of the sinus node impulse propagating to ...
What are the symptoms of AV block?
These include palpitations, skipped-beats, dizziness, lightheadedness, syncope (loss of consciousness), fatigue and weakness, confusion, and even angina (chest pain). Any symptoms of syncope or chest pain require urgent ...
What causes AV block?
AV block can be the result of normal wear and tear on the AV node that occurs with age. In addition, patients post-cardiac surgery, particularly valvular surgery, are at a high-risk of complete AV block necessitating permanent pacemaker implantation. Medications, particularly for hypertension, can exacerbate already slow conduction through a diseased AV node leading to symptomatic AV block. Acute coronary syndromes, i.e. heart attacks, can lead to transient versus permanent degrees of AV block. Patients undergoing alcohol septal ablation for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are also at risk for developing complete heart block.
Can AV block be permanent?
Acute coronary syndromes, i.e. heart attacks, can lead to transient versus permanent degrees of AV block. Patients undergoing alcohol septal ablation for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are also at risk for developing complete heart block.
What is the difference between a 1st degree and a 2nd degree AV block?
A 1 st degree AV block is not technically a block, but rather a delay in the conduction of atrial impulses to the ventricles , which results in an extended PR interval. Meanwhile, a 2 nd degree AV block occurs when some of the atrial impulses are fully conducted to the ventricles, whereas others are blocked along the way.
What causes Mobitz block?
Other causes of Mobitz type I block include a heart attack, disorders affecting the heart muscle walls (cardiomyopathies), inflammation of the heart muscle ( myocarditis ), infection of the inner layer of the heart ( endocarditis ), inherited heart defects, infiltrative and autoimmune disorders, and cardiac surgical procedures.
Can Mobitz block cause dizziness?
Some individuals may occasionally feel light-headedness, dizziness, or fatigue when exercising. More rarely, Mobitz type I block may lead to a sudden and temporary loss of consciousness, also known as a syncope, caused by a brief decrease in the oxygen supply to the brain.
How to prevent heart block?
A healthy lifestyle contributes to overall good health — including heart health. Exercise, eat a well-balanced diet, and don’t smoke. Understanding the risks of your medicines and reviewing them with your healthcare provider can reduce the risk of medicine-induced heart block.
What happens when your heart is blocked?
When you have heart block, there is interference with the electrical signals that usually move from the atria to the ventricles. These signals tell your heart when to beat. This is known as a conduction disorder. If the electrical signals can’t move from your atria to your ventricles, they can’t tell your ventricles to contract ...
What is the difference between a first degree heart block and a second degree heart block?
The electrical signals slow down as they move from your atria to your ventricles. First-degree heart block might not require treatment of any kind. Second-degree heart block means that the electrical signals between your atria and ventricles can intermittently fail to conduct. There are 2 types of second-degree heart block.
Can heart block cause heart failure?
First degree heart block may cause minimal problems, however third degree heart block can be life-threatening. Heart block may cause no symptoms or it may cause dizziness, fainting, the feeling of skipped heart beats, chest pain, difficulty breathing, fatigue, or even cardiac arrest.
Do you need a pacemaker for a heart block?
You treatment depends on the type of heart block you have: With first-degree heart block, you might not need treatment. With second-degree heart block, you may need a pacemaker if symptoms are present or if Mobitz II heart block is seen . With third-degree heart block, you will most likely need a pacemaker.

Clinical significance
- In people with heart block, also called AV block, the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat is partially or completely blocked from reaching the ventricles.
Classification
- Heart block is classified as first-, second- or third-degree, depending on the extent of electrical signal impairment.
Overview
- Type I heart block (also called Mobitz Type I or Wenckebach's AV block) is the less serious form of second-degree heart block. In this condition, the electrical signal goes slower and slower until the heart actually skips a beat.
Symptoms
- In patients with Type II heart block (also called Mobitz Type II), some of the electrical signals do not reach the ventricles, and the pattern is irregular. Individuals with this type of heart block may have a heartbeat that is slower than normal. The area that is blocked is lower in the conduction system and is often associated with more severe conduction disease. Symptoms of second- an…
Mechanism
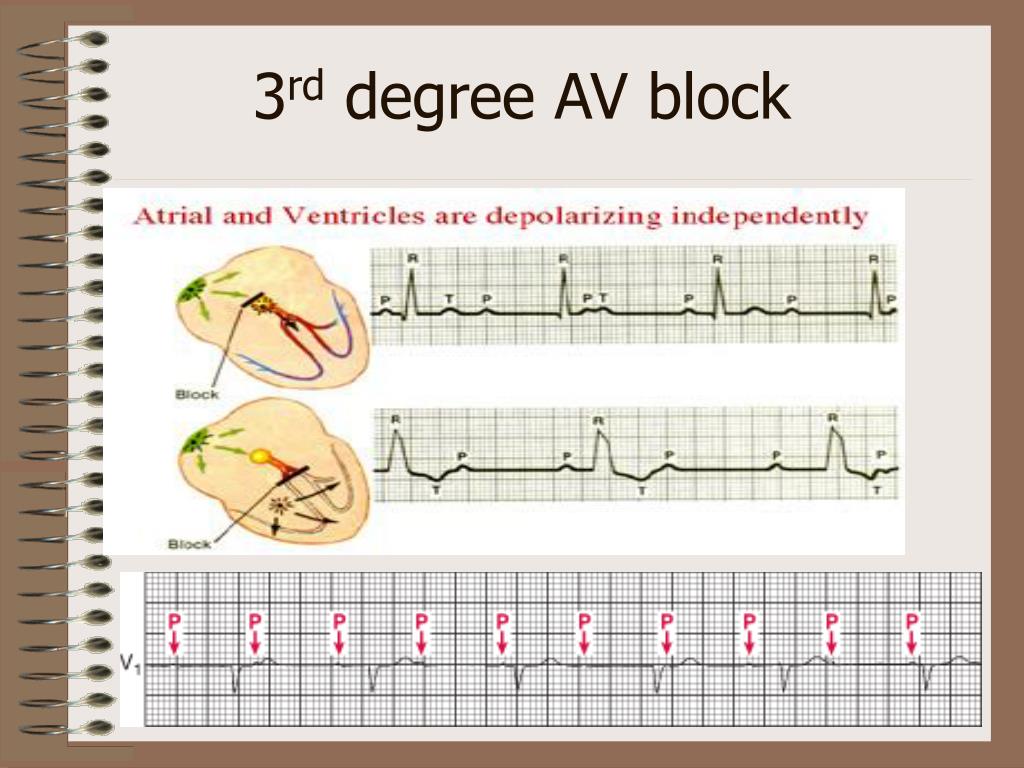
- In patients with third-degree (complete) heart block, the electrical signal is not sent from the atria to the ventricles. The heart compensates by producing electrical signals from a specialized pacemaker area in the ventricles. These signals make the heart contract and pump blood, but at a rate that is much slower than normal.
Signs and symptoms
- First-degree heart block often does not cause symptoms. It may be detected during a routine electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), but the patients heart rate and rhythm are usually normal.
Causes
- Acquired heart block has many possible causes, including heart attack (the most common cause), heart disease, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy), heart failure and rheumatic fever. Sometimes heart block occurs as a result of injury to the heart during open heart surgery, as a side effect of some drugs, or after exposure to a toxin.