
BACKGROUND: Community periodontal index of treatment needs (CPITN) index is commonly used to measure periodontal disease. It's uniqueness, apart from assessing the periodontal status, also gives the treatment needs for the underlying condition.
What is Community Periodontal Index (CPI)?
Community periodontal index (CPI) CPI is a modified version of CPITN by inclusion of measurement of ‘Loss of attachment’ and elimination of ‘Treatment needs’. The periodontal status is assessed with a 0.5 mm ball tip WHO probe taking into consideration 10 teeth in the oral cavity. The scores are: Score 0: health periodontal conditions
What is the prevalence of periodontal conditions in the US?
Community periodontal index of treatment needs and prevalence of periodontal conditions Only 8.5% of adults had at least one tooth with a 6 mm or deeper periodontal pocket when probing on 2 sites, whereas if probing is done all around the tooth, this percentage is 2.5x higher (21.4%).
What is the FDI-who Joint Working Group on periodontal diseases?
The FDI-WHO Joint Working Group 1 on periodontal diseases supports the use of the CPITN as an epidemiological screening procedure for periodontal treatment needs in populations and also, in a modified form for screening and monitoring of individuals by dental practitioners. The advantages of the CPI …
What is a Basic Periodontal Examination (BPE)?
The aim is to provide a basic screening of the tissues and to obtain an indication of the treatment requirements of the patient. Basic periodontal examination (BPE). This is performed clinically using the CPITN (community periodontal index of treatment needs) periodontal probe.
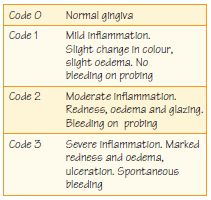
What is the periodontal disease index?
The PDI is the total of the scores for each tooth divided by the number of teeth examined: the higher the score, the more severe the periodontal disease. Further Reading: Ramfjord S. P. The Periodontal Disease Index (PDI).
What is a CPITN probe used for?
The CPITN is primarily a screening procedure which requires clinical assessment for the presence or absence of periodontal pockets, calculus and gingival bleeding. Use of a special CPITN periodontal probe (or its equivalent) is recommended.
What is PSR dental charting?
The Periodontal Screening and Recording® (PSR) system is one example of a diagnostic aid used to assess the periodontal health of patients.
What does CPI stand for in dental?
CPI = Community Periodontal Index.
What is sextants of periodontal treatment?
The six sextants consist of the four groups of teeth each containing the molars (excluding third molars) and premolars of one side of one jaw and the two groups of teeth each containing canines and incisors of one jaw.
What does a Russell periodontal index score of 6 indicates?
6 Gingivitis with pocket formation. The epithelial attachment is broken and there is a pocket. There is no interference with normal masticatory function; the tooth is firm in its socket and has not drifted. There is horizontal bone loss involving the entire alveolar crest, up to half of the length of the tooth root.
How do you calculate PSR?
Price–sales ratio, P/S ratio, or PSR, is a valuation metric for stocks. It is calculated by dividing the company's market capitalization by the revenue in the most recent year; or, equivalently, divide the per-share stock price by the per-share revenue.
How do you read periodontal charts?
The Meanings of the Measurements0-3mm without bleeding: Perfect! ... 1-3mm with bleeding: Early signs of gingivitis. ... 3-5mm with no bleeding: This is an indication that there is a potential for gum disease. ... 3-5mm with bleeding: This is an early stage of gum disease or the beginning of periodontitis.More items...•
Which probe is used for PSR?
PSR is performed using a special PSR probe which has a coloured mark from 3.5-5.5mm. This probe is 'walked' around each tooth as during the initial examination, and the deepest reading in the sextant is recorded.
Is insurance included in CPI?
Even though insurance premiums are an important part of consumers' medical spending, the CPI does not directly price health insurance policies.
What is the medical CPI for 2021?
1982-1984 = 100. Data are not seasonally adjusted....Consumer price index for medical care services and commodities in the U.S. from 1960 to 2021.CharacteristicMedical care servicesMedical care commodities2021578.6379.62020564.2377.92019549.1387.52018522.5378.29 more rows•Jun 20, 2022
What is the medical CPI for 2019?
Medical care prices rose 4.6 percent in 2019, well above a 2.0-percent increase in 2018 and the largest over-the-year increase since 2007. Prescription drug prices rose 3.0 percent from 2018 to 2019, after falling 0.6 percent from 2017 to 2018.
How many children were examined for periodontal disease?
The periodontal and dental examinations were made on 4534 children (2018 males and 2516 females) by using CPI and DMFT indices. Information concerning with parent's demographic status was obtained through a survey questionnaires. According to CPI scores; 5.1% of males and 8.9% of females had healthy periodontium. Of the entire group; 70.0% of males and 67.8% of females had bleeding on probing (score 1) and the highest percentages were obtained for 8-year-old males (88.2%) and 7-year-old females (90.8%), respectively. Mean DMFT scores were 2.66±3.0 for males and 2.30±2.8 for females, respectively. For the entire group; the most affected CPI sextants were lower anterior for both gender (males 19.4%, females 17.8%). Multiple binary logistic regression analysis showed that the parents educational level, frequency of tooth brushing, anxiety, and preventive dental visits and sleep duration were significant risk indicators for periodontal disease. This study clearly indicated that effective oral health prevention strategies need to be implemented to improve the oral health of school-children in Turkey.
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal diseases are a group of infectious diseases that mainly include gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the most prevalent form of periodontal disease in subjects of all ages, including children and adolescents. Less frequent types of periodontal disease include aggressive periodontitis, acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis and various diseases of herpesviral and fungal origin. This review aimed to retrieve relevant information from Latin America on the prevalence of periodontal diseases among children and adolescents of the region. Gingivitis was detected in 35% of young Latin American subjects and showed the highest frequencies in Colombia (77%) and Bolivia (73%) and the lowest frequency in Mexico (23%). The frequency of gingivitis in subjects from other Latin American countries was between 31% and 56%. Periodontitis may affect <10% of the young population in Latin America, but the data are based on only a few studies. A more precise assessment of the distribution and severity of periodontal disease in children and adolescents of Latin America may help policy makers and dentists to institute more effective public health measures to prevent and treat the disease at an early age to avoid major damage to the permanent dentition.
What is a partial mouth periodontal exam?
Background: Partial-mouth periodontal examination (PMPE) has been widely used in periodontal epidemiologic studies. In this study, the authors evaluate the accuracy of extent and severity estimates from PMPE protocols in a Chinese population. Methods: The study enrolled 200 individuals with periodontitis, ages 22 to 64 years. Full-mouth examination was performed to determine probing depth (PD), attachment loss (AL), and bleeding on probing (BOP) at mesio-buccal (MB), mid-buccal (B), disto-buccal (DB), mesio-lingual (ML), mid-lingual (L), and disto-lingual (DL) sites per tooth. Extent and severity estimates from 15 PMPE protocols were derived from and compared to full-mouth data. Relative bias (RB) and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were calculated. Bland-Altman plots were used to evaluate the agreement patterns across disease levels. Results: Of the 15 PMPE protocols, the random half-mouth six-sites per tooth (r6sites) protocol performed best in both extent (AL ≥ 2, ≥ 4, or ≥ 6 mm; PD ≥ 4 or ≥ 6 mm; and BOP) and severity (AL and PD) estimates, with RB within 5.0% and ICCs ≥ 0.950 in most cases. MB-B-DB and MB-B-DL protocols generally resulted in RB within 20.0% for extent and within 5.0% for severity. Protocols involving only interproximal sites (MB-DB, MB-DL, and MB-DB-ML-DL) showed good accuracy in AL (RB within 20.0% for extent and within 3.0% for severity), but overestimated PD (RB 12.5% to 54.2% for extent and >10.0% for severity). The community periodontal index teeth protocol caused severe overestimation of up to 110.4% for extent and 14.6% for severity. Conclusion: The r6sites protocol is best for assessing extent and severity for AL, PD, and BOP under the study conditions.
What is dental anxiety?
Objective:Dental anxiety is a major complication for many patients and practitioners. Dental fear often results in poor oral health in regard to poor cooperation. The aim of the present study was to determine the dental anxiety and its relation to socio-demographic status and periodontal health in adults.Materials and Methods:In this cross-sectional study, a total of 187 patients were asked to complete a questionnaire consisted of the questions gathering information on sex, age, education level, income level, smoking habits and the last dental visit. The questionnaire also included Modified Dental Anxiety scale (MDAS) administered in Turkish language. The oral health status was determined with Community Periodontal index (CPI). Results:Based on MDAS scores, 54% of the subjects had mild anxiety, 41.7% had moderate anxiety, and 4.3% had severe anxiety. Anxiety was affected by age and gender (p0.05). Participants with higher CPI scores had significantly higher dental anxiety compared to those of lower CPI scores (p
What is the WHO study on dental health?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends epidemiological studies for planning dental services to collect information about oral disease, oral health, and treatment needs of population. The periodontal and dental examinations were made on 4534 children (2018 males and 2516 females) by using CPI and DMFT indices.
What is the BPT index?
Methods: A new conceptual index was developed that includes consideration of the extent and severity of the periodontal diseases, the distribution of affected teeth, and tooth loss as a function of age. The index is referred to as the Burden of Periodontal Diseases and Tooth Loss (BPT). Results: A cohort of 1097 individuals originally seen as new patients in a dental school clinic, and evaluated for undiagnosed dysglycemia, were studied. The BPT index was applied to this data set. A modifying effect of considering the number of lost teeth was observed. The distribution of scores were skewed to the left, which gradually shifted to the right when the most involved teeth (periodontal pathology, tooth loss) were weighted more heavily. This shift was not observed when missing teeth were not considered. Conclusion: This conceptual study illustrates that the extent and severity of periodontal pathology, and number and distribution of missing teeth, are important considerations when summarizing the condition of the mouth. The BPT provides a measure of the oral disease burden, as both periodontal pathology and tooth loss are associated with both functional impairment and reduced quality of life. The dental profession and dental research community must continually seek to develop new approaches to defining and summarizing the oral disease burden. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
What is oral health?
Introduction: Oral health is an integral component of general health and is essential for well‑being. India is one of the most populated countries in the world and majority of them resides in rural areas. Moradabad is one of the oldest cities of Uttar Pradesh with diverse culture and beliefs. Aim: The aim was to evaluate the periodontal health status of the rural Moradabad population. Materials and Methods: A representative transversal study on 550 adults aged 20-49 years of rural Moradabad was conducted from February 2011 to June 2011. The survey was carried out using a self‑designed questionnaire. Periodontal health was assessed using WHO criteria (1997). Results: Overall the prevalence of periodontal diseases among study subjects was overall 91.6%. Males had a higher prevalence of periodontal disease (93.8%) as compared to females (89.5%). Out of total subjects 37.8% had Community Periodontal Index (CPI) score 4 and 32.5% had score 3. About 7.3% of subjects had loss of attachment (LOA) with 20.2% of them having LOA score 1. Statistically, there was a significant difference (P < 0.001) among the number of subjects havingdifferent CPI and LOA scores. In a multivariate binary logistic model with age > 35 years, smoking, tobacco chewing (independent risk factors) were significantly associated with CPI > 2 (dependent variable) (P < 0.05). Conclusion: The current periodontal health status of rural adult population of Moradabad city can be attributed to low literacy along with socio economic status and oral habits. To improve the periodontal health status of the rural population of Moradabad, it is suggested that a community‑based approach can be designed.
