Supportive treatment recommendations are the same for acute hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis B virus, abbreviated HBV, is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus Orthohepadnavirus and a member of the Hepadnaviridae family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.
Adefovir
This medication is used to treat a chronic viral infection of the liver in people 12 years of age and older.
When to initiate HBV treatment?
· Treatment is an oral antiviral medication. In rare cases, injections may be used. Oral antiviral medications There are five oral medications approved by the FDA. Entecavir Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) Lamivudine Adefovir Of these, tenofovir and entecavir are most commonly used.
Does HBV have a treatment?
· The trials included people with acute HBV infection of varying severity. The main interventions included hepatitis B immunoglobulin (a vaccine), interferon (protein secreted in response to viral infection), and lamivudine and entecavir (medicines) which are considered to have antiviral effects and were compared with placebo or no intervention.
When to treat chronic HBV?
There are five FDA-approved oral medications and one injection available to treat hepatitis B. The newer oral medications are stronger and less likely to develop viral resistance and have very few side effects. The medication cannot cure the disease, but can help reduce the number of viruses in the body and the risk of complications.
Who should get tested for HBV?
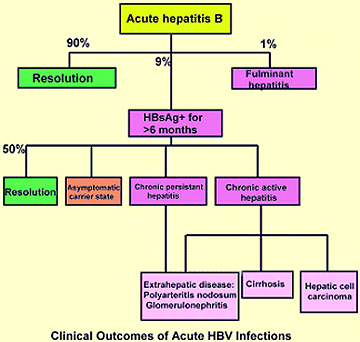
Approximately 1% of persons with acute HBV develop acute liver failure. Preventing acute HBV with vaccination is the best treatment. Although universal vaccination is now administered to newborns in many countries, the majority of adults have not been vaccinated and remain at risk. Because the majority of patients with acute HBV resolve this infection spontaneously, …
Does acute hepatitis B need treatment?
short-term (acute) hepatitis B does not usually need specific treatment, but may require treatment to relieve the symptoms. long-term (chronic) hepatitis B is often treated with medication to keep the virus under control.
How do you recover from acute hepatitis B?
While there is no cure for acute hepatitis B, treatment for it can be given within 24 hours to one week of exposure to the virus. Injections of hepatitis B-specific immune globulin (a concentrated blood protein) can be given to help the body to develop antibodies that fight the hepatitis B virus.
Can acute hepatitis B be cured totally?
A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there's no cure if you have the condition. If you're infected, taking certain precautions can help prevent spreading the virus to others.
What is acute HBV?
Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis B virus. Some people with acute hepatitis B have no symptoms at all or only mild illness. For others, acute hepatitis B causes a more severe illness that requires hospitalization.
How long does acute hepatitis B last?
When symptoms of acute hepatitis B occur, how long do they usually last? Symptoms typically last for several weeks but can persist for up to 6 months (6,12).
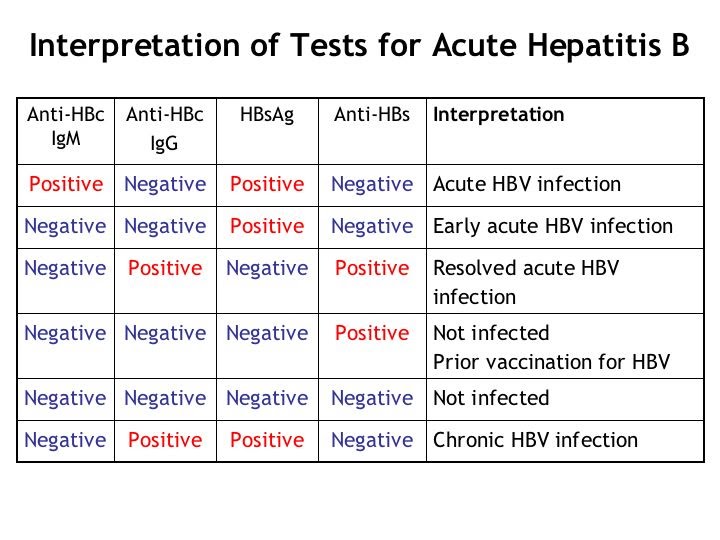
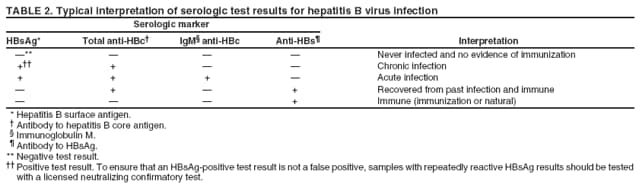
How do you know if hepatitis B is acute or chronic?
If you test positive for HBsAg for longer than six months, it means you have a chronic hepatitis B infection. But, if you no longer test positive (or “reactive”) for HBsAg after six months and you develop hepatitis B surface antibodies (HBsAb), then you have cleared hepatitis B after an “acute” infection.
What is the new treatment for hepatitis B?
VIR-2218 is an investigational GalNAc-conjugated small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) therapeutic in development for functional cure of chronic hepatitis B virus infection (CHB). VIR-2218 was created using Enhanced Stabilization Chemistry Plus, which retains in vivo potency while reducing off-target effects.
What is the fastest way to cure hepatitis B?
There's no cure for hepatitis B. The good news is it usually goes away by itself in 4 to 8 weeks. More than 9 out of 10 adults who get hepatitis B totally recover. However, about 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become “carriers,” which means they have a chronic (long-lasting) hepatitis B infection.
What is the difference between acute hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis B?
When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an "acute infection" (or a new infection). Many people are able to naturally get rid of an acute infection. If the infection persists for more than 6 months, it is considered a “chronic infection.”
Can acute hepatitis B be transmitted?
Acute Hepatitis B Infection. An acute hepatitis B infection may last up to six months (with or without symptoms) and infected persons are able to pass the virus to others during this time.
How do you get acute hepatitis?
The hepatitis A virus is the most common cause of acute hepatitis, followed by the hepatitis B virus. (mono). Engaging in certain activities, such as getting a tattoo or body piercing, sharing needles to inject drugs, or having several sex partners, increases the risk of developing hepatitis.
What is acute infection?
An acute viral infection is characterized by sudden or rapid onset of disease that may be fatal. Viral clearance during acute infection correlates with rapid induction of innate immunity, especially induction of ISGs, and subsequent induction of adaptive immune responses (Heim and Thimme, 2014).
What is the best treatment for hepatitis B?
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B may include: Antiviral medications. Several antiviral medications — including entecavir (Baraclude), tenofovir (Viread), lamivudine (Epivir), adefovir (Hepsera) and telbivudine (Tyzeka) — can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. These drugs are taken by mouth.
How to get rid of hepatitis A?
Eat a healthy diet full of fruits and vegetables, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Take care of your liver. Don't drink alcohol or take prescription or over-the-counter drugs without consulting your doctor. Get tested for hepatitis A and C. Get vaccinated for hepatitis A if you haven't been exposed.
What tests can be done to diagnose hepatitis B?
Tests that can help diagnose hepatitis B or its complications are: Blood tests . Blood tests can detect signs of the hepatitis B virus in your body and tell your doctor whether it's acute or chronic. A simple blood test can also determine if you're immune to the condition. Liver ultrasound.
Does hepatitis B go away on its own?
Treatment for acute hepatitis B infection. If your doctor determines your hepatitis B infection is acute — meaning it is short-lived and will go away on its own — you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend rest, proper nutrition and plenty of fluids while your body fights the infection.
What is the best way to test for liver damage?
Liver ultrasound. A special ultrasound called transient elastography can show the amount of liver damage. Liver biopsy. Your doctor might remove a small sample of your liver for testing (liver biopsy) to check for liver damage.
Can you take interferon while pregnant?
It's used mainly for young people with hepatitis B who wish to avoid long-term treatment or women who might want to get pregnant within a few years, after completing a finite course of therapy. Interferon should not be used during pregnancy. Side effects may include nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing and depression.
What happens if you have a damaged liver?
If your liver has been severely damaged, a liver transplant may be an option. During a liver transplant, the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver. Most transplanted livers come from deceased donors, though a small number come from living donors who donate a portion of their livers.
What is the HBV?
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a virus that affects the liver. It is usually transmitted by injectable drug abuse, transfusion of infected blood, unhygienic tattooing practices, coming into contact with blood infected with HBV, or by unprotected sex. Acute HBV infection is the period that covers the period immediately after HBV infection. Most people are asymptomatic. About 5% to 40% of people with acute HBV develop symptoms such as jaundice (yellowish discolouration of the eyes and skin), tummy pain, tiredness, nausea, and vomiting. While most people clear the virus after acute HBV infection, the virus remains in others (chronic HBV infection) and causes major health problems (excessive tiredness and eventually may end with liver failure leading to vomiting blood, confusion, and death). Occasionally, people with acute HBV may develop immediate liver failure (fulminant HBV infection). The best way to treat acute HBV is not clear. We sought to resolve this issue by performing this review. We included all randomised clinical trials (RCTs) (clinical studies where people are randomly put into one of two or more treatment groups) published to August 2016. We included only trials in which participants with acute HBV infection had not undergone liver transplantation previously and did not have liver disease due to other viral infections. Apart from using standard Cochrane methods which allow comparison of only two treatments at a time (direct comparison), we planned to use an advanced method which allows comparison of the many different treatments individually which are compared in the trials (network meta-analysis). However, because of the nature of the information available, we could not determine whether the network meta-analysis results were reliable. So, we used standard Cochrane methodology.
How is HBV transmitted?
It is usually transmitted by injectable drug abuse, transfusion of infected blood, unhygienic tattooing practices, coming into contact with blood infected with HBV, or by unprotected sex. Acute HBV infection is the period that covers the period immediately after HBV infection. Most people are asymptomatic. About 5% to 40% of people ...
What is the term for a virus that affects the liver?
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a virus that affects the liver. It is usually transmitted by injectable drug abuse, transfusion of infected blood, unhygienic tattooing practices, coming into contact with blood infected with HBV, or by unprotected sex. Acute HBV infection is the period that covers the period immediately after HBV infection.
Hepatitis B and Pregnancy
Because their immune systems aren’t fully developed, infants and young children are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B, so it’s important to limit their exposure to the virus. All expecting women should be screened for hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Treatment: Medication
There are five FDA-approved oral medications and one injection available to treat hepatitis B. The newer oral medications are stronger and less likely to develop viral resistance and have very few side effects.
Hepatitis B Treatment: Liver Transplant
A referral for a liver transplant evaluation may be needed if chronic hepatitis B infection leads to cirrhosis (severe scarring of the liver), liver cancer or end stage liver disease and its complications. Rarely, acute hepatitis B can lead to severe liver failure which requires liver transplantation.
How long does hepatitis B last?
An acute hepatitis B infection may last up to six months (with or without symptoms) and infected persons are able to pass the virus to others during this time. A simple blood test can let a person know if the hepatitis B virus is in their blood or if they have successfully gotten rid of the virus. Until your health care provider confirms that the blood test shows that there is no more hepatitis B virus in your blood, it is important to protect others from a possible infection.
How long does it take for a symtom to show up?
Although most people do not experience symptoms, they can appear 60-150 days after infection, with the average being 90 days or 3 months. Some people may experience more severe symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin), or a bloated stomach that may cause them to see a health care provider. ...
Who should be tested for hepatitis B?
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for: People born in certain countries where hepatitis B is common. People born in the United States not vaccinated as infants whose parents were born in countries with high rates of hepatitis B. Men who have sex with men. People who inject drugs.
Can you have hepatitis B without symptoms?
Talk to your health-care provider if you have risk factors for or think you might have hepatitis B. Since many people with hepatitis B do not have symptoms, blood tests are used to diagnose the infection. Several different hepatitis B tests are available. Depending on the test, they can determine whether you.
What is the cause of hepatitis?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can all cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common hepatitis viruses are hepatitis A virus, ...
Is hepatitis A a short term infection?
Hepatitis A is usually a short-term infection. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C can also begin as short-term infections but in some people, the virus remains in the body and causes chronic, or lifelong, infection. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B; however, no vaccine is available for hepatitis C.
How long does it take for hepatitis B to show symptoms?
Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis B virus. Some people with acute hepatitis B have no symptoms at all or only mild illness. For others, acute hepatitis B causes a more severe illness that requires hospitalization.
How does age affect hepatitis B?
The younger a person is when infected with the hepatitis B virus, the greater the chance of developing chronic infection. About 9 in 10 infants who become infected go on to develop life-long, chronic infection. The risk goes down as a child gets older.
How many cases of hepatitis B in 2018?
In 2018, a total of 3,322 cases of acute (short-term) hepatitis B were reported to CDC. Since many people may not have symptoms or don’t know they are infected, their illness is often not diagnosed so it can’t be reported or counted.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment to prevent hepatitis B infection after exposure
If you know you've been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and aren't sure if you've been vaccinated, call your doctor immediately. An injection of immunoglobulin (an antibody) given within 12 hours of exposure to the virus may help protect you from getting sick with hepatitis B. Because this tre… - Treatment for acute hepatitis B infection
If your doctor determines your hepatitis B infection is acute — meaning it is short-lived and will go away on its own — you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend rest, proper nutrition and plenty of fluids while your body fights the infection. In severe cases, antivira…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- If you've been infected with hepatitis B, take steps to protect others from the virus. 1. Make sex safer. If you're sexually active, tell your partner you have HBVand talk about the risk of transmitting it to him or her. Use a new latex condom every time you have sex, but remember that condoms reduce but don't eliminate the risk. 2. Tell your sexual partner to get tested. Anyone wit…
Coping and Support
- If you've been diagnosed with hepatitis B infection, the following suggestions might help you cope: 1. Learn about hepatitis B.The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is a good place to start. 2. Stay connected to friends and family.You can't spread hepatitis B through casual contact, so don't cut yourself off from people who can offer support. 3. Take care of yourself.Ea…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. However, in some cases, you may be referred immediately to a specialist. Doctors who specialize in treating hepatitis B include: 1. Doctors who treat digestive diseases (gastroenterologists) 2. Doctors who treat liver diseases (hepatologists) 3. Doctors who treat infectious diseases