Top10homeremedies.com
1. Take Rest...
2. Ice...
3. Compression...
4. Elevation...
5. Warm Compresses...
6. Massage...
7. Ginger...
8. Turmeric...
Learn More...Trueremedies.com
1. Change Some Habits...
2. Do Not Abuse Painkillers...
3. Cold Compress...
4. Eat Some Specific Foods...
5. Limit Consumption Of Certain Foods...
6. Apple Cider Vinegar...
7. Ginger...
8. Turmeric...
Learn More...How to treat bursitis naturally?
Natural Herbs To Treat Bursitis
- Apple Cider Vinegar. Apple cider vinegar is the ‘mother’ of vinegar, it is a folk remedy used to treat numerous health conditions including bursitis.
- Cayenne Pepper. Cayenne helps to stimulate circulation, you can use cayenne lotion topically on the affected areas to provide pain relief.
- Castor Oil. ...
How does flexoprin help in treating bursitis?
- Take one capsule in the morning. This will help improve your body’s immune system and its ability to reduce inflammation.
- Take another capsule in the evening. ...
- If you have an existing medical condition, consult your doctor first if you can use this supplement.
How to aspirate or inject a prepatellar bursa?
Prepare the site
- Identify the bursa's point of maximum fullness and mark it on the skin for needle entry.
- Prepare the area with antiseptic solution.
- Apply sterile drapes that widely expose the needle insertion site and the patella.
- Spray freezing spray at the needle insertion site until it just blanches and/or inject a skin wheal of local anesthetic (eg, ≤ 1 mL).
Is ice treatment effective for Retrocalcaneal bursitis?
Treatment for retrocalcaneal bursitis Doctors recommend resting and reducing or avoiding activities that cause pain for a short period. Applying ice to the heel for 15-20 minutes each several times a day during the acute phase of retrocalcaneal bursitis can help ease symptoms.

How long does it take for prepatellar bursitis to go away?
With rest and treating your prepatellar bursitis from home, the swelling and other symptoms usually go away in a couple of weeks. If your prepatellar bursitis doesn't get better after two or three weeks of rest, reach out to your healthcare provider. You may need medical treatment.
What is the fastest way to heal bursitis of the knee?
Lifestyle and home remediesRest your knee. Discontinue the activity that caused knee bursitis and avoid movements that worsen your pain.Take over-the-counter pain relievers. ... Apply ice. ... Apply compression. ... Elevate your knee.
How long does it take for bursitis of the knee to go away?
With the proper treatment, knee bursitis can be healed in an average of two to eight weeks. You must practice proper stretching, strengthening, and exercise for a speedy recovery from this condition.
Is walking good for knee bursitis?
Inflamed Bursa Treatment Don't do anything that seems to make your symptoms worse. You can still do low-impact or gentle exercises like a light walk or stationary bike ride. Ice: Put an ice pack on your knee about 3 to 4 times a day.
What happens if bursitis is left untreated?
Chronic pain: Untreated bursitis can lead to a permanent thickening or enlargement of the bursa, which can cause chronic inflammation and pain. Muscle atrophy: Long term reduced use of joint can lead to decreased physical activity and loss of surrounding muscle.
Is knee bursitis serious?
Getting a doctor to check your knee condition will ensure you get the right diagnosis and treatment. While bursitis is not a dangerous condition and can be treated, delaying a diagnosis and treatment can cause you unnecessary pain and symptoms.
What does prepatellar bursitis look like?
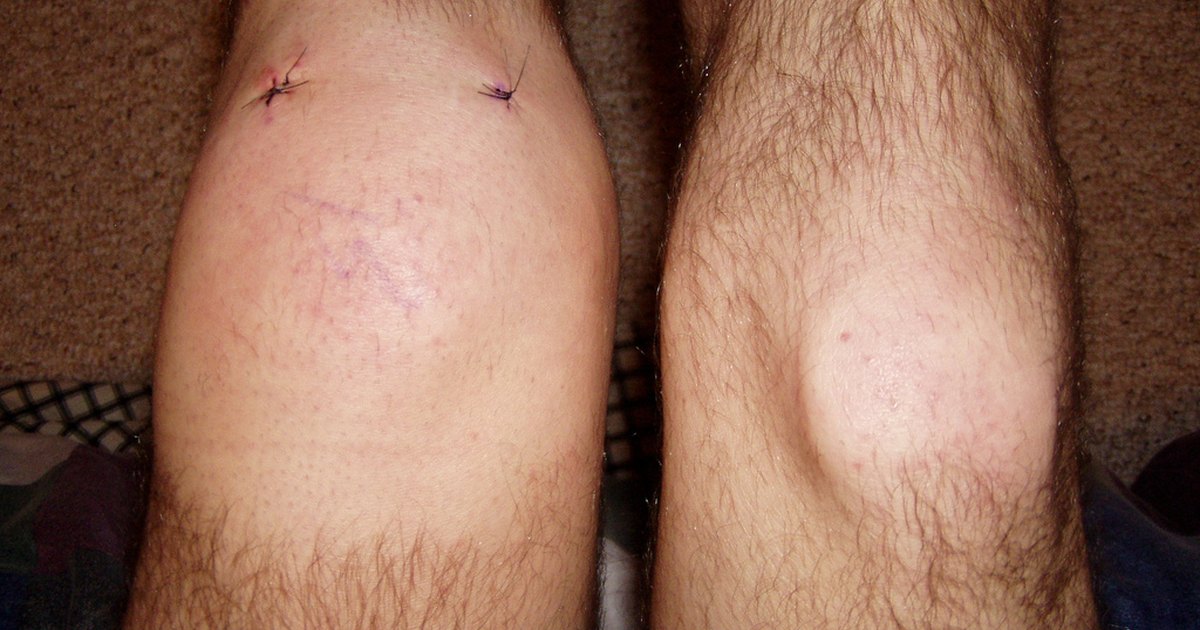
Swelling at the font of the knee An inflamed prepatellar bursa fills up with fluid, causing swelling that can be felt and seen through the skin. As it progresses, the knee joint may look double in size. The swollen area may seem “squishy” to the touch.
Does prepatellar bursitis require surgery?
Incision and drainage of the prepatellar bursa usually is performed when symptoms of septic bursitis have not improved significantly within 36-48 hours. Surgical removal of the bursa (ie, bursectomy) may be necessary for chronic or recurrent prepatellar bursitis.
What is the best anti inflammatory for bursitis?
Doctors may recommend over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, to reduce inflammation in the bursa and tendon and relieve pain. These medications are typically recommended for a few weeks while the body heals.
Will a knee brace help with bursitis?
Patience combined with treatments recommended by a doctor is the best remedy for bursitis of the knee. A big bulky brace is not needed with knee bursitis, but a comfortable compression knee brace for bursitis or knee sleeve can help reduce swelling of the affected bursa.
What causes knee bursitis to flare up?
Repetitive motions, such as a pitcher throwing a baseball over and over, commonly cause bursitis. Also, spending time in positions that put pressure on part of your body, such as kneeling, can cause a flare-up. Occasionally, a sudden injury or infection can cause bursitis.
What can be mistaken for bursitis?
Bursitis is often mistaken for arthritis because joint pain is a symptom of both conditions. There are various types of arthritis that cause joint inflammation, including the autoimmune response of rheumatoid arthritis or the breaking down of cartilage in the joints in degenerative arthritis.
What is the treatment for knee bursitis?
Septic knee bursitis—which is caused by an infection—requires urgent medical care and antibiotic therapy.
What is the best treatment for septic bursitis?
Septic prepatellar bursitis requires treatment with antibiotics. Oral antibiotics are typically successful when treating mild to moderate septic bursitis. People who show signs of severe infection or who have compromised immune systems may require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics. 1
What is the procedure to remove a bursa?
Bursectomy. Challenging cases of chronic or septic knee bursitis may warrant surgery to remove the affected bursae. This surgery is called a bursectomy. A traditional bursectomy requires making an incision in the skin over the knee to remove the prepatellar bursa. An endoscopic bursectomy uses smaller incisions.
What happens after a bursectomy?
Before a bursectomy, aspiration will be done to remove excess fluid from the bursa. Following a bursectomy or sclerotherapy, a new patellar bursa will likely develop. Prevention strategies can help ensure bursitis does not occur in this new bursa.
How to reduce bursa flare up?
While movement and exercise are essential to overall health, cutting back on activities that irritate the bursa may reduce the chance of a flare-up. Taking periodic breaks from certain activities can also help.
How to reduce swelling in knee?
Cold compress . Applying a cold compress to the knee may help decrease swelling and alleviate other symptoms. A cold compress can be purchased or made at home and applied to the knee for about 20 minutes 2 or 3 times a day. (Homemade compresses that use ice can be wrapped in a towel to prevent injury to the skin.)
Can cortisone be used for prepatellar bursitis?
Recent research suggests cortisone injections are not an effective treatment for most other cases of prepatellar bursitis.1 In addition, cortisone injections into the prepatellar bursa are associated with side effects, such as skin discoloration, degeneration, and infection near the site of injection. 1. Since cortisone may cause tissue damage, ...
What is the purpose of a prepatellar bursa?
They contain a small amount of fluid, and are positioned between bones and soft tissues, acting as cushions to help reduce friction. Prepatellar bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa in the front of the kneecap (patella). It occurs when the bursa becomes irritated and produces too much fluid, which causes it to swell and put pressure on ...
How to prevent bursitis?
You can help prevent bursitis by following these simple recommendations: 1 Wear kneepads if you work on your knees or participate in contact sports such as football, basketball, or wrestling. 2 Rest your knees regularly by stopping to stretch your legs. You may also consider switching activities on a regular basis to avoid prolonged stress on your knees. 3 Apply ice and elevate your knees after a workout.
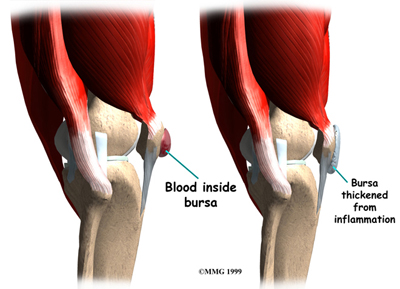
What causes a bursa to swell?
It occurs when the bursa becomes irritated and produces too much fluid, which causes it to swell and put pressure on the adjacent parts of the knee. (Left) Normal knee anatomy shown from the side. The bursa is small and located between the patella and the skin. (Right) In prepatellar bursitis, the bursa becomes inflamed and swollen.
How to treat bursitis without surgery?
Avoid the activities that worsen symptoms. Substitute another activity until the bursitis clears up. Low-impact exercise, such as cycling, is a good option.
What to do if your bursa is inflamed?
If the swelling and pain do not respond to these measures, your doctor may drain (aspirate) the bursa with a needle, then inject the bursa with a corticosteroid.
What tests are used to diagnose bursitis?
Other imaging tests. The diagnosis of bursitis is usually made on physical examination, but computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans may be ordered to check for other soft tissue injury.
Can a knee injury cause a bursa sac to be infected?
Prepatellar bursitis can also be caused by a bacterial infection. If a knee injury — such as an insect bite, scrape, or puncture wound—breaks the skin, bacteria may get inside the bursa sac and cause an infection.
What is the treatment for prepatellar bursitis?
Treatments include rest, anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, medications for other conditions, and surgery and other procedures if needed. You should visit your primary care physician ...
What is the bursa in the knee?
Prepatellar bursitis is an inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa) located in front of the knee (prepatellar) that normally acts as a cushion to help reduce friction. It can be caused by prolonged kneeling, such as for work, or due to injury or infection, and can either be acute or chronic. Symptoms of acute prepatellar bursitis include warmth, ...
What causes pain in the front of the knee?
Warmth, redness, swelling, and pain in the front of the knee: The most common finding in acute prepatellar bursitis is knee redness, swelling, and pain in the front of the knee. The knee will feel warm to the touch and will cause pain when pushed. Fluid in front of the knee: Inflammation causes fluid to leak out of the blood vessels into ...
What causes a bursa to be inflamed?
The most common cause of long-term prepatellar bursitis is prolonged kneeling. The prolonged and repeated kneeling puts pressure on the knee and causes inflammation of the prepatellar bursa. This is commonly seen in people whose jobs require them to frequently kneel, such as: Plumbers. Roofers.
Where is the bursa located in the knee?
View tags Arrow Icon. Knee. Prepatellar bursitis is an inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa) located in front of the knee that normally acts as a cushion to help reduce friction.
Does prepatellar bursitis hurt when you push on it?
Symptoms of chronic prepatellar bursitis include: Soft, non-painful lump in front of the knee: People with chronic prepatellar bursitis develop a soft lump in front of the knee, but it does not hurt when you push on it. The lump may be slightly warm or cold.
Can injury cause prepatellar bursitis?
Injury or infection can lead to prepatellar bursitis and associated inflammation. Injury to the knee: An injury to the knee, especially one that penetrates the skin, can also cause prepatellar bursitis.
What is the primary goal of treatment for prepatellar bursitis?
The primary goal of treatment is to control the inflammation.
How to prevent prepatellar bursitis?
In order to prevent prepatellar bursitis you should avoid injury or an overload of your muscles. It is very important to do an appropriate warm-up and cool down, while playing sports. For example, if you play volleyball, it is advisable to wear knee pads. This will prevent falling on the kneecap.
How often does prepatellar bursitis occur?
Prepatellar bursitis occurs often, with at least an annual incidence of 10/100 000. The incidence of prepatellar bursa is probably underestimated because most of the case are non-septic and only patients with the most severe cases of prepatellar bursitis requires admission in the hospital.
What is the bursa of a carpenter's knee?
Prepatellar bursitis is also called housemaid's knee or carpenter's knee. A bursa is a fluid-filled sac which ensures there is less friction between body parts. The prepatellar bursa is located superficially between the skin and the patella. The inflammation of a bursa is called bursitis. This inflammation can take form by either an infectious nature (30%) or a non-infectious nature (70%). A direct fall on the patella, an acute trauma, repeated blows or friction on the knee may cause prepatellar bursitis. Other causes include infections or low-grade inflammatory conditions, such as gout, syphilis, tuberculosis or rheumatoid arthritis. Prepatellar bursitis often occurs in specific jobs which involves a position where they work on their knees for a prolonged period of time such as miners, gardeners, carpet layers and mechanics.
Why is my bursal sac swollen?
Actually, a bacterial seeding of the bursal sac caused by a hematoma is rare, because of the limited vascular supply of the bursal tissue . Infection:Typically for a septic prepatellar bursitis is a break in the skin near the bursa, which leads to swelling and pain around this area.
What is the best treatment for septic prepatellar bursitis?
Also, for cases of septic prepatellar bursitis, antibiotics are used to treat the infection. Corticosteroid injections.
How to diagnose bursitis?
Bursitis can be diagnosed through a detailed history (about the onset of symptoms, the pattern of knee pain and swelling and how the symptoms affect their lifestyle) and a physical examination, however, X-ray, MRI and CT-scan can be done to rule out the possibility of a fracture or soft tissue injury. If it is uncertain whether or not the bursa is infected, an arthrocentesis can be done. It is typically done for three reasons: necessary information is needed to make a diagnose, to relieve the pressure in the joint and will help alleviate the pain and excess fluid also needs to be removed before a therapeutic injection is given.
How to treat bursitis in the early stages?
It is important to treat bursitis in the early stages to reduce the symptoms, minimize damage and maintain motion and strength in your knee. Eliminate any squatting, repetitive knee bending, crossing your legs, kneeling or any other activities that add pressure on your bursa.
How to treat knee bursitis?
By treating your knee bursitis with a Cold Compress or Ice Pack in the early stages and Blood Circulation Boost ( once swelling is reduced), you are more likely to prevent long-term damage and chronic conditions from setting in.
What is the pain in the front of the knee?
Prepatellar bursitis (also referred to as patellar bursitis) is a painful condition affecting the front of the kneecap (patella). The prepatellar bursa is usually very thin and serves as a cushion between the patella and your skin, protecting your kneecap and the soft tissue that holds it is place. The prepatellar bursa is commonly affected due ...
What happens when your knee bursa is inflamed?
Any actions that put pressure on the inflamed bursa can increase irritation and cause further inflammation and pain. Prepatellar bursitis (also referred to as patellar bursitis) is a painful condition affecting the front of the kneecap (patella).
What is the bursa sac in the knee?
What Is Prepatellar Bursitis? Bursitis in the knee is a very painful condition in which a bursa sac becomes irritated and inflamed, affecting the bursa and the soft tissue around it. A bursa is a sac of synovial fluid, rich in protein and collagen. These fluid-filled sacs form in areas where 2 surfaces in your body, ...
Why does my prepatellar bursa hurt?
The prepatellar bursa is commonly affected due to repetitive pressure on the kneecap during frequent kneeling. Prepatellar bursitis is also known as Clergyman's knee, Carpet Layer's knee, or Housemaid's knee due to the nature of their work requiring kneeling for long periods of time. This prolonged pressure can begin to irritate the bursa, ...
What is the pain in the kneecap area?
You will experience tenderness just below and over top of the kneecap with prepatellar bursitis. You may also notice warmth and visible redness on your skin in the area as inflammation in the bursa and along the tendons becomes more severe.
How to treat knee bursitis?
Surgical and other procedures. More-invasive treatments for knee bursitis treatment include: Corticosteroid injection. If the bursitis is persistent and not responding to basic treatments, your doctor might inject a corticosteroid drug into an affected bursa to reduce inflammation.
How to relieve knee bursitis pain?
To ease pain and discomfort of knee bursitis: Rest your knee. Discontinue the activity that caused knee bursitis and avoid movements that worsen your pain. Take over-the-counter pain relievers.
How to diagnose bursitis in the knee?
Doctors often can make a diagnosis of knee bursitis with a medical history and physical exam. Your doctor will: Compare the condition of both knees, particularly if only one is painful. Gently press on areas of your knee to detect warmth, swelling and the source of pain. Inspect the skin over the tender area for redness or other signs of infection.
How to visualize bursa?
MRI. MRIs use radio waves and a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of structures within your body. This technology visualizes soft tissues, such as bursae. Ultrasound. Using sound waves to produce images in real time, ultrasound can help your doctor better visualize swelling in the affected bursa.
How to test for gout in bursa?
If your doctor suspects that you have an infection or gout in the bursa, he or she might take a sample of the bursa fluid for testing by inserting a needle into the affected area and draining some of the fluid. This can also be used as treatment.
How to get rid of a swollen knee?
Apply an ice pack to your knee for 20 minutes at a time several times a day until the pain goes away and your knee no longer feels warm to the touch. Apply compression . Use of a compressive wrap or knee sleeve can help reduce swelling. Elevate your knee.
What tests can be done to determine if you have bursitis?
To help rule out injuries that can cause signs and symptoms similar to those of bursitis, your doctor might request one or more of the following imaging tests: X-ray. These can be useful in revealing a problem with a bone or arthritis. MRI.
Definition/ Description
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
Epidemiology
Etiology
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnostic Procedures
Outcome Measures
Physical Examination
Medical Management
- The treatment for prepatellar bursitis depends primarily on the cause of the bursitis and secondarily on the pathological changes in the bursa.The primary goal of treatment is to control the inflammation. 1. Conservatively, the R.I.C.E regime in the first 72 hours after the injury or when the first signs of inflammation appear. 1. Medications inclu...