
Explore
Treatment of Thrombotic Disorders Treatment is summarized elsewhere in THE MANUAL specific to the location of the thrombus. Anticoagulation is often required, typically beginning with parenteral heparin or low molecular weight heparin, and then followed by oral warfarin or one of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs).
What are the treatment options for thrombotic disorders?
What is a Thrombotic Stroke? In a thrombotic stroke, a blood clot (thrombus) forms inside one of the brain's arteries. The clot blocks blood flow to a part of the brain. This causes brain cells in that area to stop functioning and die quickly.
What is a thrombotic stroke and how is it treated?
Once thrombosis is identified, the primary goal is preventing the blood clot from growing any larger. It's also preferable to prevent the clot from breaking up and traveling throughout the body.
What is the goal of thrombosis treatment?
Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. In most cases, TTP occurs suddenly and lasts for days or weeks, but it can go on for months. Relapses (flareups) can occur in up to 60 percent of people who have acquired TTP. Flareups also occur in most people who have inherited TTP. Plasma treatments are the most common way to treat TTP.
What is the treatment for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
What is the best treatment for thrombosis?
DVT is most commonly treated with anticoagulants, also called blood thinners. These drugs don't break up existing blood clots, but they can prevent clots from getting bigger and reduce your risk of developing more clots. Blood thinners may be taken by mouth or given by IV or an injection under the skin.
What does thrombotic mean?
: the formation or presence of a blood clot within a blood vessel.
What causes thrombosis?
Conditions like atherosclerosis, where arteries stiffen because of a buildup of plaque (a waxy substance related to cholesterol) inside them, often cause clots. This happens when a clot forms over a rupture or break in a section of plaque.
Can you heal thrombosis?
When a clot like this forms (also known as a thrombus), it can have varied health effects depending on where it occurs. Depending on your general condition, thrombosis may be a singular incident or a more chronic problem. However, the good news is that generally, Thrombosis can be cured.
What are the symptoms of a thrombosis?
DVT (deep vein thrombosis)throbbing or cramping pain in 1 leg (rarely both legs), usually in the calf or thigh.swelling in 1 leg (rarely both legs)warm skin around the painful area.red or darkened skin around the painful area.swollen veins that are hard or sore when you touch them.
What is thrombotic risk?
Major risk factors for thrombosis, other than age, include exogenous factors such as surgery, hospitalization, immobility, trauma, pregnancy and the puerperium and hormone use, and endogenous factors such as cancer, obesity, and inherited and acquired disorders of hypercoagulation.
What is the most common cause of thrombus?
Injury to a vein, such as from surgery, a broken bone, or other trauma. Lack of movement, such as after surgery or on a long trip. Inherited blood clotting disorders. A central venous catheter.
What are 5 causes of a thrombus?
What Causes a Thrombus?Injury to the leg veins.Illness that affects the veins.Immobility.Broken bone.Certain medications.Obesity.Inherited (genetic) disorders.Autoimmune disorders that increase the risk of blood clots.More items...•
What causes thrombosis in the legs?
What causes a venous blood clot? Blood clots in the veins are usually caused by slowed blood flow to the legs and feet, which can cause the blood to clot. Venous blood clots may also be caused by damage to a vein from an injury or infection.
How long does it take for blood clots to dissolve?
It is important to start treatment right away for DVT. It takes about 3 to 6 months for a blood clot to go away. During this time, there are things you can do to relieve symptoms.
How do doctors treat blood clots?
Blood-thinning medications are commonly used to prevent blood clots from forming or getting bigger. Thrombolytic medications can break up existing clots. Catheter-directed treatments, such as percutaneous transcatheter treatment, are done by inserting a catheter into a blood vessel in the groin.
How long can you live with deep vein thrombosis?
Overall 7-day survival was 74.8%; however, 96.2% of those with deep vein thrombosis were still alive at 7 days compared with only 59.1% of those with pulmonary embolism.
What is the treatment for a blood clot?
Treatment may include: Blood-thinning medicines (anticoagulants) Thin tubes (catheters) to widen the affected vessels. A wire mesh tube (stent) that holds a blood vessel open and stops it from closing. Medicines to interfere with or dissolve blood clots. Your healthcare provider may advise other treatments.
How to treat a clot in the blood?
Treatment includes medicines that thin the blood or prevent clots, and using stents or catheters to open blocked vessels. Prevention includes being active, quitting smoking, losing weight, and managing other health conditions.
What are the risk factors for venous thrombosis?
Risk factors for venous thrombosis may include: A family history of a blood clot in a vein deep in the body, called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) A history of DVT. Hormone therapy or birth control pills. Pregnancy. Injury to a vein, such as from surgery, a broken bone, or other trauma.
What is thrombosis in the heart?
What is thrombosis? Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block your blood vessels. There are 2 main types of thrombosis: Venous thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks a vein. Veins carry blood from the body back into the heart. Arterial thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks an artery. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to ...
What is the condition where blood clots block veins?
Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block veins or arteries. Symptoms include pain and swelling in one leg, chest pain, or numbness on one side of the body. Complications of thrombosis can be life-threatening, such as a stroke or heart attack. Treatment includes medicines that thin the blood or prevent clots, and using stents or catheters ...
How do you know if you have thrombosis?
Symptoms may include: Pain in one leg (usually the calf or inner thigh) Swelling in the leg or arm. Chest pain. Numbness or weakness on one side of the body. Sudden change in your mental state. The symptoms of thrombosis may look like other blood disorders or health problems.
What tests are done to see if blood clots?
Blood tests. These may include tests to see how well your blood can clot. Venography. For this test, a dye is injected into your veins. Then X-rays are taken to show blood flow and look for clots. The dye makes your veins easier to see on the X-rays. MRI, MRA or CT.
Arterial thrombosis
This involves a thrombus developing in an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to other areas of the body.
Venous thrombosis
This involves a thrombus developing in a vein. Veins are blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. A venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a broader term that describes blood clots in veins. There are two subtypes: deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
Treatment side effects
People taking anticoagulation medications have an increased risk of excessive bleeding. Signs of this issue include:
Prevention in at-risk individuals
A doctor can perform a VTE risk assessment, and they should do this whenever a person is admitted to a hospital.
Long-term complications
In some cases, thrombosis resolves on its own, as the body breaks down and removes the thrombus. However, around 33–50% of people with DVT develop post-thrombotic syndrome. This stems from damage to the valves within the veins, which help direct blood flow.
Subsequent blood clots
Most people who develop thrombosis go on to have further or recurrent blood clots. However, the likelihood of this happening depends on the factors that caused the initial clot.
Overview
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare blood disorder. With TTP, thrombi ( blood clots) develop in small vessels throughout your body. These thrombi can restrict the flow of blood to your body’s vital organs, including the heart, kidneys and brain. As a result, serious medical problems can arise.
Symptoms and Causes
People with TTP may experience a number of warning signs. Common thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura symptoms include:
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms and health history. If your provider suspects TTP, they will order diagnostic tests.
Management and Treatment
In most cases, plasma therapy is used to treat TTP. Other options include medication and surgery.
Prevention
Both types of TTP develop suddenly with no clear cause. As a result, it’s not possible to prevent it. However, if you’ve had TTP, you can talk to your healthcare provider about ways to reduce your risk of flare-ups.
Living With
You should schedule a visit with your healthcare provider anytime you notice TTP symptoms, such as fatigue, shortness of breath or purplish spots on your skin. If you’ve already been diagnosed with TTP, watch out for relapse symptoms. In most cases, your provider will restart plasma therapy to get your symptoms under control again.
What are the etiology of thrombosis?
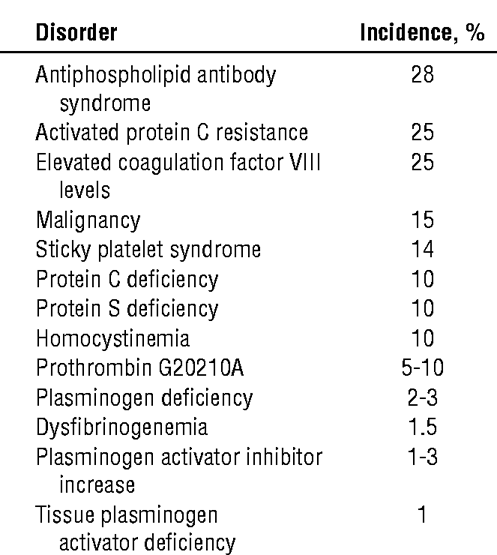
Etiology of Thrombotic Disorders. Acquired defects also predispose to venous and arterial thrombosis (see table Acquired Causes of Thromboembolism ). Other disorders and environmental factors can increase the risk of thrombosis, especially if a genetic abnormality is also present.
What causes thrombosis?
Overview of Thrombotic Disorders. Thrombotic disorders can be caused by genetic defects, which increase the risk of venous thromboembolism, or acquired defects , which increase the risk of arterial and venous thrombosis.
What is the risk of arterial thrombi?
Increases risk of arterial thrombi. Higher risk in patients with preexisting stenosis. When atherosclerotic plaques rupture, they expose or release tissue factor, activate coagulation, initiate local platelet adhesion and aggregation, and cause thrombosis.
Can thrombophlebitis cause a stroke?
Superficial thrombophlebitis can also develop. Other consequences may include arterial thrombosis (eg, causing stroke or mesenteric ischemia ). Symptoms depend on the location of the clot, as in the following examples: Chest pain and shortness of breath: Possible PE. Leg warmth, redness, and swelling: DVT.
Can acquired defects cause thromboembolism?
Acquired defects also predispose to venous and arterial thrombosis (see table Acquired Causes of Thromboembolism ). Other disorders and environmental factors can increase the risk of thrombosis, especially if a genetic abnormality is also present. Table. Acquired Causes of Thromboembolism.
What is the goal of venous thromboembolism?
The goals of treating acute venous thromboembolism in cancer patients are to prevent recurrence, minimize the risk of anticoagulant-induced bleeding, and improve quality of life.
What is thrombosis precipitated by?
Clinical episodes of thrombosis are precipitated by acquired thrombogenic triggers, which may be overt (e.g., pregnancy) or subclinical. In Section II, Dr. Mark Levine discusses the complex problem of thrombosis in patients with cancer.
What is a hematologist?
Hematologists are increasingly involved in the diagnosis and management of patients with venous and arterial thromboembolic disorders. There have been major advances in recent years in our understanding of the central role of hypercoagulability in the pathogenesis of thrombosis. This has led to new approaches to the diagnosis ...
Is venous thromboembolism genetic?
It is now recognized that most, if not all, patients with venous thromboembolism have a genetic basis for the disorder ("thro mbophilia"). The level of lifelong, baseline hypercoagulability in any individual may be determined by the type(s) and number of thrombophilia(s) that are inherited.
What is a thrombotic stroke?
This is a condition in which fatty deposits (plaques) build up inside blood vessels. Thrombotic strokes can affect large or small arteries in the brain. Strokes that affect large arteries block flow to greater portions of the brain. These strokes tend to cause the most disability.
How long after stroke can you take clotbusters?
The drug must be given within several hours after stroke symptoms begin. For this reason, it is important to seek emergency treatment immediately if you have symptoms of a stroke. Do not wait to see if the symptoms go away on their own. Clot-busters are administered through an intravenous line (IV) into a vein.
What happens when a blood clot forms in the brain?
In a thrombotic stroke, a blood clot (thrombus) forms inside one of the brain's arteries. The clot blocks blood flow to a part of the brain. This causes brain cells in that area to stop functioning and die quickly. The blood clot that triggers a thrombotic stroke usually forms inside an artery that already has been narrowed by atherosclerosis.
Where does blood clot come from?
The blood clot usually comes from the heart. At first, it can be impossible for a doctor to determine which type of stroke a person is having. That is because the symptoms can be identical. A much less common cause of thrombotic stroke is migraine headache.
How to prevent stroke?
Other things you can do to prevent stroke are to avoid drinking too much alcohol and never take cocaine or amphetamines. Talk with your doctor about whether you should take aspirin every day. Aspirin (in doses as low as 80 milligrams per day) can reduce the risk of thrombotic stroke.
What are some medications that can help prevent a stroke?
They help to prevent an additional stroke event. These drugs include dipyridamole (usually as a drug combined with aspirin called Aggrenox) and clopidogrel ( Plavix ).
What happens if a CT scan shows a blood clot?
If the CT scan shows bleeding in or around the brain, then you have had a hemorrhagic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke is treated differently than a stroke caused by a blood clot. If the CT scan does not show any bleeding, then the stroke is presumed to be caused by a blocked artery from a blood clot.
How long does it take for a thrombosis to go away?
Most thrombosed hemorrhoids will resolve on their own, although it may take two to three weeks for them to be completely gone. Self-care measures for a thrombosed hemorrhoid include: 4
What is thrombosed hemorrhoids?
1 . Thrombosed hemorrhoids may present as a single lump or a circle of lumps. In most cases, the blood clot is eventually reabsorbed by ...
How long does it take for a thrombosed hemorrhoid to get better?
The good news about a thrombosed hemorrhoid is that it will most likely start getting better after a couple of days and resolve on its own. If it doesn't seem to be resolving, your doctor should be able to help you find the right treatment so you can get rid of the discomfort and get back to your life.
Can thrombosis be a lump?
Thrombosed hemorrhoids may present as a single lump or a circle of lumps. In most cases, the blood clot is eventually reabsorbed by the body and the symptoms resolve themselves. If symptoms don't resolve, or if you have symptoms that need to be managed, multiple treatment options are available to you, ranging from topical creams to surgery.
Can a blood clot cause a hemmorhoids?
Once you have one, it's possible for it to become thrombosed. Doctors don't know why some people develop blood clots in their hemorrhoids and others don't. Some possible triggers of hemorrhoids include: 2 .
Is thrombosed hemorrhoids painful?
They're most often external but can be internal, as well. Thrombosed hemorrhoids are not considered to be dangerous, yet they can be quite painful.
